DNA, Genes, and Chromosomes
... chromosome)? Stress that when DNA is being transferred (like during mitosis and DNA replication) it must be “wound up,” but when it is being used (during interphase) it is no longer wound up. 3. Uncoil about 2 feet of thread and color it red. What do students think this represents (a nucleotide sequ ...
... chromosome)? Stress that when DNA is being transferred (like during mitosis and DNA replication) it must be “wound up,” but when it is being used (during interphase) it is no longer wound up. 3. Uncoil about 2 feet of thread and color it red. What do students think this represents (a nucleotide sequ ...
DNA Powerpoint Notes
... Cells can contain ________ feet of DNA. If all the DNA in your body was put end to end, it would reach to the sun and back over ________ times. DNA in all humans is ________ % identical. It is about one tenth of one percent that makes us all unique, or about 3 million nucleotides difference. DNA can ...
... Cells can contain ________ feet of DNA. If all the DNA in your body was put end to end, it would reach to the sun and back over ________ times. DNA in all humans is ________ % identical. It is about one tenth of one percent that makes us all unique, or about 3 million nucleotides difference. DNA can ...
doc Practice Midterm 2006
... 1. Identify three types of post-transcriptional regulation of protein-coding genes. 2. Describe three features of eukaryotic mRNAs that generally are not shared with prokaryotic mRNAs. 3. Which of the common Watson-Crick base pair in DNA is the most stable? Why? How does this property affect the mel ...
... 1. Identify three types of post-transcriptional regulation of protein-coding genes. 2. Describe three features of eukaryotic mRNAs that generally are not shared with prokaryotic mRNAs. 3. Which of the common Watson-Crick base pair in DNA is the most stable? Why? How does this property affect the mel ...
GeneticEnginStudentNotes
... The DNA ______________________ are poured into wells on a gel. An _____________________ is applied to the gel. This moves the DNA fragments across the gel. The _______________ the DNA fragment, the _____________ and ______________ it will move across the gel. Based on _________, the DNA fragments ma ...
... The DNA ______________________ are poured into wells on a gel. An _____________________ is applied to the gel. This moves the DNA fragments across the gel. The _______________ the DNA fragment, the _____________ and ______________ it will move across the gel. Based on _________, the DNA fragments ma ...
E1. A trait of pneumococci is the ability to synthesize a capsule
... D. There are multiple reasons why less than 100% of the phage protein is removed from the bacterial cells during the shearing process. Perhaps the shearing just is not strong enough to remove all of the phages. Perhaps the tail fibers remain embedded in the bacterium and only the head region is shea ...
... D. There are multiple reasons why less than 100% of the phage protein is removed from the bacterial cells during the shearing process. Perhaps the shearing just is not strong enough to remove all of the phages. Perhaps the tail fibers remain embedded in the bacterium and only the head region is shea ...
Pharmacogenetics Glossary
... guanine (G), thymine (T), and in RNA only, uracil (U). In DNA, A attaches only to T, and C attaches only to G. In RNA, A attaches only to U, and C attaches only to G. base pairs - the pairs of complementary bases that form the rungs of DNA: adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T), cytosine (C) pairs with ...
... guanine (G), thymine (T), and in RNA only, uracil (U). In DNA, A attaches only to T, and C attaches only to G. In RNA, A attaches only to U, and C attaches only to G. base pairs - the pairs of complementary bases that form the rungs of DNA: adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T), cytosine (C) pairs with ...
Determining the Structure of DNA
... http://gslc.genetics.utah.edu 12. Why do scientists use computer programs to model protein structure and function? Proteins are very small and hard to see. 13. What provides the “blueprint” for making a protein? Genes provide the blueprint for making a protein. 14. What is heredity? The passing of ...
... http://gslc.genetics.utah.edu 12. Why do scientists use computer programs to model protein structure and function? Proteins are very small and hard to see. 13. What provides the “blueprint” for making a protein? Genes provide the blueprint for making a protein. 14. What is heredity? The passing of ...
Chemical basis of Inheritance Review KEY - Pelletier Pages
... molecule. DNA ligase forms the phosphodiester bonds between the okazaki fragments on the lagging strand. 14. What two bases can pair with adenine? T and U 15. How many strands of DNA serve as a template in transcription? One 16. What is the function of a ribosome? To act as the site of protein synth ...
... molecule. DNA ligase forms the phosphodiester bonds between the okazaki fragments on the lagging strand. 14. What two bases can pair with adenine? T and U 15. How many strands of DNA serve as a template in transcription? One 16. What is the function of a ribosome? To act as the site of protein synth ...
Microsoft Word
... (ii)To examine whether the millets differ from the other grasses at the molecular level and if so, did the differences in the molecular properties of millets offer a selective advantage to them. (iii)To know the molecular basis for species isolation in family Cucurbitaceae. (iv)To determine the exte ...
... (ii)To examine whether the millets differ from the other grasses at the molecular level and if so, did the differences in the molecular properties of millets offer a selective advantage to them. (iii)To know the molecular basis for species isolation in family Cucurbitaceae. (iv)To determine the exte ...
DNA Ligase Joke (insert laughter here)
... The Newfoundland population is an excellent example of this phenomenon, as researchers estimate 90% are descendants from just 20,000 - 30,000 people who migrated from south west England and Southern Ireland and settled in isolated communities along the coast. These descendants settled in distinct se ...
... The Newfoundland population is an excellent example of this phenomenon, as researchers estimate 90% are descendants from just 20,000 - 30,000 people who migrated from south west England and Southern Ireland and settled in isolated communities along the coast. These descendants settled in distinct se ...
ppt - Department of Computer Science
... RNA and DNA are similar, except that RNA is single stranded and thus less stable than DNA – Also, in RNA, the base uracil (U) is used instead of thymine (T), the DNA counterpart ...
