What does DNA stand for?
... What are the 3 parts of the DNA molecule? Phosphate group Deoxyribose Sugar Nitrogen Base ...
... What are the 3 parts of the DNA molecule? Phosphate group Deoxyribose Sugar Nitrogen Base ...
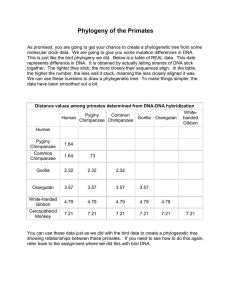
Phylogeny of the Primates
... As promised, you are going to get your chance to create a phylogenetic tree from some molecular clock data. We are going to give you some mutation differences in DNA. This is just like the bird phylogeny we did. Below is a table of REAL data. This date represents difference in DNA. It is obtained by ...
... As promised, you are going to get your chance to create a phylogenetic tree from some molecular clock data. We are going to give you some mutation differences in DNA. This is just like the bird phylogeny we did. Below is a table of REAL data. This date represents difference in DNA. It is obtained by ...
KOX1, KAP1
... modification and remodeling activities (Fig. 1). Presumably, gene activation requires at least one such factor that can bind its recognition sequence within 'inactive' chromatin and recruit other factors that collaborate in altering local chromatin structure. These altered regions of chromatin would ...
... modification and remodeling activities (Fig. 1). Presumably, gene activation requires at least one such factor that can bind its recognition sequence within 'inactive' chromatin and recruit other factors that collaborate in altering local chromatin structure. These altered regions of chromatin would ...
DNA fingerprint - cloudfront.net
... the DNA. Since you can’t see DNA in gel electrophoresis, this helps show how far it has run. We loaded the DNA into gel wells and ran through the chamber for 30-50 minutes ...
... the DNA. Since you can’t see DNA in gel electrophoresis, this helps show how far it has run. We loaded the DNA into gel wells and ran through the chamber for 30-50 minutes ...
Lecture 1 - Graham Ellis
... Why is DNA important? 1. DNA contains the instructions needed to construct other components of cells such as protein and RNA. 2. There are 20 different kinds of amino acid that combine to make proteins. There are many possible combinations, resulting in many different types of protein. 3. The cell ...
... Why is DNA important? 1. DNA contains the instructions needed to construct other components of cells such as protein and RNA. 2. There are 20 different kinds of amino acid that combine to make proteins. There are many possible combinations, resulting in many different types of protein. 3. The cell ...
Answer Key DNA Review - John Bowne High School
... D) evolution, reproduction, and digestion 24. Researchers have found that formaldehyde and asbestos can alter DNA base sequences. Based on this research, the use of these chemicals has been greatly reduced because they A) may act as fertilizers, increasing the growth of algae in ponds B) have been r ...
... D) evolution, reproduction, and digestion 24. Researchers have found that formaldehyde and asbestos can alter DNA base sequences. Based on this research, the use of these chemicals has been greatly reduced because they A) may act as fertilizers, increasing the growth of algae in ponds B) have been r ...
Many practical applications of recombinant DNA are
... Recombinant DNA technology engineers microbial cells for producing foreign proteins, and its success solely depends on the precise reading of equivalent genes made with the help of bacterial cell machinery. This process has been responsible for fueling many advances related to modern molecular biolo ...
... Recombinant DNA technology engineers microbial cells for producing foreign proteins, and its success solely depends on the precise reading of equivalent genes made with the help of bacterial cell machinery. This process has been responsible for fueling many advances related to modern molecular biolo ...
Lecture 3
... isolated from langsdorfii. The DNA treated pollen were used to pollinate emasculated glauca plants. One group claimed that the sexual progeny thus obtained formed tumors on the stem. However, these experiments were not reproduced in other labs. ...
... isolated from langsdorfii. The DNA treated pollen were used to pollinate emasculated glauca plants. One group claimed that the sexual progeny thus obtained formed tumors on the stem. However, these experiments were not reproduced in other labs. ...
STUDY GUIDE SEMESTER 2 EXAM 4 Dr. Marks Name: Class
... The enzymes responsible for adding nucleotides to the exposed DNA bases during replication are ...
... The enzymes responsible for adding nucleotides to the exposed DNA bases during replication are ...
Genetics, Exam 2, Sample A Name ___________________________
... Left-handed double helix Right-handed double helix Right-handed beta sheet Counter clockwise single helix ...
... Left-handed double helix Right-handed double helix Right-handed beta sheet Counter clockwise single helix ...
