THE UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLE The uncertainty principle states
... THE UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLE MICHAEL G COWLING ...
... THE UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLE MICHAEL G COWLING ...
Quantum Optics and Quantum Engineering for Undergraduates
... Lab. 1: Entanglement and Bell inequalities; Lab. 2: Single-photon interference: Young’s double slit experiment and Mach-Zehnder interferometer; Lab. 3: Confocal microscope imaging of single-emitter fluorescence; Lab. 4: Hanbury Brown and Twiss setup. Fluorescence antibunching and fluorescence lifeti ...
... Lab. 1: Entanglement and Bell inequalities; Lab. 2: Single-photon interference: Young’s double slit experiment and Mach-Zehnder interferometer; Lab. 3: Confocal microscope imaging of single-emitter fluorescence; Lab. 4: Hanbury Brown and Twiss setup. Fluorescence antibunching and fluorescence lifeti ...
What is the World Made of?
... Electric and magnetic field ? Maxwell’s theory explained electric and magnetic phenomena. It combined electric and magnetic field into ONE theory of the electromagnetic field. It also showed that light is an electromagnetic wave! … and then in the 1900s people came to the question of atoms (particle ...
... Electric and magnetic field ? Maxwell’s theory explained electric and magnetic phenomena. It combined electric and magnetic field into ONE theory of the electromagnetic field. It also showed that light is an electromagnetic wave! … and then in the 1900s people came to the question of atoms (particle ...
The end of classical physics: photons, electrons, atoms
... Electric and magnetic field ? Maxwell’s theory explained electric and magnetic phenomena. It combined electric and magnetic field into ONE theory of the electromagnetic field. It also showed that light is an electromagnetic wave! … and then in the 1900s people came to the question of atoms (particle ...
... Electric and magnetic field ? Maxwell’s theory explained electric and magnetic phenomena. It combined electric and magnetic field into ONE theory of the electromagnetic field. It also showed that light is an electromagnetic wave! … and then in the 1900s people came to the question of atoms (particle ...
PPT
... Particles have position (and trajectories). If we measure position (e.g., which slit it went through) we have observed a particle property. That’s why the “which slit” measurement destroys the interference pattern. Note that particle and wave properties are incompatible. One can’t simultaneously mea ...
... Particles have position (and trajectories). If we measure position (e.g., which slit it went through) we have observed a particle property. That’s why the “which slit” measurement destroys the interference pattern. Note that particle and wave properties are incompatible. One can’t simultaneously mea ...
An Introduction to Quantum Computing
... Over the last 20 years, the field of quantum computing has been catapulted from a distant vision of celebrated physicist Richard Feynman into a rapidly expanding area of research intersecting computer science, mathematics, physics, and engineering. In this talk, we give a gentle introduction to the ...
... Over the last 20 years, the field of quantum computing has been catapulted from a distant vision of celebrated physicist Richard Feynman into a rapidly expanding area of research intersecting computer science, mathematics, physics, and engineering. In this talk, we give a gentle introduction to the ...
QUIZ: History of Atomic Structure
... B) all forms of matter contain electrons C) all positive rays were actually protons D) all alpha particles are heavier than protons 3. Many classic experiments have given us indirect evidence of the nature of the atom. Which of the experiments listed below did not give the results described? A) The ...
... B) all forms of matter contain electrons C) all positive rays were actually protons D) all alpha particles are heavier than protons 3. Many classic experiments have given us indirect evidence of the nature of the atom. Which of the experiments listed below did not give the results described? A) The ...
Ian Walmsley
... Definition of distinguishable detector modes • Each state of the system mapped to a specific space-time mode ...
... Definition of distinguishable detector modes • Each state of the system mapped to a specific space-time mode ...
4-1. 1 - Riverside Local Schools
... ● Calculations: Calculate the following and fill in the table on the front 1. Find the distance ( z ) from the diffraction grating to the image of the spectral line using the following equation: z = √ x2 + y2 ...
... ● Calculations: Calculate the following and fill in the table on the front 1. Find the distance ( z ) from the diffraction grating to the image of the spectral line using the following equation: z = √ x2 + y2 ...
Aug 31 - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... The variance defines how wide/narrow a distribution is intensity ...
... The variance defines how wide/narrow a distribution is intensity ...
Section 3.1 and 3.2
... 2. The experimental evidence that led to the Rutherford model was the results of bombarding a thin metal foil with an alpha particle beam. The beam was mostly undeflected, as expected; however, a small but significant number of alpha particles were deflected—some, through very large angles. 3. (a) R ...
... 2. The experimental evidence that led to the Rutherford model was the results of bombarding a thin metal foil with an alpha particle beam. The beam was mostly undeflected, as expected; however, a small but significant number of alpha particles were deflected—some, through very large angles. 3. (a) R ...
incident angle
... Strange things happen on very small size scales. Things sometime behave like particles (usually when they interact with other things), sometimes they behave like waves (usually when they are traveling). This is called waveparticle duality, and is the key feature of quantum mechanics. Though many day ...
... Strange things happen on very small size scales. Things sometime behave like particles (usually when they interact with other things), sometimes they behave like waves (usually when they are traveling). This is called waveparticle duality, and is the key feature of quantum mechanics. Though many day ...
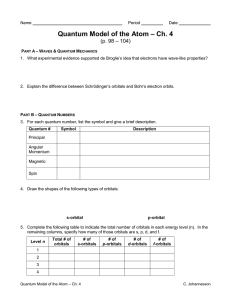
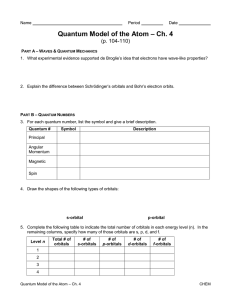
Quantum Model Worksheet
... PART A – WAVES & QUANTUM MECHANICS 1. What experimental evidence supported de Broglie’s idea that electrons have wave-like properties? ...
... PART A – WAVES & QUANTUM MECHANICS 1. What experimental evidence supported de Broglie’s idea that electrons have wave-like properties? ...
Quantum Model Worksheet
... PART A – WAVES & QUANTUM MECHANICS 1. What experimental evidence supported de Broglie’s idea that electrons have wave-like properties? ...
... PART A – WAVES & QUANTUM MECHANICS 1. What experimental evidence supported de Broglie’s idea that electrons have wave-like properties? ...
Quantum Theory 1 - Home Exercise 4
... 4. Particle on a ring - Consider a particle that is free to move on a ring of circumference L, such that ψ(x, t) = ψ(x + L, t) (a) Find the normalized stationary states of the system and explicitly show that they form an orthonormal basis. (b) Calculate the dispersion relation ωn (kn ) and show that ...
... 4. Particle on a ring - Consider a particle that is free to move on a ring of circumference L, such that ψ(x, t) = ψ(x + L, t) (a) Find the normalized stationary states of the system and explicitly show that they form an orthonormal basis. (b) Calculate the dispersion relation ωn (kn ) and show that ...