Contextual modulation and stimulus selectivity in extrastriate cortex
... Normalization Surround Extrastriate cortex Neurophysiology Macaque ...
... Normalization Surround Extrastriate cortex Neurophysiology Macaque ...
Linking Neural Activity to Visual Perception: Separating Sensory and
... discrimination sensitivity of MT neurons in the 2AFC task (see Appendix). For this, two distributions of spike counts were compared against each other, the distribution of counts from trials when the coherent motion was in the neuron’s preferred direction (distribution Y in Figure 2A) versus the dis ...
... discrimination sensitivity of MT neurons in the 2AFC task (see Appendix). For this, two distributions of spike counts were compared against each other, the distribution of counts from trials when the coherent motion was in the neuron’s preferred direction (distribution Y in Figure 2A) versus the dis ...
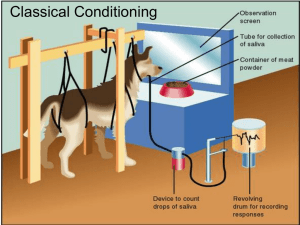
Classical Conditioning
... – Conditioned to become aroused by nonsexual stimuli – Conditioned to elicit increased sperm release – Fetishes for inanimate objects • Difficult to test connections to human sexual fetishes ...
... – Conditioned to become aroused by nonsexual stimuli – Conditioned to elicit increased sperm release – Fetishes for inanimate objects • Difficult to test connections to human sexual fetishes ...
Undulatory locomotion of polychaete annelids - FORTH-ICS
... Direct implementation of various undulatory locomotion gaits can be achieved if a wave of joint activation is propagated along the mechanism, e.g. one generated by setting φi (t) = A sin(2πft + i φlag) − ψ, i=0,..,5, where A is the maximum angular deflection for each joint and φlag is the phase offs ...
... Direct implementation of various undulatory locomotion gaits can be achieved if a wave of joint activation is propagated along the mechanism, e.g. one generated by setting φi (t) = A sin(2πft + i φlag) − ψ, i=0,..,5, where A is the maximum angular deflection for each joint and φlag is the phase offs ...
a PowerPoint presentation of Module 20
... stabbing you with a needle. The next time you hear “This won’t hurt,” you cringe in fear. You have a meal at a fast food restaurant that causes food poisoning. The next time you see a sign for that restaurant, you feel nauseated. ...
... stabbing you with a needle. The next time you hear “This won’t hurt,” you cringe in fear. You have a meal at a fast food restaurant that causes food poisoning. The next time you see a sign for that restaurant, you feel nauseated. ...
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF VISUAL AREA MT
... First published online as a Review in Advance on March 17, 2005 0147-006X/05/07210157$20.00 ...
... First published online as a Review in Advance on March 17, 2005 0147-006X/05/07210157$20.00 ...
Structure and Function of Visual Area MT
... These MT-projecting 4B neurons are predominantly spiny stellate in morphology (Shipp & Zeki 1989a) (though, see also Elston & Rosa 1997), are the largest cells in this layer (Sincich & Horton 2003), and appear to receive exclusively M-inputs via layer 4Cα (Yabuta et al. 2001). In addition to this di ...
... These MT-projecting 4B neurons are predominantly spiny stellate in morphology (Shipp & Zeki 1989a) (though, see also Elston & Rosa 1997), are the largest cells in this layer (Sincich & Horton 2003), and appear to receive exclusively M-inputs via layer 4Cα (Yabuta et al. 2001). In addition to this di ...
- Princeton University
... There are two general approaches for TPM in awake mice: head-mounted microscopes and head restraint. A head-mounted microscope requires innovative engineering to miniaturize the excitation, laser scanning, and fluorescence collection. One such device demonstrated stable TPM of capillaries in awake a ...
... There are two general approaches for TPM in awake mice: head-mounted microscopes and head restraint. A head-mounted microscope requires innovative engineering to miniaturize the excitation, laser scanning, and fluorescence collection. One such device demonstrated stable TPM of capillaries in awake a ...
