Genetics 3500 winter Test ii_ansers
... See table in paper by Gerstein Expectation is that you enumeration several examples and include a few words of explanation. Should include: Much of the genome is transcribed as NcRNA some of which overlap protein sequences Exons can be shared by unrelated proteins. Introns can contain open reading f ...
... See table in paper by Gerstein Expectation is that you enumeration several examples and include a few words of explanation. Should include: Much of the genome is transcribed as NcRNA some of which overlap protein sequences Exons can be shared by unrelated proteins. Introns can contain open reading f ...
1 Genetics (BIL-250) Review Questions #1 (2
... (4-2) Discuss problems and limitations of the “One gene – one enzyme hypothesis” and how it can be better formulated. (4-3) Explain one example of how mutations in either the α- or β-hemoglobins can produce an altered phenotype that may be adaptive to a particular geographic region. (5-1) Distingui ...
... (4-2) Discuss problems and limitations of the “One gene – one enzyme hypothesis” and how it can be better formulated. (4-3) Explain one example of how mutations in either the α- or β-hemoglobins can produce an altered phenotype that may be adaptive to a particular geographic region. (5-1) Distingui ...
Biotechnology: Tools and Techniques of the Trade
... Explain what a restriction enzyme is and what role they play in the cell Explain how restriction enzymes have been used by biologists as a tool in the manipulation of DNA ...
... Explain what a restriction enzyme is and what role they play in the cell Explain how restriction enzymes have been used by biologists as a tool in the manipulation of DNA ...
Chapter 19 - Biology Junction
... 6. In the diagram below – highlight all of the potential locations for gene expression regulation in eukaryotic cells. How does this compare with prokaryotic cells? ...
... 6. In the diagram below – highlight all of the potential locations for gene expression regulation in eukaryotic cells. How does this compare with prokaryotic cells? ...
Our new understanding of genetic mechanisms is leading to
... The viral DNA enters healthy DNA and make more viral DNA that assembles into new viruses. We now understand a huge amount about how the HIV virus works. ...
... The viral DNA enters healthy DNA and make more viral DNA that assembles into new viruses. We now understand a huge amount about how the HIV virus works. ...
Laboratory #1 Lecture Guide: Forensic DNA Fingerprinting
... 2. Why must we always load the DNA on the negative end of the chamber? 3. What is the relationship between the gel’s density and the movement of the DNA ...
... 2. Why must we always load the DNA on the negative end of the chamber? 3. What is the relationship between the gel’s density and the movement of the DNA ...
DNA intro review - Ms Kim`s Biology Class
... 1. A nucleotide is made of three parts: a ___________________ group, a five carbon __________________, and a ...
... 1. A nucleotide is made of three parts: a ___________________ group, a five carbon __________________, and a ...
Practice Multiple Choice- Set 1 - mvhs
... 13. Translation is the second step of protein synthesis. How does the translation of RNA into protein begin? a) A G cap is added to the RNA b) The promoter sequence is recognized c) A release factor binds to the RNA d) Transcription Factors bind to the RNA e) The start codon is recognized by the rib ...
... 13. Translation is the second step of protein synthesis. How does the translation of RNA into protein begin? a) A G cap is added to the RNA b) The promoter sequence is recognized c) A release factor binds to the RNA d) Transcription Factors bind to the RNA e) The start codon is recognized by the rib ...
Multiple choice questions
... is used in analyzing transcriptomes requires computers is more accurate than the clone contig method is normally used with large genomes takes more time than other genome sequencing approaches Restriction endonucleases are located in the nucleus of cells degrade DNA completely bind to DNA are enzyme ...
... is used in analyzing transcriptomes requires computers is more accurate than the clone contig method is normally used with large genomes takes more time than other genome sequencing approaches Restriction endonucleases are located in the nucleus of cells degrade DNA completely bind to DNA are enzyme ...
14-3 Human Molecular Genetics
... is replaced by a normal, working gene. - This way the body can make the correct protein or enzyme it needs, which eliminates the cause of the disorder. ...
... is replaced by a normal, working gene. - This way the body can make the correct protein or enzyme it needs, which eliminates the cause of the disorder. ...
