Chromosomes in prokaryotes
... These DNA sequences do not code for proteins and include: 1) promoters (sites that bind RNA polymerases), 2) regulatory elements (enhancers, silencers, and locus control regions LCRs) that bind regulatory proteins, 3) the origin of replication (sites that bind the DNA replication complex), 4) the ce ...
... These DNA sequences do not code for proteins and include: 1) promoters (sites that bind RNA polymerases), 2) regulatory elements (enhancers, silencers, and locus control regions LCRs) that bind regulatory proteins, 3) the origin of replication (sites that bind the DNA replication complex), 4) the ce ...
Biotechnology Cloning of a Gene Cloning a human gene
... • Gene therapy is the insertion of genetic material into human cells for the treatment of a disorder. • A patient would be given healthy genes to make up for any faulty genes. • Many researchers are trying to cure cancer by inserting genes to make healthy cells tolerant of chemotherapy or use a gene ...
... • Gene therapy is the insertion of genetic material into human cells for the treatment of a disorder. • A patient would be given healthy genes to make up for any faulty genes. • Many researchers are trying to cure cancer by inserting genes to make healthy cells tolerant of chemotherapy or use a gene ...
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
... • The next level of packing forms the 30-nm chromatin fiber • Interactions between histone tails, linker DNA, and other nucleosomes cause the 10-nm fiber to coil and fold, forming a chromatin fiber approximately 30 nm in diameter ...
... • The next level of packing forms the 30-nm chromatin fiber • Interactions between histone tails, linker DNA, and other nucleosomes cause the 10-nm fiber to coil and fold, forming a chromatin fiber approximately 30 nm in diameter ...
Topic 1: Cell biology (15 hours)
... 10. Application: Use of Taq DNA polymerase to produce depends on complementary base pairing. multiple copies of DNA rapidly by the polymerase 3. Helicase unwinds the double helix and separates the chain reaction (PCR). two strands by breaking hydrogen bonds. 11. Application: Production of human insu ...
... 10. Application: Use of Taq DNA polymerase to produce depends on complementary base pairing. multiple copies of DNA rapidly by the polymerase 3. Helicase unwinds the double helix and separates the chain reaction (PCR). two strands by breaking hydrogen bonds. 11. Application: Production of human insu ...
國立嘉義大學九十二學年度
... 23. Single strand binding proteins are important for this activity: (1) Prevent single-stranded DNA from rewinding. (2) Protect single-stranded DNA from enzymatic degradation. (3) Prevent double helical DNA from unwinding. (4) Prevent double helical DNA from becoming a triple helix. (5) Prevent sing ...
... 23. Single strand binding proteins are important for this activity: (1) Prevent single-stranded DNA from rewinding. (2) Protect single-stranded DNA from enzymatic degradation. (3) Prevent double helical DNA from unwinding. (4) Prevent double helical DNA from becoming a triple helix. (5) Prevent sing ...
BERRY FULL OF DNA
... therefore not visible. When molecules are insoluble, they clump together and become visible. The colder the ethanol, the less soluble the DNA will be in it. This is why it is important for the ethanol to be kept in the freezer or in an ice bath. ...
... therefore not visible. When molecules are insoluble, they clump together and become visible. The colder the ethanol, the less soluble the DNA will be in it. This is why it is important for the ethanol to be kept in the freezer or in an ice bath. ...
Analytical and Chromatography - Sigma
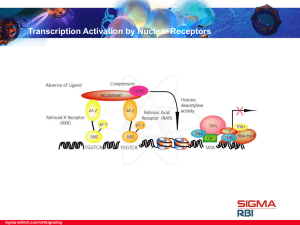
... • Retinoid X receptor (RXR) and Retinoic Acid receptor (RAR) are nuclear receptors that bind either all trans-retinoic (tRA) or 9-cis-retinoic acid (9cis-RA). In the absence of ligand, corepressors, such as Nuclear Receptor Corepressor (NCoR), Silencing Mediator of Retinoid and Thyroid Hormone Recep ...
... • Retinoid X receptor (RXR) and Retinoic Acid receptor (RAR) are nuclear receptors that bind either all trans-retinoic (tRA) or 9-cis-retinoic acid (9cis-RA). In the absence of ligand, corepressors, such as Nuclear Receptor Corepressor (NCoR), Silencing Mediator of Retinoid and Thyroid Hormone Recep ...
Chapter 12 Powerpoint
... The 3 billion base pairs in each human cell provide the blueprint for producing a human being. The specific sequence of base pairing is important in conveying the mechanism of how genetic information is expressed. The expression is seen through proteins. Through directing the synthesis of proteins, ...
... The 3 billion base pairs in each human cell provide the blueprint for producing a human being. The specific sequence of base pairing is important in conveying the mechanism of how genetic information is expressed. The expression is seen through proteins. Through directing the synthesis of proteins, ...
Name: Period: ______
... So far, we’ve learned that DNA is the genetic material that organisms inherit from their parents, but have you thought about what exactly is encoded for by this DNA? How do our cells use DNA as a set of instructions for life? How is the information in our DNA and genes used by our bodies? And what h ...
... So far, we’ve learned that DNA is the genetic material that organisms inherit from their parents, but have you thought about what exactly is encoded for by this DNA? How do our cells use DNA as a set of instructions for life? How is the information in our DNA and genes used by our bodies? And what h ...