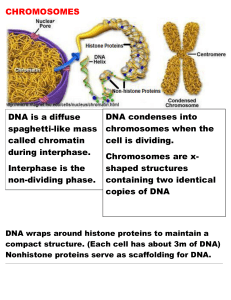
Chromosomes Notes
... DNA wraps around histone proteins to maintain a compact structure. (Each cell has about 3m of DNA) Nonhistone proteins serve as scaffolding for DNA. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... DNA wraps around histone proteins to maintain a compact structure. (Each cell has about 3m of DNA) Nonhistone proteins serve as scaffolding for DNA. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Name Class Date Skills Worksheet Look
... In the spaces provided, write the letters of the two terms or phrases that are linked together by the term or phrase in the middle. The choices can be placed in any order. 15. ______ transformation ______ 16. ______ transformation not stopped by proteindestroying enzymes _______ 17. ______ five-carb ...
... In the spaces provided, write the letters of the two terms or phrases that are linked together by the term or phrase in the middle. The choices can be placed in any order. 15. ______ transformation ______ 16. ______ transformation not stopped by proteindestroying enzymes _______ 17. ______ five-carb ...
DNA Similarities
... Suppose you could compare the total DNA sequences of various organisms (some billions of base pairs). How much similarity would you expect between a whale and a fish? A whale and a dog? A dog and a shrimp? A shrimp and a bacterium? As always, there are two types of similarity to be considered: analo ...
... Suppose you could compare the total DNA sequences of various organisms (some billions of base pairs). How much similarity would you expect between a whale and a fish? A whale and a dog? A dog and a shrimp? A shrimp and a bacterium? As always, there are two types of similarity to be considered: analo ...
DNA STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... the DNases and will quickly be degraded. However, these enzymes are temperature sensitive and cooling the solution slows down .the process of degradation. What does the cold ethanol do? Everything except the DNA will dissolve in ethanol. The ethanol pulls water from the DNA molecule so that it then ...
... the DNases and will quickly be degraded. However, these enzymes are temperature sensitive and cooling the solution slows down .the process of degradation. What does the cold ethanol do? Everything except the DNA will dissolve in ethanol. The ethanol pulls water from the DNA molecule so that it then ...
Neuroepigenetica
... provide finally the biological basis for the integration of nature and nurture, and reveal the degree to which the study of one enriches our understanding of the other. I. D Sweatt. Epigenetic Regulation in the Nervous System. Elsevier. 2013 ...
... provide finally the biological basis for the integration of nature and nurture, and reveal the degree to which the study of one enriches our understanding of the other. I. D Sweatt. Epigenetic Regulation in the Nervous System. Elsevier. 2013 ...
Biology DNA Extraction
... First, you need to find something that contains DNA. Since DNA is the blueprint for life, everything living contains DNA. For this experiment, we like to use Strawberries. Ripe strawberries are an excellent source for extracting DNA because they are easy to pulverize and contain enzymes called pecti ...
... First, you need to find something that contains DNA. Since DNA is the blueprint for life, everything living contains DNA. For this experiment, we like to use Strawberries. Ripe strawberries are an excellent source for extracting DNA because they are easy to pulverize and contain enzymes called pecti ...
SBI4U: DNA Replication - SBI4U with Ms. Taman!
... ◦ DNA strands are ____________________ ◦ A small portion of RNA is __________ to the exposed strands to “prime” them for replication Stage 2: Elongation ◦ DNA polymerase III builds a __________ of DNA by incorporating _________________ Stage 3: Termination ...
... ◦ DNA strands are ____________________ ◦ A small portion of RNA is __________ to the exposed strands to “prime” them for replication Stage 2: Elongation ◦ DNA polymerase III builds a __________ of DNA by incorporating _________________ Stage 3: Termination ...
Lab/Activity: Prot
... is modified in several ways. Introns (intervening non-coding units) are edited out and exons (expressed coding sequences) are spliced together. In addition, a 5ʹ′ GTP cap and a 3ʹ′ poly-A tail are added to the mRNA to protect it from RNase enzymes in the cytoplasm. This mature mRNA transcript then l ...
... is modified in several ways. Introns (intervening non-coding units) are edited out and exons (expressed coding sequences) are spliced together. In addition, a 5ʹ′ GTP cap and a 3ʹ′ poly-A tail are added to the mRNA to protect it from RNase enzymes in the cytoplasm. This mature mRNA transcript then l ...
word - marric.us
... strand transcribed from the DNA template: 3'GCGA5'. What is the next nucleotide that RNA polymerase will attach? 3 pts Remember to base pair with orientation and polymerase directionality ...
... strand transcribed from the DNA template: 3'GCGA5'. What is the next nucleotide that RNA polymerase will attach? 3 pts Remember to base pair with orientation and polymerase directionality ...
Chapter 13 Notes
... Offspring are homozygous for most traits Pure breeds-is a selected group of organisms within a species that has been bred because of a specific characteristic they portrait Hybrids plants can increase productivity of food for humans because it is usually bigger in size and has more nutrients Gen ...
... Offspring are homozygous for most traits Pure breeds-is a selected group of organisms within a species that has been bred because of a specific characteristic they portrait Hybrids plants can increase productivity of food for humans because it is usually bigger in size and has more nutrients Gen ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.