Gibson Assembly™ – Building a Synthetic Biology Toolset
... sequence-verified and assembled into larger DNA fragments using the same approach. Because assembly itself does not generally introduce new errors, the final assembled product can be retrieved at high efficiencies. Using this approach, many of the costly and time consuming steps currently used to sy ...
... sequence-verified and assembled into larger DNA fragments using the same approach. Because assembly itself does not generally introduce new errors, the final assembled product can be retrieved at high efficiencies. Using this approach, many of the costly and time consuming steps currently used to sy ...
ch 15 clicker systems
... a) In mitosis, some chromosomes in triploids have no partner at synapsis, but chromosomes in tetraploids do have partners. b) In meiosis, some chromosomes in triploids have no partner at synapsis, but chromosomes in tetraploids do have partners. c) In mitosis, some chromosomes in tetraploids have no ...
... a) In mitosis, some chromosomes in triploids have no partner at synapsis, but chromosomes in tetraploids do have partners. b) In meiosis, some chromosomes in triploids have no partner at synapsis, but chromosomes in tetraploids do have partners. c) In mitosis, some chromosomes in tetraploids have no ...
Nature Rev.Genet. 8
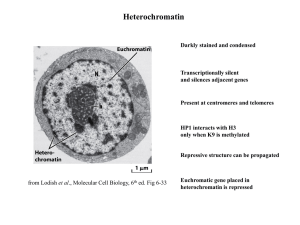
... Counteracts the action of PcG proteins Memory system composed of PcG and trxG complexes is linked to the histone code ...
... Counteracts the action of PcG proteins Memory system composed of PcG and trxG complexes is linked to the histone code ...
Genes in Context Gene–Environment Interplay
... of heritable material. Since the discovery of DNA, the study of genetics has come to mean the study of DNA, with gene defined as a particular sequence of DNA. Due to the complex nature of DNA, it is perhaps easier to employ an analogy that conveys the basic notions of gene function. Think of an indi ...
... of heritable material. Since the discovery of DNA, the study of genetics has come to mean the study of DNA, with gene defined as a particular sequence of DNA. Due to the complex nature of DNA, it is perhaps easier to employ an analogy that conveys the basic notions of gene function. Think of an indi ...
TCSS Biology Unit 2 – Genetics Information
... Cellular Growth Notes (9.1) - Student Copy – For student handouts. Includes blanks for fill-in that correspond to the boldfaced words in the Screen Copy. Asexual Reproduction & Mitosis Notes-Screen Copy (9.2) – PPT for lecture covering asexual reproduction and mitosis. Asexual Reproduction & Mitosis ...
... Cellular Growth Notes (9.1) - Student Copy – For student handouts. Includes blanks for fill-in that correspond to the boldfaced words in the Screen Copy. Asexual Reproduction & Mitosis Notes-Screen Copy (9.2) – PPT for lecture covering asexual reproduction and mitosis. Asexual Reproduction & Mitosis ...
pdf
... provided with any of the three metabolic intermediates, substances A, B, and C. Thus the gene altered in this mutant must encode an enzyme that catalyzes a step downstream of those that generate substances A, B or C. So one can place enzyme A at the end of the pathway, presumably catalyzing the fina ...
... provided with any of the three metabolic intermediates, substances A, B, and C. Thus the gene altered in this mutant must encode an enzyme that catalyzes a step downstream of those that generate substances A, B or C. So one can place enzyme A at the end of the pathway, presumably catalyzing the fina ...
PartOneAnswers.doc
... provided with any of the three metabolic intermediates, substances A, B, and C. Thus the gene altered in this mutant must encode an enzyme that catalyzes a step downstream of those that generate substances A, B or C. So one can place enzyme A at the end of the pathway, presumably catalyzing the fina ...
... provided with any of the three metabolic intermediates, substances A, B, and C. Thus the gene altered in this mutant must encode an enzyme that catalyzes a step downstream of those that generate substances A, B or C. So one can place enzyme A at the end of the pathway, presumably catalyzing the fina ...
Spectroscopy of nucleic acids
... determine the concentrations of DNA and RNA in extracts of calf liver cells. Nucleic acids are isolated by first homogenizing fresh calf liver to disrupt the cells in the tissue followed by precipitating the nucleic acids with trichloroacetic acid (TCA) and ethanol. Because spectrophotmeters that me ...
... determine the concentrations of DNA and RNA in extracts of calf liver cells. Nucleic acids are isolated by first homogenizing fresh calf liver to disrupt the cells in the tissue followed by precipitating the nucleic acids with trichloroacetic acid (TCA) and ethanol. Because spectrophotmeters that me ...
INDIAN SCHOOL AL WADI AL KABIR SECOND REHEARSAL
... (b) Why do internodal segments of sugarcane fail to propagate vegetatively even when they are in contact with damp soil? Page 1of 4 ...
... (b) Why do internodal segments of sugarcane fail to propagate vegetatively even when they are in contact with damp soil? Page 1of 4 ...
(FA-SAT) in a Cat Fibrosarcoma Might Be Related to Chromosomal
... chromosomal instability (Gagos and Irminger-Finger 2005). Our results demonstrate that in the tumor analyzed, there is evident chromosomal instability, revealed by the several marker chromosomes detected and the presence of chromatin strings between interphase nuclei. Gisselsson et al. (1999) analyz ...
... chromosomal instability (Gagos and Irminger-Finger 2005). Our results demonstrate that in the tumor analyzed, there is evident chromosomal instability, revealed by the several marker chromosomes detected and the presence of chromatin strings between interphase nuclei. Gisselsson et al. (1999) analyz ...
