Transcription
... snRNAs - small nuclear RNAs, function in a variety of nuclear processes, including the splicing of pre-mRNA snoRNAs - small nucleolar RNAs, used to process and chemically modify rRNAs miRNAs - microRNAs, regulate gene expression typically by blocking translation of selective mRNAs siRNAs - small int ...
... snRNAs - small nuclear RNAs, function in a variety of nuclear processes, including the splicing of pre-mRNA snoRNAs - small nucleolar RNAs, used to process and chemically modify rRNAs miRNAs - microRNAs, regulate gene expression typically by blocking translation of selective mRNAs siRNAs - small int ...
MITOCHONDRIA BIOLOGY - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... A lot of the DNA must be non-coding; don’t have many more genes than liverwort Mt DNA. There are a lot of Cp-DNA sequences • “promiscuous DNA", integrates by illegitimate ...
... A lot of the DNA must be non-coding; don’t have many more genes than liverwort Mt DNA. There are a lot of Cp-DNA sequences • “promiscuous DNA", integrates by illegitimate ...
USMLE Step 1 Web Prep — Transcription and RNA Processing: Part
... The primary transcript must undergo extensive posttranscriptional processing inside the nucleus to form the mature mRNA molecule A 7-methylguanosine cap is added to the 5' end while the RNA molecule is still being synthesized. The cap structure serves as a ribosome-binding site and also helps to pro ...
... The primary transcript must undergo extensive posttranscriptional processing inside the nucleus to form the mature mRNA molecule A 7-methylguanosine cap is added to the 5' end while the RNA molecule is still being synthesized. The cap structure serves as a ribosome-binding site and also helps to pro ...
Part B - Modeling Transcription: How is RNA modified? Name:
... functions as part of an "attach here" sign for ribosomes. The other end of an mRNA molecule, the 3' end, is also modified before the message exits the nucleus. At the 3' end, an enzyme makes a poly(A) tail consisting of some 50 to 250 adenine nucleotides. Like the 5' cap, the poly(A) tail inh ...
... functions as part of an "attach here" sign for ribosomes. The other end of an mRNA molecule, the 3' end, is also modified before the message exits the nucleus. At the 3' end, an enzyme makes a poly(A) tail consisting of some 50 to 250 adenine nucleotides. Like the 5' cap, the poly(A) tail inh ...
chapter 17 - faculty at Chemeketa
... Rosalind Franklin is most associated with the discovery of the structure of DNA. At 26, after she had her PhD, Franklin began working in x-ray diffraction - using x-rays to create images of crystallized solids. She pioneered the use of this method in analyzing complex, unorganized matter such as la ...
... Rosalind Franklin is most associated with the discovery of the structure of DNA. At 26, after she had her PhD, Franklin began working in x-ray diffraction - using x-rays to create images of crystallized solids. She pioneered the use of this method in analyzing complex, unorganized matter such as la ...
RNA - Granbury ISD
... amino acids; they provide instructions for making the protein. • More than one codon can code for the same amino acid. • However, for any one codon, there can be only one amino acid. ...
... amino acids; they provide instructions for making the protein. • More than one codon can code for the same amino acid. • However, for any one codon, there can be only one amino acid. ...
Chapter 14 Review
... NO NEED for complete sentences! 6. Use the following DNA sequence to show examples of the three gene mutations. Write the mutated sequence, circle the mutation and label the mutation type. You should end up with three separate DNA sequences. ...
... NO NEED for complete sentences! 6. Use the following DNA sequence to show examples of the three gene mutations. Write the mutated sequence, circle the mutation and label the mutation type. You should end up with three separate DNA sequences. ...
Class Outline 1. Understanding polynucleotide structure (Read) 2
... HOW DNAs AND RNAs ARE USED BY LIVING CELLS Transcription is the process by which the information contained in a section of DNA is transferred to a newly assembled piece of messenger RNA (mRNA) and other types of RNA (e.g. ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA etc.). It is facilitated by RNA polymerase and tra ...
... HOW DNAs AND RNAs ARE USED BY LIVING CELLS Transcription is the process by which the information contained in a section of DNA is transferred to a newly assembled piece of messenger RNA (mRNA) and other types of RNA (e.g. ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA etc.). It is facilitated by RNA polymerase and tra ...
transcription - moleculesoflife1
... For the the following sequences, fill in either the DNA, the mRNA sequence, the tRNA anticodons, or the amino acid sequences (Refer to Genetic code) that have been left blank. If several sequences might work choose any one. 1. DNA mRNA ...
