Pierce chapter 10
... nucleotides may be complementary and pair – forming doublestranded regions • Hairpin – Region of complementary bases form base; loop formed by unpaired bases in the middle ...
... nucleotides may be complementary and pair – forming doublestranded regions • Hairpin – Region of complementary bases form base; loop formed by unpaired bases in the middle ...
Last Name - JhaveriChemBioWiki
... Where is it found? Complimentary strand to DNA of GATTACTACGA? Complimentary strand to DNA of TTTAGGGCCCAT ...
... Where is it found? Complimentary strand to DNA of GATTACTACGA? Complimentary strand to DNA of TTTAGGGCCCAT ...
Biology Test Topics Chapters 11-12 Slideshows
... If the DNA of all organisms uses the same four bases (A, T, G, and C) then what accounts for the diversity of organisms? What is the process called by which DNA copies itself? What does it mean to say that DNA has “complimentary” strands? What does it mean to say that this process is “semi-conservat ...
... If the DNA of all organisms uses the same four bases (A, T, G, and C) then what accounts for the diversity of organisms? What is the process called by which DNA copies itself? What does it mean to say that DNA has “complimentary” strands? What does it mean to say that this process is “semi-conservat ...
DNA & Heredity
... different traits can segregate independently during gamete formation – This help to account for the many genetic variations observed in plants and animals ...
... different traits can segregate independently during gamete formation – This help to account for the many genetic variations observed in plants and animals ...
DNA, Chromosomes & Genes - Blountstown Middle School
... • A specific sequence of bases – Sequences carry the information needed for constructing proteins • Proteins provide the structural components of cells and tissues as well as enzymes for essential biochemical reactions. ...
... • A specific sequence of bases – Sequences carry the information needed for constructing proteins • Proteins provide the structural components of cells and tissues as well as enzymes for essential biochemical reactions. ...
microbio 40 [4-20
... usually by direct skin to skin contact, and even then it requires a skin break can also be spread by exfoliation onto inanimate objects 3. What is the result when HPV is transferred to a child during birth? What rare condition are the immunocompromised susceptible to? Respiratory papillomatosi ...
... usually by direct skin to skin contact, and even then it requires a skin break can also be spread by exfoliation onto inanimate objects 3. What is the result when HPV is transferred to a child during birth? What rare condition are the immunocompromised susceptible to? Respiratory papillomatosi ...
[Type the document title] Microbial Genetics Molecular biology is the
... - Vertical gene transfer Genetic information passed from an organism to its offspring. - Horizontal gene transfer Bacteria transfer genetic information form one organism to another in the same ...
... - Vertical gene transfer Genetic information passed from an organism to its offspring. - Horizontal gene transfer Bacteria transfer genetic information form one organism to another in the same ...
7echap20guidedreading
... 9. What is a complementary, short, single stranded nucleic acid that can be either DNA or RNA called? ...
... 9. What is a complementary, short, single stranded nucleic acid that can be either DNA or RNA called? ...
lecture2
... 3' CCGG 5' This type of palindrome serves as the target for most restriction enzymes. The graphic shows the palindromic sequences "seen" by five restriction enzymes (named in blue) commonly used in recombinant DNA work. 2. Inverted Repeats In these cases, two different segments of the double helix r ...
... 3' CCGG 5' This type of palindrome serves as the target for most restriction enzymes. The graphic shows the palindromic sequences "seen" by five restriction enzymes (named in blue) commonly used in recombinant DNA work. 2. Inverted Repeats In these cases, two different segments of the double helix r ...
Electrical induction hypothesis to explain enhancer-promoter
... focus on mechanistic aspects of enhancer action. Despite their analysis, the enhancer field remains driven by the concept of recruiting (Ptashne 1986). During recruiting, an activator protein increases local concentration of RNA polymerase, in the vicinity of its binding site. But, even if a protein ...
... focus on mechanistic aspects of enhancer action. Despite their analysis, the enhancer field remains driven by the concept of recruiting (Ptashne 1986). During recruiting, an activator protein increases local concentration of RNA polymerase, in the vicinity of its binding site. But, even if a protein ...
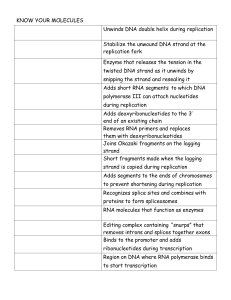
Know your molecules organizer
... Adds deoxyribonucleotides to the 3’ end of an existing chain Removes RNA primers and replaces them with deoxyribonucleotides Joins Okazaki fragments on the lagging ...
