Transformation and Transduction File
... between two bacterial cells ( of same or different species) that are temporarily joined. The DNA transfer is one way: One cell donates the DNA,a nd the other receives ti. The donor uses sex pili to attach to the recipient. After contacting a recipient cell, each sex pilus retracts, pulling the two c ...
... between two bacterial cells ( of same or different species) that are temporarily joined. The DNA transfer is one way: One cell donates the DNA,a nd the other receives ti. The donor uses sex pili to attach to the recipient. After contacting a recipient cell, each sex pilus retracts, pulling the two c ...
Final Exam Study Guide
... proteins? Amino acids 7. Genes are a segment of ____ that code for ____? DNA/trait 8. What are the nucleotides found in DNA? Deoxyribose + phosphate group + cytosine 9. The overall structure of DNA can be described as? Double helix or two strands that are twisted 10. Explain the process of translati ...
... proteins? Amino acids 7. Genes are a segment of ____ that code for ____? DNA/trait 8. What are the nucleotides found in DNA? Deoxyribose + phosphate group + cytosine 9. The overall structure of DNA can be described as? Double helix or two strands that are twisted 10. Explain the process of translati ...
UNIT 4 PART1 MODERN GENETICS
... • The work of the cell is carried out by the proteins it assembles. • Proteins are made up of chains of amino acids –i.e. polypeptide chains. • There are 20 different types of amino acids. • The sequence of amino acids determines the protein created and the shape it takes on. • Examples of proteins ...
... • The work of the cell is carried out by the proteins it assembles. • Proteins are made up of chains of amino acids –i.e. polypeptide chains. • There are 20 different types of amino acids. • The sequence of amino acids determines the protein created and the shape it takes on. • Examples of proteins ...
Document
... • Be able to describe the components of DNA electrophoresis, and recognize patterns in a gel • Be able to describe the form and function of restriction enzymes (restriction endonucleases) • Be able to describe the process of DNA-mediated transformation of bacterial cells • Discuss the molecular basi ...
... • Be able to describe the components of DNA electrophoresis, and recognize patterns in a gel • Be able to describe the form and function of restriction enzymes (restriction endonucleases) • Be able to describe the process of DNA-mediated transformation of bacterial cells • Discuss the molecular basi ...
Whippo - cloudfront.net
... All vertebrates have genes that make hemoglobin Like many other genes, hemoglobin genes mutates at a fairly constant rate, even if they are in different animal groups Rate of change can be used to estimate how long ago groups or organisms diverged from one another! ...
... All vertebrates have genes that make hemoglobin Like many other genes, hemoglobin genes mutates at a fairly constant rate, even if they are in different animal groups Rate of change can be used to estimate how long ago groups or organisms diverged from one another! ...
Chapter 8 Microbial Genetics
... • Sequence of AA – based on the sequence of mRNA – based on the NB sequence of the gene from which it was transcribed • Genetic information flows from the gene to mRNA to protein. • Change in the NB of the gene – change the codon on mRNA – change AA sequence of the protein – protein becomes ...
... • Sequence of AA – based on the sequence of mRNA – based on the NB sequence of the gene from which it was transcribed • Genetic information flows from the gene to mRNA to protein. • Change in the NB of the gene – change the codon on mRNA – change AA sequence of the protein – protein becomes ...
Whippo
... All vertebrates have genes that make hemoglobin Like many other genes, hemoglobin genes mutates at a fairly constant rate, even if they are in different animal groups Rate of change can be used to estimate how long ago groups or organisms diverged from one another! ...
... All vertebrates have genes that make hemoglobin Like many other genes, hemoglobin genes mutates at a fairly constant rate, even if they are in different animal groups Rate of change can be used to estimate how long ago groups or organisms diverged from one another! ...
Chapter 13: Genetic Engineering
... replicated sides, using both as templates Copies are made at an exponential rate of only the desired gene ...
... replicated sides, using both as templates Copies are made at an exponential rate of only the desired gene ...
Satiable Curiosity - Journal of Genetic Genealogy
... over most of their length, but microsatellites (Short Tandem Repeats or STRs) contained within these segments tend to be more variable, due to their relatively high mutation rate. Genetic genealogists take advantage of this variability when testing the multi-copy markers DYS385a/b, DYS459a/b, DYS464 ...
... over most of their length, but microsatellites (Short Tandem Repeats or STRs) contained within these segments tend to be more variable, due to their relatively high mutation rate. Genetic genealogists take advantage of this variability when testing the multi-copy markers DYS385a/b, DYS459a/b, DYS464 ...
Text S1. Supporting Information Supporting Information Figure
... (1.153 10-5)x + 0.1872. A. The plot is shown for all depth values on a logarithmic scale B. Same plot as in A but only showing depth values between 15-1200, which are the values selected for downstream analysis because the effect of depth on calculated nucleotide diversity is ~.01%. Figure S6: HCMV ...
... (1.153 10-5)x + 0.1872. A. The plot is shown for all depth values on a logarithmic scale B. Same plot as in A but only showing depth values between 15-1200, which are the values selected for downstream analysis because the effect of depth on calculated nucleotide diversity is ~.01%. Figure S6: HCMV ...