... For the the following sequences, fill in either the DNA, the mRNA sequence, the tRNA anticodons, or the amino acid sequences (Refer to Genetic code) that have been left blank. If several sequences might work choose any one. 1. DNA mRNA ...
Unfinished Material - Answer Key
... o This happens because there is no nuclear envelope to separate the processes. - In eukaryotes, translation and transcription occur at separate times and in separate locations. o Transcription is conducted in the nucleus to produce a mature mRNA; the mRNA is then exported to the cytoplasm of the cel ...
... o This happens because there is no nuclear envelope to separate the processes. - In eukaryotes, translation and transcription occur at separate times and in separate locations. o Transcription is conducted in the nucleus to produce a mature mRNA; the mRNA is then exported to the cytoplasm of the cel ...
Transcription/Translation foldable
... • WHAT? DNA is transcribed into mRNA. That means I am copying DNA and making mRNA. • Location? Nucleus • Why? DNA cannot leave the nucleus, so the messenger RNA has to take the nucleotide sequence to the ribosome to make proteins. Cut out the picture below. Label and color the DNA blue and the mRNA ...
... • WHAT? DNA is transcribed into mRNA. That means I am copying DNA and making mRNA. • Location? Nucleus • Why? DNA cannot leave the nucleus, so the messenger RNA has to take the nucleotide sequence to the ribosome to make proteins. Cut out the picture below. Label and color the DNA blue and the mRNA ...
Chapter 1 Notes
... Ribosomes are made of 2 subunits that are constructed of proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) - contains a binding site for mRNA - contains 3 binding sites for tRNA - P site: holds the tRNA carrying the growing peptide chain ...
... Ribosomes are made of 2 subunits that are constructed of proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) - contains a binding site for mRNA - contains 3 binding sites for tRNA - P site: holds the tRNA carrying the growing peptide chain ...
Molecular Evolution
... Nearly all extant organisms have DNA-based genomes. Why did DNA-based (instead of RNA-based) genomes win? - DNA is mutationally less vulnerable than RNA. [e.g., RNA doesn’t correct the very common mutation from C->U] - This chemical advantage lead to more reliable production of progeny genotypes. ...
... Nearly all extant organisms have DNA-based genomes. Why did DNA-based (instead of RNA-based) genomes win? - DNA is mutationally less vulnerable than RNA. [e.g., RNA doesn’t correct the very common mutation from C->U] - This chemical advantage lead to more reliable production of progeny genotypes. ...
The control of complexity in the human genome
... double helix of base pairs A, C, T, G A – T, G - C ribosomal, messenger, transfer (U for T) discovered structure DNA discovered transforming principle of DNA blender experiment sequence of amino acids, selected by codons and tRNA for proteins codon => amino acid three base pairs-together see slide ...
... double helix of base pairs A, C, T, G A – T, G - C ribosomal, messenger, transfer (U for T) discovered structure DNA discovered transforming principle of DNA blender experiment sequence of amino acids, selected by codons and tRNA for proteins codon => amino acid three base pairs-together see slide ...
answers
... __JAMES WATSON____ & _FRANCIS CRICK_____ used _Rosalind Franklin’s X-ray images to help them figure out the structure of DNA. SUBUNIT PROTEINS ...
... __JAMES WATSON____ & _FRANCIS CRICK_____ used _Rosalind Franklin’s X-ray images to help them figure out the structure of DNA. SUBUNIT PROTEINS ...
RNA and protein synthesis
... 4. A sequence of three mRNA nucleotides is called a codon. 5. One codon codes for one amino acid. 6. tRNA molecules enter the ribosome carrying the correct amino acid. The tRNA has an anticodon that matches the codon on the mRNA. 7. Amino acids are linked together to form a protein! ...
... 4. A sequence of three mRNA nucleotides is called a codon. 5. One codon codes for one amino acid. 6. tRNA molecules enter the ribosome carrying the correct amino acid. The tRNA has an anticodon that matches the codon on the mRNA. 7. Amino acids are linked together to form a protein! ...
Jeopardy!!
... free floating in the cytoplasm In Eukaryotes, the DNA is safely contained within the nucleus ...
... free floating in the cytoplasm In Eukaryotes, the DNA is safely contained within the nucleus ...