... Adds deoxyribonucleotides to the 3’ end of an existing chain Removes RNA primers and replaces them with deoxyribonucleotides Joins Okazaki fragments on the lagging ...
Name___________ Midterm Review 1. What is an organism? 2
... 11. What molecule contains the cells hereditary information? 12. What is a gene? 13. New cells or organisms from asexual reproduction have information. 14. Name a unicellular organism that reproduces by asexual reproduction. 15. Define autotroph. ...
... 11. What molecule contains the cells hereditary information? 12. What is a gene? 13. New cells or organisms from asexual reproduction have information. 14. Name a unicellular organism that reproduces by asexual reproduction. 15. Define autotroph. ...
Document
... 1. RNA-only genes produce functional RNA’s (tRNA, rRNA, miRNA, and more) 2. Protein-coding genes produce mRNA’s (17.3) 3. Transcription makes an RNA copy of a gene (17.4, 17.7) 4. Transcription begins when transcription factors bind to the promoter of a gene (17.8) G. Translation is the process of a ...
... 1. RNA-only genes produce functional RNA’s (tRNA, rRNA, miRNA, and more) 2. Protein-coding genes produce mRNA’s (17.3) 3. Transcription makes an RNA copy of a gene (17.4, 17.7) 4. Transcription begins when transcription factors bind to the promoter of a gene (17.8) G. Translation is the process of a ...
How to measure DNA methylation
... of the first exon, is much more tightly linked to transcriptional silencing than is methylation in the upstream promoter region ...
... of the first exon, is much more tightly linked to transcriptional silencing than is methylation in the upstream promoter region ...
Biotechnology and Gel Electrophoresis
... In DNA Fingerprinting, the DNA of an organism is cut up into fragments using restriction enzymes producing a large number of fragments of DNA Because no two individuals have identical DNA, no two individuals will have the same length fragments This technique allows us to identify families because th ...
... In DNA Fingerprinting, the DNA of an organism is cut up into fragments using restriction enzymes producing a large number of fragments of DNA Because no two individuals have identical DNA, no two individuals will have the same length fragments This technique allows us to identify families because th ...
Eucharyotic Chromatin Organization
... proteins to form chromatin fibers. - Histone proteins are small and contain a high proportion of positively charged ...
... proteins to form chromatin fibers. - Histone proteins are small and contain a high proportion of positively charged ...
Mutations are heritable alteration in DNA sequence Most common
... proteins) must discriminate between the correct strand and the strand with the mismatch. Discrimination is based on the degree of methylation. GATC sequences are methylated on the adenine residues. The newly synthesized DNA is not immediately methylated The methylated template strand is cons ...
... proteins) must discriminate between the correct strand and the strand with the mismatch. Discrimination is based on the degree of methylation. GATC sequences are methylated on the adenine residues. The newly synthesized DNA is not immediately methylated The methylated template strand is cons ...
File
... 1- It allows a large number of recombinant DNA molecules to be produced from a limited amount of starting material In this way cloning can supply the large amounts of DNA needed for molecular biological studies of gene structure and expression ...
... 1- It allows a large number of recombinant DNA molecules to be produced from a limited amount of starting material In this way cloning can supply the large amounts of DNA needed for molecular biological studies of gene structure and expression ...
Unit 5 Free Response
... b. Cells regulate both protein synthesis and protein activity. Discuss TWO specific mechanisms of protein regulation in eukaryotic cells. c. The central dogma does not apply to some viruses. Select a specific virus or type of virus and explain how it deviates from the central dogma. ...
... b. Cells regulate both protein synthesis and protein activity. Discuss TWO specific mechanisms of protein regulation in eukaryotic cells. c. The central dogma does not apply to some viruses. Select a specific virus or type of virus and explain how it deviates from the central dogma. ...
Study Guide 3 Bio 4 C
... Morgan and white eyed vs. wild type fruit flies, mutant phenotype, sex-linked genes, examples like hemophilia, sex-influenced trait, nondisjunction, aneuploidy, translocation, Down Syndrome, Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, metafemale, XYY syndrome Ch. 20 DNA Technology genetic engineering, re ...
... Morgan and white eyed vs. wild type fruit flies, mutant phenotype, sex-linked genes, examples like hemophilia, sex-influenced trait, nondisjunction, aneuploidy, translocation, Down Syndrome, Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, metafemale, XYY syndrome Ch. 20 DNA Technology genetic engineering, re ...








![[Type the document title] Microbial Genetics Molecular biology is the](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010247892_1-83bf00ba7ef17902054c2b83fe295408-300x300.png)