DNA Methylation, Imprinting and X
... essentially all methylation in the PGC is thought to be linked to the low number of transgenerational inheritance events in mammals Pressure less strong on plants, imprinting mainly occurs in extra-embryonic tissue ...
... essentially all methylation in the PGC is thought to be linked to the low number of transgenerational inheritance events in mammals Pressure less strong on plants, imprinting mainly occurs in extra-embryonic tissue ...
Ch.16 17 Study Guide
... 15. Explain the general process of transcription, including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. 16. Explain how RNA is modified after transcription in eukaryotic cells. 17. Define and explain the role of ribozymes. What three properties allow some RNA molecules to funct ...
... 15. Explain the general process of transcription, including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. 16. Explain how RNA is modified after transcription in eukaryotic cells. 17. Define and explain the role of ribozymes. What three properties allow some RNA molecules to funct ...
ProteinSynthesis
... molecules of life (proteins). • DNA stays in the nucleus, but molecules are built in the cytoplasm of the cell. • So, the code must be copied and moved out into the cytoplasm, where proteins are assembled. • This process is called PROTEIN ...
... molecules of life (proteins). • DNA stays in the nucleus, but molecules are built in the cytoplasm of the cell. • So, the code must be copied and moved out into the cytoplasm, where proteins are assembled. • This process is called PROTEIN ...
bacterial plasmids - Acta Medica Medianae
... Plasmids, extrachromosomal DNA, were identified in bacteria pertaining to family of Enterobacteriacae for the very first time. After that, they were discovered in almost every single observed strain. The structure of plasmids is made of circular double chain DNA molecules which are replicated autono ...
... Plasmids, extrachromosomal DNA, were identified in bacteria pertaining to family of Enterobacteriacae for the very first time. After that, they were discovered in almost every single observed strain. The structure of plasmids is made of circular double chain DNA molecules which are replicated autono ...
Chapter 15 - ShoultzScience
... Changes to codons that have the same amino acid have no effect; UAU to UAC both code tyrosine. A change from UAC to UAG (a stop codon) results in a shorter protein, and a change from UAC to CAC incorporates histidine instead of tyrosine. Sickle cell disease results from a single base change in ...
... Changes to codons that have the same amino acid have no effect; UAU to UAC both code tyrosine. A change from UAC to UAG (a stop codon) results in a shorter protein, and a change from UAC to CAC incorporates histidine instead of tyrosine. Sickle cell disease results from a single base change in ...
Horizontal gene transfer and the origin of species: lessons from
... genes are fixed. On the evolutionary scale, the acquisition of pathogenicity islands occurs at a much slower pace than that of plasmids, and would obviously create new bacterial subspecies (i.e. the recombinants have discernibly different phenotypes). Because multiple pathogenicity islands, varying ...
... genes are fixed. On the evolutionary scale, the acquisition of pathogenicity islands occurs at a much slower pace than that of plasmids, and would obviously create new bacterial subspecies (i.e. the recombinants have discernibly different phenotypes). Because multiple pathogenicity islands, varying ...
The effect of sodium ion concentration on
... respectively. Thus equation (2) predicts that A\p for the ssDNA—dsDNA transition (the number of sodium ions taken up per phosphate during DNA renaturation, or equivalently, the number released per phosphate during denaturation) is 0.17; this is close to the measured value of 0.15 (12). This indicate ...
... respectively. Thus equation (2) predicts that A\p for the ssDNA—dsDNA transition (the number of sodium ions taken up per phosphate during DNA renaturation, or equivalently, the number released per phosphate during denaturation) is 0.17; this is close to the measured value of 0.15 (12). This indicate ...
Document
... How B cells express one light chain species and one heavy chain species even though every B cell possesses a maternal and paternal locus of both genes. Since all other genes known at the time appeared to be expressed codominantly, how could B cells shut down the genes on one of their ...
... How B cells express one light chain species and one heavy chain species even though every B cell possesses a maternal and paternal locus of both genes. Since all other genes known at the time appeared to be expressed codominantly, how could B cells shut down the genes on one of their ...
NAME OF GAME
... Look at the diagram above comparing DNA sequences. The colored segments show differences in DNA Which two species are more closely related? B and C; these have fewer differences than A and C OR A and B Image from: Biology by Miller and Levine; Prentice Hall Publishing©2006 ...
... Look at the diagram above comparing DNA sequences. The colored segments show differences in DNA Which two species are more closely related? B and C; these have fewer differences than A and C OR A and B Image from: Biology by Miller and Levine; Prentice Hall Publishing©2006 ...
What is Bio-technology?
... What is Bio-technology? Why is it important to understand your genetic make up? How does this information affect your life? Society? Advancement of technology for research associated with life science. Especially Genetic Engineering (changing genes and recombinant DNA (changing DNA sequences) ...
... What is Bio-technology? Why is it important to understand your genetic make up? How does this information affect your life? Society? Advancement of technology for research associated with life science. Especially Genetic Engineering (changing genes and recombinant DNA (changing DNA sequences) ...
WUHSD Final Exam Review
... organism contain the same genes, explain how they appear and function differently? -cells only transcribe those portions of genes that they need ...
... organism contain the same genes, explain how they appear and function differently? -cells only transcribe those portions of genes that they need ...
CHAPTER 16 THE MOLECULE BASIS OF INHERITANCE
... It takes E. coli less than an hour to copy each of the 4.6 million nucleotide pairs in its single chromosome and divide to form two identical daughter cells. ...
... It takes E. coli less than an hour to copy each of the 4.6 million nucleotide pairs in its single chromosome and divide to form two identical daughter cells. ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.