Figure 2.10
... Stimulus-Response (S-R) system versus the State system • Habituation processes occur in the S-R system • activated every time an eliciting stimulus is presented • shortest path (circuit) between sense organs and muscles • Sensitization processes occur in the state system • emotional and motivationa ...
... Stimulus-Response (S-R) system versus the State system • Habituation processes occur in the S-R system • activated every time an eliciting stimulus is presented • shortest path (circuit) between sense organs and muscles • Sensitization processes occur in the state system • emotional and motivationa ...
Stimulus-Dependent Synchronization of Neuronal Responses in the
... evoked by a particular stimulus need to be identified and bound together for further joint processing and must not be confounded with responses to other, nearby stimuli. Such selection of related responses could be achieved by synchronizing the respective discharges at a time scale of milliseconds, ...
... evoked by a particular stimulus need to be identified and bound together for further joint processing and must not be confounded with responses to other, nearby stimuli. Such selection of related responses could be achieved by synchronizing the respective discharges at a time scale of milliseconds, ...
WHAT IS LEARNING
... stabbing you with a needle. The next time you hear “This won’t hurt,” you cringe in fear. You have a meal at a fast food restaurant that causes food poisoning. The next time you see a sign for that restaurant, you feel nauseated. ...
... stabbing you with a needle. The next time you hear “This won’t hurt,” you cringe in fear. You have a meal at a fast food restaurant that causes food poisoning. The next time you see a sign for that restaurant, you feel nauseated. ...
The neural basis for combinatorial coding in a cortical population response
... Visual stimuli were presented in discrete trials. Each stimulus appeared and remained stationary for 256 ms, then stepped to a constant velocity for 256 ms, and was again stationary for 256 ms. A brief pause separated successive trials, and directions of motion were pseudorandomly interleaved. A typ ...
... Visual stimuli were presented in discrete trials. Each stimulus appeared and remained stationary for 256 ms, then stepped to a constant velocity for 256 ms, and was again stationary for 256 ms. A brief pause separated successive trials, and directions of motion were pseudorandomly interleaved. A typ ...
Chapter 8: Stimulus Control of Behavior
... • Note that the pigeons treated the 590 nm stimulus nearly the same as the 580 nm • Can they tell the difference? ...
... • Note that the pigeons treated the 590 nm stimulus nearly the same as the 580 nm • Can they tell the difference? ...
Meaningful auditory information enhances perception of visual
... that the perceptual performance was improved by the additional information from the second sensory channel. However, the increase in sensitivity increment was greater when the auditory and visual stimuli were in phase than when they were out of phase. Figure 5 shows the results for all subjects. On ...
... that the perceptual performance was improved by the additional information from the second sensory channel. However, the increase in sensitivity increment was greater when the auditory and visual stimuli were in phase than when they were out of phase. Figure 5 shows the results for all subjects. On ...
Bayesian Computation in Recurrent Neural Circuits
... Bayesian Computation in Recurrent Neural Circuits Rajesh P. N. Rao ...
... Bayesian Computation in Recurrent Neural Circuits Rajesh P. N. Rao ...
Functional Sub-regions for Optic Flow Processing in the
... were presented. Also, radial sinusoidal gratings, rotating clockwise or counterclockwise were used. For these two stimuli, responses as a function of spatial and temporal frequencies were studied. The cell’s direction selectivity (e.g. expansion versus contraction) was determined and quantified as p ...
... were presented. Also, radial sinusoidal gratings, rotating clockwise or counterclockwise were used. For these two stimuli, responses as a function of spatial and temporal frequencies were studied. The cell’s direction selectivity (e.g. expansion versus contraction) was determined and quantified as p ...
Classical Conditioning
... Midge goes to Disneyland looking forward to seeing her favorite characters. Upon entering, she is surrounded by all seven dwarves and begins to panic when she loses sight of her parents. From then on, Midge runs screaming from the room every time her siblings put on Snow White and she sees the dwarv ...
