File
... 2. RNA polymerase enzyme moves to the specific section of DNA and unwinds and unzips the DNA double helix at that point 3. RNA nucleotides pair with complementary DNA base pairs (A-U, G-C) forming mRNA 4. RNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the 3’ end of mRNA ...
... 2. RNA polymerase enzyme moves to the specific section of DNA and unwinds and unzips the DNA double helix at that point 3. RNA nucleotides pair with complementary DNA base pairs (A-U, G-C) forming mRNA 4. RNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the 3’ end of mRNA ...
Chapter 16 Research Discovery of DNA`s Structure and Function
... ➢ Promoter - RNA polymerase can bind with the DNA to begin transcription ➢ Genes - nucleotide sequences that encode subunits of the enzyme Repressor Protein - binds to the operator and blocks the attachment of RNA polymerase to the promoter, preventing transcription of genes Regulatory Genes - cod ...
... ➢ Promoter - RNA polymerase can bind with the DNA to begin transcription ➢ Genes - nucleotide sequences that encode subunits of the enzyme Repressor Protein - binds to the operator and blocks the attachment of RNA polymerase to the promoter, preventing transcription of genes Regulatory Genes - cod ...
DNA and RNA Part 2 Protein Synthesis
... Steps of Translation 1. The first codon of the mRNA strand attaches to a ribosome 2. tRNA molecules, each carrying a specific amino acid approach the ribosome 3. tRNA anticodon pairs with mRNA codon 4. The first codon on mRNA is AUG which codes for amino acid methionine. AUG is the start codon for p ...
... Steps of Translation 1. The first codon of the mRNA strand attaches to a ribosome 2. tRNA molecules, each carrying a specific amino acid approach the ribosome 3. tRNA anticodon pairs with mRNA codon 4. The first codon on mRNA is AUG which codes for amino acid methionine. AUG is the start codon for p ...
The Genetic Code The nucleotide bases of the DNA strand
... This step of assembling an RNA molecule according to the DNA sequence is called transcription – the original information is now a message in form of an RNA strand. This message is moving from the nucleus into the cytoplasm where it is read, employing the same principle of complementary nucleotide ba ...
... This step of assembling an RNA molecule according to the DNA sequence is called transcription – the original information is now a message in form of an RNA strand. This message is moving from the nucleus into the cytoplasm where it is read, employing the same principle of complementary nucleotide ba ...
The Universal Dogma of Genetics
... The Genetic Code • The genetic code is a set of instructions indicating which codons are translated into which amino acid • The genetic code does not only specify which codons code for which amino acids, but also specify ‘start’ and ‘stop’ signals, which begin and end protein synthesis, respectivel ...
... The Genetic Code • The genetic code is a set of instructions indicating which codons are translated into which amino acid • The genetic code does not only specify which codons code for which amino acids, but also specify ‘start’ and ‘stop’ signals, which begin and end protein synthesis, respectivel ...
Pa I I, hl. L. Blasticidin-S: on... Cycloheximide has been used widely as ...
... the medium or the incubation temperature. At any fixed temperafvre, the RNA content is greater for the foster growing mycelio: D linear relationship may be found between the log of the RNA content and the rote of growth. When the rote of growth is enhanced by increasi~ the tempemture, the RNA conten ...
... the medium or the incubation temperature. At any fixed temperafvre, the RNA content is greater for the foster growing mycelio: D linear relationship may be found between the log of the RNA content and the rote of growth. When the rote of growth is enhanced by increasi~ the tempemture, the RNA conten ...
Genetics
... What is the genetic material? In eukaryotes & prokaryotes it is DNA, in viruses it can be either DNA or RNA. What do DNA & RNA stand for? DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid / RNA: ribonucleic ...
... What is the genetic material? In eukaryotes & prokaryotes it is DNA, in viruses it can be either DNA or RNA. What do DNA & RNA stand for? DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid / RNA: ribonucleic ...
chapter 17 and 18 study guide
... the mRNA to leave the nucleus, and helps the ribosome attach for translation Alternative splicing? How multiple polypeptides can be made from the same mRNA transcript depending on which introns are removed from the transcript Introns? Exons? UTRs? Introns are noncoding regions that get removed from ...
