Fines imperii – imperium sine fine?
... he fought against them.17 Probably the military situation in Pannonia, on the fringes of Italy, became so precarious that it demanded the presence of an experienced army leader. One year later, command was given to the best Roman general, M. Vipsanius Agrippa, who inspired such terror among the Pann ...
... he fought against them.17 Probably the military situation in Pannonia, on the fringes of Italy, became so precarious that it demanded the presence of an experienced army leader. One year later, command was given to the best Roman general, M. Vipsanius Agrippa, who inspired such terror among the Pann ...
The Biblical City of Philippi, Greece
... then became a Roman colony, i.e. a settlement for veteran Roman soldiers who possessed the rights of self-government under Roman laws and freedom from taxes. Further veterans were settled there after the defeat of Antony and Cleopatra at Actium in 31 BC. According to RSV it was the leading city of t ...
... then became a Roman colony, i.e. a settlement for veteran Roman soldiers who possessed the rights of self-government under Roman laws and freedom from taxes. Further veterans were settled there after the defeat of Antony and Cleopatra at Actium in 31 BC. According to RSV it was the leading city of t ...
Word File - UNESCO World Heritage Centre
... founded by Paul the Apostle. During the early Christian period the city experienced a major economic and spiritual boom, a fact demonstrated by the fortification programme instigated by Justinian and the plethora of monuments which adorned the city. The administrative reorganization of the Byzantine ...
... founded by Paul the Apostle. During the early Christian period the city experienced a major economic and spiritual boom, a fact demonstrated by the fortification programme instigated by Justinian and the plethora of monuments which adorned the city. The administrative reorganization of the Byzantine ...
Consequences of Severus` campaigns: permanent annexation of
... This statue is that of Septimius Hairan, son of Odainat, the illustrious senator and chief of Palmyra (ras Tadmor), which has been set up to him by Aurelius Philinus, son of Marius Philinus, (son of) Ra‘ai, the soldier who was in the legion of Bostra: to his honour. In the month of Tishri of the yea ...
... This statue is that of Septimius Hairan, son of Odainat, the illustrious senator and chief of Palmyra (ras Tadmor), which has been set up to him by Aurelius Philinus, son of Marius Philinus, (son of) Ra‘ai, the soldier who was in the legion of Bostra: to his honour. In the month of Tishri of the yea ...
EU Grudtvig Project“Ancient Cities And Reflections To
... its name from the Bithyni, a tribe that had emigrated from Thrace. The country ...
... its name from the Bithyni, a tribe that had emigrated from Thrace. The country ...
Tongeren
... products included cow hide and bone. The Romans imported different varieties of fruit and introduced more use of wine, olive oil, shellfish, figs and herbs. From 150 AD Roman coinage was in common use amongst tradesmen, which facilitated the development of local markets as residents could buy goods ...
... products included cow hide and bone. The Romans imported different varieties of fruit and introduced more use of wine, olive oil, shellfish, figs and herbs. From 150 AD Roman coinage was in common use amongst tradesmen, which facilitated the development of local markets as residents could buy goods ...
History: The Romans Core Knowledge
... Wealthy Romans ate while reclining on couches, served by slaves. This would be a social occasion and guests would be entertained with music or poetry readings. Q. What were Roman buildings like? A. The Romans were excellent builders. The remains of many Roman buildings still exist today. Houses were ...
... Wealthy Romans ate while reclining on couches, served by slaves. This would be a social occasion and guests would be entertained with music or poetry readings. Q. What were Roman buildings like? A. The Romans were excellent builders. The remains of many Roman buildings still exist today. Houses were ...
6th Grade Math Lesson Plans - d
... document, find 3 main ideas, draw an image to represent each idea, and write a paragraph about the article. What is the article mainly about? Who thinks they found Anthony and Cleopatra’s tomb? ...
... document, find 3 main ideas, draw an image to represent each idea, and write a paragraph about the article. What is the article mainly about? Who thinks they found Anthony and Cleopatra’s tomb? ...
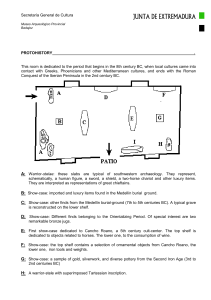
Secretaría General de Cultura PROTOHISTORY . This room is
... Museo Arqueológico Provincial Badajoz ...
... Museo Arqueológico Provincial Badajoz ...