... RNA and DNA are similar, except that RNA is single stranded and thus less stable than DNA – Also, in RNA, the base uracil (U) is used instead of thymine (T), the DNA counterpart ...
regulatory transcription factors
... CpG islands near their promoters (not common in yeast and Drosophila) – These CpG islands are 1,000 to 2,000 nucleotides long – In housekeeping genes • The CpG islands are unmethylated • Genes tend to be expressed in most cell types ...
... CpG islands near their promoters (not common in yeast and Drosophila) – These CpG islands are 1,000 to 2,000 nucleotides long – In housekeeping genes • The CpG islands are unmethylated • Genes tend to be expressed in most cell types ...
BINF 730 Biological Sequence Analysis Lecture 1 Biological
... circular DNA molecule • Eukaryotic chromosomes appear in pairs (diploid), each inherited from one parent – Homologous chromosomes carry the same genes – Some genes are same in both parents – Some genes appear in different forms called alleles • E.g. human blood has three alleles: A, B, and O ...
... circular DNA molecule • Eukaryotic chromosomes appear in pairs (diploid), each inherited from one parent – Homologous chromosomes carry the same genes – Some genes are same in both parents – Some genes appear in different forms called alleles • E.g. human blood has three alleles: A, B, and O ...
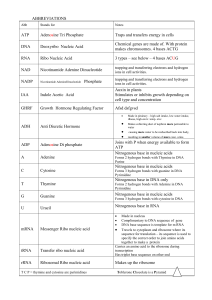
abbreviations - Spanish Point Biology
... Complimentary to DNA sequence of gene DNA base sequence is template for m RNA Travels to cytoplasm and ribosome where its sequence for translation – its sequence is used to specify the correct order to join amino acids together to make a protein Carries an amino acid to the ribosome during transcr ...
... Complimentary to DNA sequence of gene DNA base sequence is template for m RNA Travels to cytoplasm and ribosome where its sequence for translation – its sequence is used to specify the correct order to join amino acids together to make a protein Carries an amino acid to the ribosome during transcr ...
DNA Extraction from Bacteria
... Step 3. Remove the tube from the hot water bath. Add cold alcohol to the test tube (about 2/3 full) to create an alcohol layer on top of the bacterial solution. Do this by slowly pouring the alcohol down the inside of the test tube with a Pasteur pipette or medicine dropper. DO NOT MIX! DNA is solu ...
... Step 3. Remove the tube from the hot water bath. Add cold alcohol to the test tube (about 2/3 full) to create an alcohol layer on top of the bacterial solution. Do this by slowly pouring the alcohol down the inside of the test tube with a Pasteur pipette or medicine dropper. DO NOT MIX! DNA is solu ...
DNA polymerase
... to different locations in the cell where proteins are made, based on the information provided by the DNA. These proteins are then used by the cells to accomplish various tasks. ...
... to different locations in the cell where proteins are made, based on the information provided by the DNA. These proteins are then used by the cells to accomplish various tasks. ...
Genetics Study Guide
... Gregor Mendel found through his experiments that alleles can be _____________ or _______________ . DNA is condensed into structures called ____________________________ . Which nitrogen base is in RNA but not in DNA? _______________________ Deoxyribose in DNA is a _________________ . DNA can be desc ...
... Gregor Mendel found through his experiments that alleles can be _____________ or _______________ . DNA is condensed into structures called ____________________________ . Which nitrogen base is in RNA but not in DNA? _______________________ Deoxyribose in DNA is a _________________ . DNA can be desc ...
Unit 1 - Moodle
... Identify how complimentary base pairing and the hydrogen bonding between two complimentary strands are involved in the formation of the DNA double helix. Identify how Meselson and Stahl’s classic experiment provided new data that supported the accepted theory of replication of DNA and refuted compet ...
... Identify how complimentary base pairing and the hydrogen bonding between two complimentary strands are involved in the formation of the DNA double helix. Identify how Meselson and Stahl’s classic experiment provided new data that supported the accepted theory of replication of DNA and refuted compet ...
Protein Synthesis (Transcription and Translation) Really Think about
... 16. How many codons would you need to code for a protein with 12 amino acids? 17. Using the 20 different amino acids how can you create proteins that are different from each other? ...
... 16. How many codons would you need to code for a protein with 12 amino acids? 17. Using the 20 different amino acids how can you create proteins that are different from each other? ...
DNA, RNA, and Protein
... living things. Some have modifications. o o o • Amino acids form 1 , 2 & 3 protein structures – Structures are essential to protein function ...
... living things. Some have modifications. o o o • Amino acids form 1 , 2 & 3 protein structures – Structures are essential to protein function ...
The Universal Genetic Code - Willimon-PHS
... phosphate group and the deoxyribose sugar • The two DNA strands connect by bonds between nitrogenous bases o A always bonds with T o G always bonds with C Role of DNA DNA is the genetic material of organisms. • Information coded in the order of the bases used to create proteins • Proteins act as enz ...
... phosphate group and the deoxyribose sugar • The two DNA strands connect by bonds between nitrogenous bases o A always bonds with T o G always bonds with C Role of DNA DNA is the genetic material of organisms. • Information coded in the order of the bases used to create proteins • Proteins act as enz ...
Heredity
... dominant or recessive in your family? – What would you have done differently to figure out if a trait is dominant or recessive? ...
... dominant or recessive in your family? – What would you have done differently to figure out if a trait is dominant or recessive? ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.