... the mRNA to leave the nucleus, and helps the ribosome attach for translation Alternative splicing? How multiple polypeptides can be made from the same mRNA transcript depending on which introns are removed from the transcript Introns? Exons? UTRs? Introns are noncoding regions that get removed from ...
SB2a Build DNA using the Nucleotides Then Print
... copied to form the new nucleic acid called RNA? Complete the key for the nitrogen bases for your DNA Model ...
... copied to form the new nucleic acid called RNA? Complete the key for the nitrogen bases for your DNA Model ...
A comprehensive catalogue of human RNA-binding
... the team were able to map so-called connectivity quantitative trait loci (cQTLs). These cQTLs are natural genetic variants that influence the regulatory interactions of specific transcription factors and their target genes (for example, a polymorphism that occurs in the coding or promoter sequence o ...
... the team were able to map so-called connectivity quantitative trait loci (cQTLs). These cQTLs are natural genetic variants that influence the regulatory interactions of specific transcription factors and their target genes (for example, a polymorphism that occurs in the coding or promoter sequence o ...
Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein
... 4. Distinguish between the “one gene–one enzyme” hypothesis and the “one gene–one polypeptide” hypothesis and explain why the original hypothesis was changed. 5. Explain how RNA differs from DNA. 6. Briefly explain how information flows from gene to protein. 7. Distinguish between transcription and ...
... 4. Distinguish between the “one gene–one enzyme” hypothesis and the “one gene–one polypeptide” hypothesis and explain why the original hypothesis was changed. 5. Explain how RNA differs from DNA. 6. Briefly explain how information flows from gene to protein. 7. Distinguish between transcription and ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... The Structure of RNA List the three main differences between RNA and DNA. 1. RNA has ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose. 2. RNA is generally single-stranded, instead of double-stranded. 3.RNA contains uracil in place of thymine. ...
... The Structure of RNA List the three main differences between RNA and DNA. 1. RNA has ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose. 2. RNA is generally single-stranded, instead of double-stranded. 3.RNA contains uracil in place of thymine. ...
13 Transcription and translation
... ● Only 20 amino acids found in proteins, depend on combination of bases in codon - 4 bases, 3 in codon = 64 possible different combinations for the 20 different amino acids - therefore some amino acids have more than one codon ● Start and stop codons initiate or terminate protein synthesis ...
... ● Only 20 amino acids found in proteins, depend on combination of bases in codon - 4 bases, 3 in codon = 64 possible different combinations for the 20 different amino acids - therefore some amino acids have more than one codon ● Start and stop codons initiate or terminate protein synthesis ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis: Power Point presentation
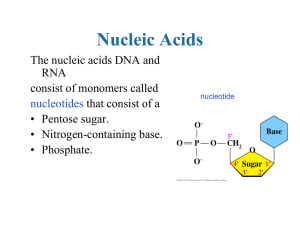
... Nucleic Acids The nucleic acids DNA and RNA consist of monomers called nucleotides that consist of a • Pentose sugar. • Nitrogen-containing base. • Phosphate. ...
... Nucleic Acids The nucleic acids DNA and RNA consist of monomers called nucleotides that consist of a • Pentose sugar. • Nitrogen-containing base. • Phosphate. ...
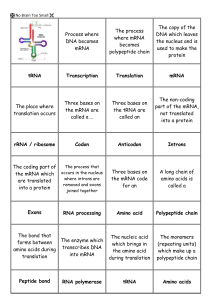
Gene expression flash cards
... The process that The coding part of the mRNA which occurs in the nucleus where introns are are translated removed and exons into a protein joined together ...
... The process that The coding part of the mRNA which occurs in the nucleus where introns are are translated removed and exons into a protein joined together ...