Unit 1: Pupil Book
... built in 122 AD to protect the south from any possible attacks from the north. You can still see the remains of Hadrian’s Wall in parts of northern Britain today. ...
... built in 122 AD to protect the south from any possible attacks from the north. You can still see the remains of Hadrian’s Wall in parts of northern Britain today. ...
The Roman Invasion of Britain!
... What was Britain like before the Romans? Who were the Romans and who founded Rome? When did the Romans invade Britain? Why did the Romans invade Britain? Why was the Roman Empire important? Why did Hadrian build his wall? Who was in the Roman Army? How did Roman Britain defend itself? What did the R ...
... What was Britain like before the Romans? Who were the Romans and who founded Rome? When did the Romans invade Britain? Why did the Romans invade Britain? Why was the Roman Empire important? Why did Hadrian build his wall? Who was in the Roman Army? How did Roman Britain defend itself? What did the R ...
Julio-Claudians (r. 27 BC – 68 AD)
... *Romans were more international: they made an effort to control the world, as they knew it Palestina – now known as Judea or Syria – where Hadrian began the Diaspora of the Jews Dacia – now known as Romania - north of the Danube – conquered by Tragean Macedonia – where Alexander the Great hail ...
... *Romans were more international: they made an effort to control the world, as they knew it Palestina – now known as Judea or Syria – where Hadrian began the Diaspora of the Jews Dacia – now known as Romania - north of the Danube – conquered by Tragean Macedonia – where Alexander the Great hail ...
5. Roman Medicine - Garforth Academy
... These icons indicate that teacher’s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are not editable. For more detailed instructions, see the Getting Started presentation. 1 of 16 ...
... These icons indicate that teacher’s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are not editable. For more detailed instructions, see the Getting Started presentation. 1 of 16 ...
Roman Medicine - kings-grove.cheshire.sch.uk
... These icons indicate that teacher’s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are not editable. For more detailed instructions, see the Getting Started presentation. 1 of 16 ...
... These icons indicate that teacher’s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are not editable. For more detailed instructions, see the Getting Started presentation. 1 of 16 ...
Appendices extracts - Goodfellow Publishers
... confusion over his real name, being identified as C. Petronius Arbiter, but the manuscript text of the Satyricon, used in this volume calls him Titus Petronius. ...
... confusion over his real name, being identified as C. Petronius Arbiter, but the manuscript text of the Satyricon, used in this volume calls him Titus Petronius. ...
Novice Questions (replacements)
... MYTH. Let’s talk about mythological couples. What pair were rewarded for their piety and turned into trees to protect a temple after they showed hospitality to gods who came in the guise of beggars? BAUCIS and PHILEMON B1. What two Roman gods came to them disguised as beggars? JUPITER and MERCURY B2 ...
... MYTH. Let’s talk about mythological couples. What pair were rewarded for their piety and turned into trees to protect a temple after they showed hospitality to gods who came in the guise of beggars? BAUCIS and PHILEMON B1. What two Roman gods came to them disguised as beggars? JUPITER and MERCURY B2 ...
Why Did the Romans Invade Britain?
... world “civilised” like them. Read the quote on the next slide to see what they believed about this! ...
... world “civilised” like them. Read the quote on the next slide to see what they believed about this! ...
Why Did the Romans Invade Britain?
... the world “civilised” like them. Read the quote on the next slide to see what they believed about this! ...
... the world “civilised” like them. Read the quote on the next slide to see what they believed about this! ...
Historical information / Variant / Development notes - PD
... 43 AC the Romans landed again and began to gradually conquer the province. They benefited from internal conflicts between the British tribes and crushed one tribe after another. In order to secure the conquests they erected forts and military bases throughout Britannia. In 59 AC there was an upheava ...
... 43 AC the Romans landed again and began to gradually conquer the province. They benefited from internal conflicts between the British tribes and crushed one tribe after another. In order to secure the conquests they erected forts and military bases throughout Britannia. In 59 AC there was an upheava ...
The etymology and classification of the Germanic tribes. Greek writer
... inhabitants of Gaul is designated different from their neighbors (in particular, living beyond the Rhine) tribes. The assumption is based on the Welsh of ger, Irish gearr - terms, meaning the proximity. In the Late Iron Age in north-eastern Iberia lived a tribe of Herman, but most historians regard ...