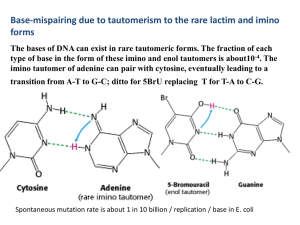
4 . The imino tautomer of adenine can pair with cytosine
... Why not polyamide backbone as illustrated in PNA (Peptide Nucleic Acid) TOO MUCH inter-chain binding (H-bonds and other forces as found in protein secondary structures; also no electrostatic repulsion as present in phosphate ...
... Why not polyamide backbone as illustrated in PNA (Peptide Nucleic Acid) TOO MUCH inter-chain binding (H-bonds and other forces as found in protein secondary structures; also no electrostatic repulsion as present in phosphate ...
Genetics Unit Study guide
... What is the name for the sugar in RNA nucleotides? What type of structure is an RNA strand? How many RNA nucleotide bases are there? What are their names? What types of RNA are there? What is the function of each type of RNA? How is mRNA made? Where is mRNA made? What is transcription? What is trans ...
... What is the name for the sugar in RNA nucleotides? What type of structure is an RNA strand? How many RNA nucleotide bases are there? What are their names? What types of RNA are there? What is the function of each type of RNA? How is mRNA made? Where is mRNA made? What is transcription? What is trans ...
aptamers04
... Mitochondrial group I introns (GR –catalyzed) also can self-splice Then group II introns in mitochondria (lariat-formers) Mutations (100’s): Internal guide sequence GR-binding site secondary structure Conserved base analysis (100’s) confirms structure X-ray diffraction: a few 3-D structures ...
... Mitochondrial group I introns (GR –catalyzed) also can self-splice Then group II introns in mitochondria (lariat-formers) Mutations (100’s): Internal guide sequence GR-binding site secondary structure Conserved base analysis (100’s) confirms structure X-ray diffraction: a few 3-D structures ...
Document
... 1. Ribosomal RNA – rRNA – exist outside the nucleus in ribosomes, small structures where protein synthesis takes place. A ribosome is a complex consisting of 60% rRNA and 50% proteins. 2. Messenger RNA – mRNA – nucleic acis that record information copied (transcription) from a DNA segment and carry ...
... 1. Ribosomal RNA – rRNA – exist outside the nucleus in ribosomes, small structures where protein synthesis takes place. A ribosome is a complex consisting of 60% rRNA and 50% proteins. 2. Messenger RNA – mRNA – nucleic acis that record information copied (transcription) from a DNA segment and carry ...
Chapter 17
... The processing of genetic information is imperfect and is a source of genetic variation Changes in genotype can result in changes in phenotype. 1. Alterations in a DNA sequence can lead to changes in the type or amount of the protein produced and the consequent phenotype. 2. DNA mutations can be po ...
... The processing of genetic information is imperfect and is a source of genetic variation Changes in genotype can result in changes in phenotype. 1. Alterations in a DNA sequence can lead to changes in the type or amount of the protein produced and the consequent phenotype. 2. DNA mutations can be po ...
Laboratory of RNA – ebook
... neurodegenerative diseases A second line of research is aimed at studying some very small RNA molecules called microRNAs (miRNAs) that have only recently been discovered. Due to their size these RNA molecules were overlooked for a long time, but it has become clear in the last decade that thousands ...
... neurodegenerative diseases A second line of research is aimed at studying some very small RNA molecules called microRNAs (miRNAs) that have only recently been discovered. Due to their size these RNA molecules were overlooked for a long time, but it has become clear in the last decade that thousands ...
1. ELONGATION
... separately through the nuclear pores . The pores are structured to allow transit of only the subunits. Whole ribosomes are formed outside in the cytoplasm. This prevents protein synthesis from occurring in the nucleus. Genetica per Scienze Naturali a.a. 05-06 prof S. Presciuttini ...
... separately through the nuclear pores . The pores are structured to allow transit of only the subunits. Whole ribosomes are formed outside in the cytoplasm. This prevents protein synthesis from occurring in the nucleus. Genetica per Scienze Naturali a.a. 05-06 prof S. Presciuttini ...
DNA Protein synthesis Review Answer Key.doc
... The first step in making a protein is to make a copy of the ___________ in the nucleus. DNA or Gene What nucleic acid contains the master code for making proteins? DNA What nucleic acids acts as a blueprint in copying the master code? mRNA Compare and contrast the nitrogen bases on DNA and R ...
... The first step in making a protein is to make a copy of the ___________ in the nucleus. DNA or Gene What nucleic acid contains the master code for making proteins? DNA What nucleic acids acts as a blueprint in copying the master code? mRNA Compare and contrast the nitrogen bases on DNA and R ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.