L14 Gene to Protein Fa08
... • mRNA binds to small subunit • Initiator tRNA (UAC anticodon) binds to mRNA at start ...
... • mRNA binds to small subunit • Initiator tRNA (UAC anticodon) binds to mRNA at start ...
Chapter 16 and 17 Review
... What kind of bond holds DNA strands together? The two DNA strands are said to be antiparallel. What does this mean? DNA Replication ...
... What kind of bond holds DNA strands together? The two DNA strands are said to be antiparallel. What does this mean? DNA Replication ...
A1985ASW1100001
... the amino acids was bound to the new RNA reversibly and at a separate site. The clincher as to its role in protein synthesis was that after it was charged with amino acids and reisolated, its bound amino acids were rapidly and quantitatively transferred to peptide linkages in protein on ribosomes~An ...
... the amino acids was bound to the new RNA reversibly and at a separate site. The clincher as to its role in protein synthesis was that after it was charged with amino acids and reisolated, its bound amino acids were rapidly and quantitatively transferred to peptide linkages in protein on ribosomes~An ...
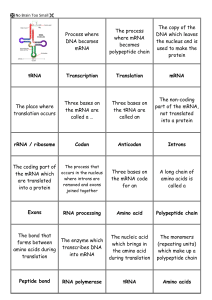
Gene expression flash cards
... The process that The coding part of the mRNA which occurs in the nucleus where introns are are translated removed and exons into a protein joined together ...
... The process that The coding part of the mRNA which occurs in the nucleus where introns are are translated removed and exons into a protein joined together ...
CHAPTER 7 From DNA to Protein
... The site where protein synthesis begins on the mRNA is crucial, because it sets the reading frame for the whole length of the massage. An error of one nucleotide either way at this stage will cause every subsequent codon in the massage to be misread, so that a nonfunctional protein with a garbled se ...
... The site where protein synthesis begins on the mRNA is crucial, because it sets the reading frame for the whole length of the massage. An error of one nucleotide either way at this stage will cause every subsequent codon in the massage to be misread, so that a nonfunctional protein with a garbled se ...
Transcription is the process by which RNA polymerase copies a
... scientists also noticed that DNA is like a zipper – in it can be split into a two single strands by separating the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs. Check out this video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0CMIgZQakHY ...
... scientists also noticed that DNA is like a zipper – in it can be split into a two single strands by separating the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs. Check out this video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0CMIgZQakHY ...
GENE REGULATION IN PROKARYOTES AND EUKARYOTES
... mRNA must be exported from the nucleus before it can be translated. This means that other factors being equal, protein synthesis in a prokaryote can be faster than in a eukaryote. It also means that the primary mRNA transcript can be processed before it is exported from the nucleus, with translation ...
... mRNA must be exported from the nucleus before it can be translated. This means that other factors being equal, protein synthesis in a prokaryote can be faster than in a eukaryote. It also means that the primary mRNA transcript can be processed before it is exported from the nucleus, with translation ...
Topic 3 The chemistry of life
... 56. The genetic code is actually composed of triplets of bases called codons. The codons are present on the RNA formed during translation. Therefore, codons do not contain thymine. 57. The RNA formed during transcription is called messenger or mRNA. This mRNA carries the genetic code out of the nucl ...
... 56. The genetic code is actually composed of triplets of bases called codons. The codons are present on the RNA formed during translation. Therefore, codons do not contain thymine. 57. The RNA formed during transcription is called messenger or mRNA. This mRNA carries the genetic code out of the nucl ...
2.7 Review - Peoria Public Schools
... 56. The genetic code is actually composed of triplets of bases called codons. The codons are present on the RNA formed during translation. Therefore, codons do not contain thymine. 57. The RNA formed during transcription is called messenger or mRNA. This mRNA carries the genetic code out of the nucl ...
... 56. The genetic code is actually composed of triplets of bases called codons. The codons are present on the RNA formed during translation. Therefore, codons do not contain thymine. 57. The RNA formed during transcription is called messenger or mRNA. This mRNA carries the genetic code out of the nucl ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.