Introduction and review Lecture 1: Jan. 18, 2006
... Genotype- The genetic constitution of an organism. Phenotype- The visible appearance of an organism. Homologous chromosomes- in a diploid organism, the 2 copies of a chromosome inherited from the mother and the father. Locus- Location of a gene on a chromosome. Allelomorph (allele)- different versio ...
... Genotype- The genetic constitution of an organism. Phenotype- The visible appearance of an organism. Homologous chromosomes- in a diploid organism, the 2 copies of a chromosome inherited from the mother and the father. Locus- Location of a gene on a chromosome. Allelomorph (allele)- different versio ...
Genomics: A Mapping Analogy - University of Wisconsin
... With this map, can you know the function of all the buildings on campus? Is it possible to know the names and locations of all the buildings without knowing their functions? Likewise, is it possible to know the names and locations of all the genes of an organism without knowing their function? In m ...
... With this map, can you know the function of all the buildings on campus? Is it possible to know the names and locations of all the buildings without knowing their functions? Likewise, is it possible to know the names and locations of all the genes of an organism without knowing their function? In m ...
Basic Genetics
... 2. What diseases can appear in one twin but not the other? 3. Why do scientists often study twins? 4. What is the difference between identical and fraternal twins? 5. What can be determined if a characteristic appears more frequently in identical twin pairs compared to fraternal twin pairs? WHAT ARE ...
... 2. What diseases can appear in one twin but not the other? 3. Why do scientists often study twins? 4. What is the difference between identical and fraternal twins? 5. What can be determined if a characteristic appears more frequently in identical twin pairs compared to fraternal twin pairs? WHAT ARE ...
DOC
... the DNA strand containing the mismatched base. 7. How do E. coli distinguish between parental and newly replicated strands when performing DNA mismatch repair? For instance, if a T was wrongly paired with a G, how does the cell know which base to replace? DNA strand methylation. For a short period a ...
... the DNA strand containing the mismatched base. 7. How do E. coli distinguish between parental and newly replicated strands when performing DNA mismatch repair? For instance, if a T was wrongly paired with a G, how does the cell know which base to replace? DNA strand methylation. For a short period a ...
PTC bioinformatics
... In the table find Homo sapiens and click on the B icon next to the build with the highest number Enter the primer sequences into the search window, except for the non-nucleotide letters. Selected BLASTN from the drop-down menu then clicked "Begin Search" 1. Then clicked "View Report" 2. Next clicked ...
... In the table find Homo sapiens and click on the B icon next to the build with the highest number Enter the primer sequences into the search window, except for the non-nucleotide letters. Selected BLASTN from the drop-down menu then clicked "Begin Search" 1. Then clicked "View Report" 2. Next clicked ...
Who Owns the Human Genome?
... complete the sequence in about 10 years, after spending the first couple of years on mapping and developing new technologies in several areas of activity, including sequencing. He openly admits to being a "technologic optimist." Most other researchers believe that sequencing cannot be done quickly o ...
... complete the sequence in about 10 years, after spending the first couple of years on mapping and developing new technologies in several areas of activity, including sequencing. He openly admits to being a "technologic optimist." Most other researchers believe that sequencing cannot be done quickly o ...
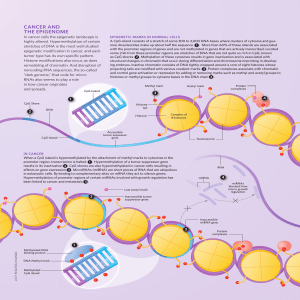
CaNCer aND THe ePIGeNOMe
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
Full Text - Harvard University
... molecular pages. This capability has unlocked not only the human genome but also those of thousands of other species, revealing their genes, regulatory sequences and overall structures, which has in turn led to many important advances in biology and medicine. The next frontier in genome biology is t ...
... molecular pages. This capability has unlocked not only the human genome but also those of thousands of other species, revealing their genes, regulatory sequences and overall structures, which has in turn led to many important advances in biology and medicine. The next frontier in genome biology is t ...
Chapter 14
... entire DNA content of different organisms the genome is the full complement of genetic information of an organism (i.e., all of its genes and other DNA) DNA sequencing is a process that allows scientists to read each nucleotide in a strand of DNA ...
... entire DNA content of different organisms the genome is the full complement of genetic information of an organism (i.e., all of its genes and other DNA) DNA sequencing is a process that allows scientists to read each nucleotide in a strand of DNA ...
Restriction Enzyme
... for Southern Blots : single-stranded DNA for Northern Blots : single-stranded mRNA ...
... for Southern Blots : single-stranded DNA for Northern Blots : single-stranded mRNA ...
Bacterial Comparative Genomics
... Bacteria and GWAS • Most GWAS methods depend on linkage disequilibrium being slowly broken up by meiotic recombination, such that alleles physically distant from each other are independent • Many bacteria have limited or no recombination, making GWAS difficult • Adapting GWAS to bacteria is an acti ...
... Bacteria and GWAS • Most GWAS methods depend on linkage disequilibrium being slowly broken up by meiotic recombination, such that alleles physically distant from each other are independent • Many bacteria have limited or no recombination, making GWAS difficult • Adapting GWAS to bacteria is an acti ...