... Midge goes to Disneyland looking forward to seeing her favorite characters. Upon entering, she is surrounded by all seven dwarves and begins to panic when she loses sight of her parents. From then on, Midge runs screaming from the room every time her siblings put on Snow White and she sees the dwarv ...
The Biological Bases of Time-to
... respond vigorously to stimuli moving on paths directly towards the eye. However from these early studies many of the appropriate controls were not performed to conclusively exclude the possibility that these neurons were not simply responding to some aspect of the lateral motion of an approaching st ...
... respond vigorously to stimuli moving on paths directly towards the eye. However from these early studies many of the appropriate controls were not performed to conclusively exclude the possibility that these neurons were not simply responding to some aspect of the lateral motion of an approaching st ...
Visual pathway class..
... • We do not have a descriptive or mechanistic model that predicts response properties of downstream visual areas, or behavior. • A descriptive model would vastly transform technology: the primate visual system is far superior to anything that engineers can build. • A mechanistic model is the ultimat ...
... • We do not have a descriptive or mechanistic model that predicts response properties of downstream visual areas, or behavior. • A descriptive model would vastly transform technology: the primate visual system is far superior to anything that engineers can build. • A mechanistic model is the ultimat ...
A GPU-accelerated cortical neural network model for visually guided
... model for visually guided navigation that has been embodied on a physical robot exploring a realworld environment. The model includes a rate based motion energy model for area V1, and a spiking neural network model for cortical area MT. The model generates a cortical representation of optic flow, de ...
... model for visually guided navigation that has been embodied on a physical robot exploring a realworld environment. The model includes a rate based motion energy model for area V1, and a spiking neural network model for cortical area MT. The model generates a cortical representation of optic flow, de ...
Neuronal mechanisms for the perception of ambiguous stimuli
... spatial luminance profile is formed by the multiplication of a sinusoidal waveform with a Gaussian envelope.) Orientation jitter breaks up any pattern, therefore favouring eye-rivalry rather than percept-rivalry. There is a gradual shift from eye-rivalry to percept-rivalry as pattern coherence is in ...
... spatial luminance profile is formed by the multiplication of a sinusoidal waveform with a Gaussian envelope.) Orientation jitter breaks up any pattern, therefore favouring eye-rivalry rather than percept-rivalry. There is a gradual shift from eye-rivalry to percept-rivalry as pattern coherence is in ...
Some Speculative Hypotheses about the Nature
... the ball. What’s more, when tracking an object with binoculars or a camera, the eyes are fixed and the body adjusts to keep the object within view. I would therefore like to suggest that the mechanisms for tracking a moving target — eyes, head or attention — form a continuum and as such share a comm ...
... the ball. What’s more, when tracking an object with binoculars or a camera, the eyes are fixed and the body adjusts to keep the object within view. I would therefore like to suggest that the mechanisms for tracking a moving target — eyes, head or attention — form a continuum and as such share a comm ...
Depth perception by the active observer
... motion between observer and object) is the same [24,26,27]. It turns out, however, that this equivalence is false: the same optic flow can lead to very different perceptions of 3D shape when generated by the observer’s own movement than when generated by object motion [28–31]. One illustration of th ...
... motion between observer and object) is the same [24,26,27]. It turns out, however, that this equivalence is false: the same optic flow can lead to very different perceptions of 3D shape when generated by the observer’s own movement than when generated by object motion [28–31]. One illustration of th ...
Classical Conditioning
... Conditioned stimulus (CS) – a previously neutral stimulus that has, through conditioning, acquired the capacity to evoke a conditioned response Conditioned response (CR) – a learned reaction to a conditioned stimulus that occurs because of previous conditioning ...
... Conditioned stimulus (CS) – a previously neutral stimulus that has, through conditioning, acquired the capacity to evoke a conditioned response Conditioned response (CR) – a learned reaction to a conditioned stimulus that occurs because of previous conditioning ...