SBI4U: Molecular Genetics Unit Review
... 12. What are Okazaki fragments? 13. Describe the roles of the following enzymes/proteins in DNA replication: a. DNA helicase b. DNA gyrase c. DNA polymerase d. Single-stranded binding proteins e. DNA ligase f. RNA primase 14. Why is it beneficial to have multiple replication bubbles at the same time ...
... 12. What are Okazaki fragments? 13. Describe the roles of the following enzymes/proteins in DNA replication: a. DNA helicase b. DNA gyrase c. DNA polymerase d. Single-stranded binding proteins e. DNA ligase f. RNA primase 14. Why is it beneficial to have multiple replication bubbles at the same time ...
Chapter 10 Study Guide Know the definitions for: Cross
... mRNA – transcription of DNA sequence that can move from the nucleus to cytoplasm to site of ribosomes. tRNA – translation of mRNA sequence carried from the nucleus by carrying appropriate amino acids to construct polypeptide sequence (protein). rRNA – ribosomes are composed of rRNA and protein that ...
... mRNA – transcription of DNA sequence that can move from the nucleus to cytoplasm to site of ribosomes. tRNA – translation of mRNA sequence carried from the nucleus by carrying appropriate amino acids to construct polypeptide sequence (protein). rRNA – ribosomes are composed of rRNA and protein that ...
molecular scissors to study gene function Marta Oliveira
... it, and by doing so, they unpredictably add or remove pieces of that gene, mutating it. Therefore, this new tool can be used to disturb and silence any gene of interest, allowing researchers to know more about the function of the proteins they code for by studying what happens to an organism when ce ...
... it, and by doing so, they unpredictably add or remove pieces of that gene, mutating it. Therefore, this new tool can be used to disturb and silence any gene of interest, allowing researchers to know more about the function of the proteins they code for by studying what happens to an organism when ce ...
Principles of Biology Lake Tahoe Community College
... 6. DNA packing tends to prevent transcription and translation B. In female mammals, one x chromosome is inactivated in each cell 1. early in embryonic development. C. control of eukaryotic transcription 1. eukaryotes have transcription factors D. Eukaryotic RNA may be spliced in more than one way E. ...
... 6. DNA packing tends to prevent transcription and translation B. In female mammals, one x chromosome is inactivated in each cell 1. early in embryonic development. C. control of eukaryotic transcription 1. eukaryotes have transcription factors D. Eukaryotic RNA may be spliced in more than one way E. ...
Lecture 10
... The DNA contents does not reflect the complexity of the organism! Related and structurally similar species may have variation in the amount of their total DNA by a factor of 100 In humans: ~5% of DNA is transcribed and 1.5% represents coding regions (exons). The rest is made of repeats with no obvio ...
... The DNA contents does not reflect the complexity of the organism! Related and structurally similar species may have variation in the amount of their total DNA by a factor of 100 In humans: ~5% of DNA is transcribed and 1.5% represents coding regions (exons). The rest is made of repeats with no obvio ...
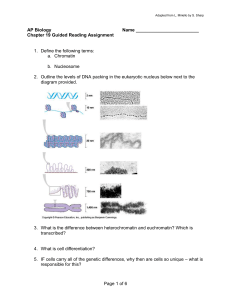
DNA Control Mechanisms
... D. Heterochromatin - This refers to DNA that remains condensed even during interphase. – It is NOT active. 1. This CANNOT do transcription so it is inactivated. (“hetero” means “different”) E. Euchromatin - This refers to DNA that IS loose during interphase. – It IS active. 1. It CAN do transcriptio ...
... D. Heterochromatin - This refers to DNA that remains condensed even during interphase. – It is NOT active. 1. This CANNOT do transcription so it is inactivated. (“hetero” means “different”) E. Euchromatin - This refers to DNA that IS loose during interphase. – It IS active. 1. It CAN do transcriptio ...
The Major Transitions in Evolution
... associates with another form of the RNA polymerase IV complex, NRPD1B–NRPD2. AGO4 that is ‘programmed’ with siRNAs can then locate homologous genomic sequences and guide the protein DRM2, which has de novo cytosine methyltransferase activity. Targeting of DRM2 to DNA sequences also involves the SWI– ...