... inhabitants of Gaul is designated different from their neighbors (in particular, living beyond the Rhine) tribes. The assumption is based on the Welsh of ger, Irish gearr - terms, meaning the proximity. In the Late Iron Age in north-eastern Iberia lived a tribe of Herman, but most historians regard ...
Roman invasion of Britain - Primary Leap Worksheets.
... Roman Invasion of Britain Before the Romans invaded Britain the Celts ruled Britain. In those times there were no roads and no towns. The Celts travelled along muddy tracks. The Celts had different tribes that constantly fought each other. When Julius Caesar ruled Rome, he made two attempts to invad ...
... Roman Invasion of Britain Before the Romans invaded Britain the Celts ruled Britain. In those times there were no roads and no towns. The Celts travelled along muddy tracks. The Celts had different tribes that constantly fought each other. When Julius Caesar ruled Rome, he made two attempts to invad ...
Iberian Peninsula
... Roman Iberia • In 219 BC, Roman troops invaded the Iberian Peninsula, during the Second Punic war against the Carthaginians. • They annexed it under Augustus, after two centuries of war with the Celtic and Iberian tribes and the Phoenician, Greek and Carthaginian colonies, resulting in the creation ...
... Roman Iberia • In 219 BC, Roman troops invaded the Iberian Peninsula, during the Second Punic war against the Carthaginians. • They annexed it under Augustus, after two centuries of war with the Celtic and Iberian tribes and the Phoenician, Greek and Carthaginian colonies, resulting in the creation ...
The Roman Empire in 218 BC
... Romans built was the frontier between England and Scotland, called Hadrian’s Wall, named after the Emperor who ordered it built. It was started in 120 A.D. and took nine years to build. ...
... Romans built was the frontier between England and Scotland, called Hadrian’s Wall, named after the Emperor who ordered it built. It was started in 120 A.D. and took nine years to build. ...
Judith Cheston Publicity
... And Furrina whose festival the Romans celebrated every 25 July but by 100 BC no one could remember what exactly she was goddess of! Romans also had a lot of strange superstitions and customs: Woman thought combing their hair with the spear of someone just killed in the arena would bring them luc ...
... And Furrina whose festival the Romans celebrated every 25 July but by 100 BC no one could remember what exactly she was goddess of! Romans also had a lot of strange superstitions and customs: Woman thought combing their hair with the spear of someone just killed in the arena would bring them luc ...
Romania in Antiquity

The Antiquity in Romania spans the period between the foundation of Greek colonies in present-day Dobruja and the withdrawal of the Romans from ""Dacia Trajana"" province. The earliest records of the history of the regions which now form Romania were made after the establishment of three Greek towns—Histria, Tomis, and Callatis—on the Black Sea coast in the 7th and 6th centuries BC. They developed into important centers of commerce and had a close relationship with the natives. The latter were first described by Herodotus, who made mention of the Getae of the Lower Danube region, the Agathyrsi of Transylvania and the Sygannae of Crişana.Archaeological research prove that Celts dominated Transylvania between the middle of the 5th century and the end of the 3rd century BC. The Bastarnae—a warlike Germanic tribe—settled in the regions to the east of the Carpathian Mountains around 200 BC. Confrontations between the natives and the Roman Empire began in the late 1st century BC. Among the former, the Dacians—who were closely connected to the Getae—rose to eminence under King Burebista (c. 80–44 BC). He unified the tribes dwelling between the Middle Danube, the Northern Carpathians, the Dniester and the Balkan Mountains into a powerful, but ephemeral empire. It disintegrated into at least four parts after his death. Large territories to the north of the Lower Danube—the lands between the Tisa, the Northern Carpathians, the Dniester and the Lower Danube—were again unified for less than two decades by King Decebalus of the Dacians (87–106 AD).Modern Dobruja—the territory between the Lower Danube and the Black Sea—was the first historical region of Romania to have been incorporated in the Roman Empire. The region was attached to the Roman province of Moesia between 46 and 79 AD. The Romans also occupied Banat, Oltenia and Transylvania after the fall of Decebalus and the disintegration of his kingdom in 106. The three regions together formed the new province of Dacia. The new province was surrounded by ""barbarian"" tribes, including the Costoboci, the Iazyges and the Roxolani. New Germanic tribes—the Buri and the Vandals—arrived and settled in the vicinity of Dacia province in the course of the Marcomannic Wars in the second half of the 2nd century.