12th International Workshop on Radiation Damage to DNA
... two years physicists, chemists and biologists with common interest in radiation damage to DNA. The meeting will explore recent advances in our understanding of complex and interdependent events associated with DNA macromolecules exposed to various types of radiation and radiomimetic agents. The prog ...
... two years physicists, chemists and biologists with common interest in radiation damage to DNA. The meeting will explore recent advances in our understanding of complex and interdependent events associated with DNA macromolecules exposed to various types of radiation and radiomimetic agents. The prog ...
Bio Ch. 12-1 DNA and RNA notes
... The Hershey-Chase experiment was based on the fact that a) DNA has both sulfur and phosphorus in its ...
... The Hershey-Chase experiment was based on the fact that a) DNA has both sulfur and phosphorus in its ...
TAKS Review - SchoolNotes
... • As an organism grows their cells do not get bigger, they increase in number. • Mitosis is the formation of two new daughter cells that are identical to each other and the original parent cell • If mitosis is not controlled, cells multiply too quickly---this forms a tumor. • Cancer is uncontrolled ...
... • As an organism grows their cells do not get bigger, they increase in number. • Mitosis is the formation of two new daughter cells that are identical to each other and the original parent cell • If mitosis is not controlled, cells multiply too quickly---this forms a tumor. • Cancer is uncontrolled ...
File - Siegel Science
... • One or more genes are artificially inserted into the DNA of the plant’s chromosomes. • The gene can come from the same type of plant or even another type of organism ...
... • One or more genes are artificially inserted into the DNA of the plant’s chromosomes. • The gene can come from the same type of plant or even another type of organism ...
DNA, RNA, & Protein Synthesis
... amino acids in the correct order according to the codon – Every 3 bases codes for a particular amino acid – Look up the codon on page 303 of textbook to find amino acid • Amino acid sequence determines the type of protein ...
... amino acids in the correct order according to the codon – Every 3 bases codes for a particular amino acid – Look up the codon on page 303 of textbook to find amino acid • Amino acid sequence determines the type of protein ...
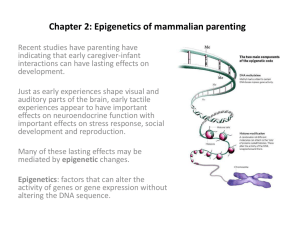
Chapter 2: Epigenetics of mammalian parenting
... • Decrease hippocampal plasticity – reduced learning and memory capacity • All these effects are traceable to changes in neurotransmitter receptor and activity levels in the brain. ...
... • Decrease hippocampal plasticity – reduced learning and memory capacity • All these effects are traceable to changes in neurotransmitter receptor and activity levels in the brain. ...
lesson viii - MisterSyracuse.com
... 14. This signals RNA Polymerase to fall off of the DNA, and release the new mRNA. 15. In bacteria, this is it. It’s done. Let’s take a look at eukaryotes, though. 16. The promoter usually contains the sequence TATAAA, so is called the Tata box. This is where RNA polymerase attaches. 17. Eukaryotes a ...
... 14. This signals RNA Polymerase to fall off of the DNA, and release the new mRNA. 15. In bacteria, this is it. It’s done. Let’s take a look at eukaryotes, though. 16. The promoter usually contains the sequence TATAAA, so is called the Tata box. This is where RNA polymerase attaches. 17. Eukaryotes a ...
Chapter 12
... Approximately 145 bp are in contact with the histone octamer Connection between nucleosomes requires approximately 60 bp of linker DNA ...
... Approximately 145 bp are in contact with the histone octamer Connection between nucleosomes requires approximately 60 bp of linker DNA ...
Beginning to crack the code of `junk DNA`
... Kazazian, 71, has no plans to slow down. He is investigating whether this type of self-replicating junk DNA holds more power over human illness than has previously been imagined. It might influence our risk for cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and other common conditions. "The one thing that drew ...
... Kazazian, 71, has no plans to slow down. He is investigating whether this type of self-replicating junk DNA holds more power over human illness than has previously been imagined. It might influence our risk for cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and other common conditions. "The one thing that drew ...
Two Epigenetic Mechanisms
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
MITOCHONDRIA BIOLOGY - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... CRTA sequence (R = purine) within 20 bp of transcription start site. 2. Phage-like RNA polymerase – Single, large catalytic subunit – Small specificity factor protein ...
... CRTA sequence (R = purine) within 20 bp of transcription start site. 2. Phage-like RNA polymerase – Single, large catalytic subunit – Small specificity factor protein ...
Chapter 12 Assessment
... Cold-resistant tomatoes, supersweet corn, and maize are all the results of _____. ...
... Cold-resistant tomatoes, supersweet corn, and maize are all the results of _____. ...
DNA Extraction from Strawberries
... alcohol. What does this fact have to do with our method of extraction? Explain what happened when the isopropyl alcohol came in contact with the strawberry extract. – Answer: The DNA was soluble in the DNA extraction buffer so we could not see it. When it got stirred into the alcohol, it clumped tog ...
... alcohol. What does this fact have to do with our method of extraction? Explain what happened when the isopropyl alcohol came in contact with the strawberry extract. – Answer: The DNA was soluble in the DNA extraction buffer so we could not see it. When it got stirred into the alcohol, it clumped tog ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.