... associates with another form of the RNA polymerase IV complex, NRPD1B–NRPD2. AGO4 that is ‘programmed’ with siRNAs can then locate homologous genomic sequences and guide the protein DRM2, which has de novo cytosine methyltransferase activity. Targeting of DRM2 to DNA sequences also involves the SWI– ...
The Major Transitions in Evolution
... associates with another form of the RNA polymerase IV complex, NRPD1B–NRPD2. AGO4 that is ‘programmed’ with siRNAs can then locate homologous genomic sequences and guide the protein DRM2, which has de novo cytosine methyltransferase activity. Targeting of DRM2 to DNA sequences also involves the SWI– ...
... associates with another form of the RNA polymerase IV complex, NRPD1B–NRPD2. AGO4 that is ‘programmed’ with siRNAs can then locate homologous genomic sequences and guide the protein DRM2, which has de novo cytosine methyltransferase activity. Targeting of DRM2 to DNA sequences also involves the SWI– ...
Interspersed Repetitive Noncoding DNA
... – Submitting the work one has done for one class or project to a second class, or as a second project, without the prior informed consent of the relevant instructors; – Submitting work prepared in collaboration with another or other member(s) of a class, when collaborative work on a project has not ...
... – Submitting the work one has done for one class or project to a second class, or as a second project, without the prior informed consent of the relevant instructors; – Submitting work prepared in collaboration with another or other member(s) of a class, when collaborative work on a project has not ...
Cribado genético del cáncer colorrectal mediante el estudio del
... mainly by colonoscopy, is low, particularly if compared with those for breast and cervical cancer. This fact must be due, among other reasons, to the discomfort generated in the patients, the high cost, the lack of awareness and, in general, to the low acceptability of the screening methods. For the ...
... mainly by colonoscopy, is low, particularly if compared with those for breast and cervical cancer. This fact must be due, among other reasons, to the discomfort generated in the patients, the high cost, the lack of awareness and, in general, to the low acceptability of the screening methods. For the ...
26.1 and 26.2 Notes - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... a. May be whole-organism cloning i. Complete organism reproduction through asexual means ii. E.g. Identical twins, “Dolly” the sheep b. Gene Cloning i. Production of many identical copies of a single gene ii. Used to produce the gene’s protein product (e.g. insulin), or to alter the phenotype of an ...
... a. May be whole-organism cloning i. Complete organism reproduction through asexual means ii. E.g. Identical twins, “Dolly” the sheep b. Gene Cloning i. Production of many identical copies of a single gene ii. Used to produce the gene’s protein product (e.g. insulin), or to alter the phenotype of an ...
组蛋白甲基化
... of RNAPII, the initiating form of polymerase situated at the transcription start site (TSS). In contrast, the Set2 H3K36 methyltransferase binds to the serine 2 phosphorylated CTD of RNAPII, the transcriptional elongating form of polymerase. Thus, the two enzymes are recruited to genes via interacti ...
... of RNAPII, the initiating form of polymerase situated at the transcription start site (TSS). In contrast, the Set2 H3K36 methyltransferase binds to the serine 2 phosphorylated CTD of RNAPII, the transcriptional elongating form of polymerase. Thus, the two enzymes are recruited to genes via interacti ...
Slide 1
... a start and stop codon – Compare sequences found in one organism and look for similar sequence in other organsims • Microarray assay: microscope slide with known genes in wells – mRNA from a cell is obtained, reacted with cDNA, if bases match they will pair up and when hybrid DNA is placed on slide ...
... a start and stop codon – Compare sequences found in one organism and look for similar sequence in other organsims • Microarray assay: microscope slide with known genes in wells – mRNA from a cell is obtained, reacted with cDNA, if bases match they will pair up and when hybrid DNA is placed on slide ...
Human Genomic DNA Quality Controls for aCGH and Microarray
... ensure your assays are performing correctly. For external controls, you can rely on ParagonDx aCGH Human Genomic DNA Quality Controls. ...
... ensure your assays are performing correctly. For external controls, you can rely on ParagonDx aCGH Human Genomic DNA Quality Controls. ...