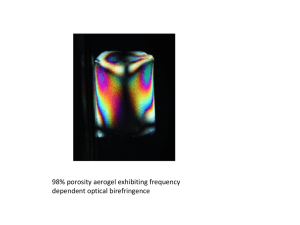
Measurements of the Geometric Phase of First-Order Optical Gaussian Beams
... Geometric phase is ubiquitous in systems that undergo cyclic transformations in either parameter or state space. Manifestations of this phase have been found in many physical systems. In optics, geometric phase has had an important effect, enhancing the way optical systems are analyzed, and stimulat ...
... Geometric phase is ubiquitous in systems that undergo cyclic transformations in either parameter or state space. Manifestations of this phase have been found in many physical systems. In optics, geometric phase has had an important effect, enhancing the way optical systems are analyzed, and stimulat ...
Electrons in Atoms
... Proposed that one cannot predict exactly where a particle will move since it’s impossible to measure the location and momentum of a particle simultaneously. Leads to the proposition that electron position around a nucleus cannot be precisely known, only predicted with a given probability. Erwi ...
... Proposed that one cannot predict exactly where a particle will move since it’s impossible to measure the location and momentum of a particle simultaneously. Leads to the proposition that electron position around a nucleus cannot be precisely known, only predicted with a given probability. Erwi ...
Quantum-limited measurements: One physicist`s crooked path from
... http://info.phys.unm.edu/~caves ...
... http://info.phys.unm.edu/~caves ...
Quantum spin
... Historically, Bethe's 1931 work on the isotropic case (gx = gy = gz), known as the XXX model, had a major impact and was the starting point for many of the subsequent developments in this area. He made an "ansatz" for the stationary states of the XXX spin-chain to be a superposition of plane waves ( ...
... Historically, Bethe's 1931 work on the isotropic case (gx = gy = gz), known as the XXX model, had a major impact and was the starting point for many of the subsequent developments in this area. He made an "ansatz" for the stationary states of the XXX spin-chain to be a superposition of plane waves ( ...
What is a photon, really - Philsci-Archive
... corresponds to its wavelength. A wave with a single wavelength is by definition an extended wave which fills all space, and therefore can be assigned no single position in space. If we squeeze the wave into a smaller volume, it will no longer have a single wavelength, but will have overtones of othe ...
... corresponds to its wavelength. A wave with a single wavelength is by definition an extended wave which fills all space, and therefore can be assigned no single position in space. If we squeeze the wave into a smaller volume, it will no longer have a single wavelength, but will have overtones of othe ...
Brief history of the atom
... Next, Millikan applied a charge to the falling drops by irradiating the bottom chamber with x-rays. This caused the air to become ionized, which basically means that the air particles lost electrons. A part of the oil droplets captured one or more of those extra electrons and became negatively charg ...
... Next, Millikan applied a charge to the falling drops by irradiating the bottom chamber with x-rays. This caused the air to become ionized, which basically means that the air particles lost electrons. A part of the oil droplets captured one or more of those extra electrons and became negatively charg ...
Hwk Set #14 - Publisher`s solutions
... The red-orange colors in the neon emission spectrum are due to transitions from excited 3p states to the lower energy but still excited 3s states. This occurs because the ground states are collisionally excited by the electrical discharge. The absorption spectrum of a gas consists of only those spec ...
... The red-orange colors in the neon emission spectrum are due to transitions from excited 3p states to the lower energy but still excited 3s states. This occurs because the ground states are collisionally excited by the electrical discharge. The absorption spectrum of a gas consists of only those spec ...
Quantum Bits - Science News
... which quantum mechanics plays a dominant role. The necessary calculations involving the behavior of atoms, electrons, or photons - invariably require huge amounts of time on a conventional computer. Feynman suggested that a computer based on some sort of quantum logic might circumvent the problem. I ...
... which quantum mechanics plays a dominant role. The necessary calculations involving the behavior of atoms, electrons, or photons - invariably require huge amounts of time on a conventional computer. Feynman suggested that a computer based on some sort of quantum logic might circumvent the problem. I ...
Conceptual Model for Diffusion
... model to predict the distribution of particle (mass) concentration , C(X,t). Note, that if we assume a unit mass per particle, we can conveniently interchange N = M. For simplicity we again consider a one-dimensional system, with the same rules of random motion described above, i.e. at each time ste ...
... model to predict the distribution of particle (mass) concentration , C(X,t). Note, that if we assume a unit mass per particle, we can conveniently interchange N = M. For simplicity we again consider a one-dimensional system, with the same rules of random motion described above, i.e. at each time ste ...
X-ray Diffraction
... what accuracy do I know the rate?” Ie. what is the error in such a measurement? 2) You will use a crystal as a diffraction grating of known spacing in order to measure the spectrum of x-rays emitted from copper bombarded with 30keV electrons. We will do a similar thing in two weeks when we look at t ...
... what accuracy do I know the rate?” Ie. what is the error in such a measurement? 2) You will use a crystal as a diffraction grating of known spacing in order to measure the spectrum of x-rays emitted from copper bombarded with 30keV electrons. We will do a similar thing in two weeks when we look at t ...
X-Ray Diffraction and Scanning Probe Microscopy
... Figure 6. A plot of tunneling current as a function of horizontal probe tip position. The absolute vertical position is held constant. When the tip is nearest the surface atoms, the current is highest. The wavy line above the shaded circles represents the contour of the surface. Challenges for STM T ...
... Figure 6. A plot of tunneling current as a function of horizontal probe tip position. The absolute vertical position is held constant. When the tip is nearest the surface atoms, the current is highest. The wavy line above the shaded circles represents the contour of the surface. Challenges for STM T ...
Polarization - Uplift Luna / Overview
... A ray of light is allowed to pass through an analyzer. If the intensity of the emergent light does not vary, when the analyzer is rotated, then the incident light is unpolarised; If the intensity of light varies between maximum and zero, when the analyzer is rotated through 900, then the incident li ...
... A ray of light is allowed to pass through an analyzer. If the intensity of the emergent light does not vary, when the analyzer is rotated, then the incident light is unpolarised; If the intensity of light varies between maximum and zero, when the analyzer is rotated through 900, then the incident li ...
Answers to Critical Thinking Questions 4
... The 2s has one radial node and the 3s has two radial nodes. 3p have one radial node. In general, the number of radial nodes is equal to n – l - 1. ...
... The 2s has one radial node and the 3s has two radial nodes. 3p have one radial node. In general, the number of radial nodes is equal to n – l - 1. ...
Chapter 7 – Quantum Theory and Atomic Structure Chapters 4 and 6
... nothing of the wave amplitude, but beyond that, begin by looking at the equation. Planck’s constant is very small (ca. 10-34) so the denominator must even smaller to make the wavelength visible in the macroscopic world. Since the objects we can see have very large masses, they have wavelengths many ...
... nothing of the wave amplitude, but beyond that, begin by looking at the equation. Planck’s constant is very small (ca. 10-34) so the denominator must even smaller to make the wavelength visible in the macroscopic world. Since the objects we can see have very large masses, they have wavelengths many ...