Chapter 26: Biotechnology
... three billion base pairs after 15 years of research. The two agencies that completed the task are The International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium and Celera Genomics, a private company. ...
... three billion base pairs after 15 years of research. The two agencies that completed the task are The International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium and Celera Genomics, a private company. ...
Chapter 26: Biotechnology
... three billion base pairs after 15 years of research. The two agencies that completed the task are The International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium and Celera Genomics, a private company. ...
... three billion base pairs after 15 years of research. The two agencies that completed the task are The International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium and Celera Genomics, a private company. ...
Sample Exam #2 ( file)
... B. used to translate an mRNA into the amino acid sequence of a protein. C. the code geneticists use to let A stand for adenine, G for guanine, C for cytosine, and T for thymidine. D. sequences of one, two or three bases depending on how many amino acids are found in a protein. ...
... B. used to translate an mRNA into the amino acid sequence of a protein. C. the code geneticists use to let A stand for adenine, G for guanine, C for cytosine, and T for thymidine. D. sequences of one, two or three bases depending on how many amino acids are found in a protein. ...
Bacterial Genetics
... for enzymes to build substance. (negative feedback) (see page 353 fig. 18.20) 2. (Pro. & Euk) Adjust the amount being made of certain enzymes by regulating expression of genes coding for enzymes Prokaryotes only - structural genes ("SG"): code for enzymes, structural proteins - regulatory genes: con ...
... for enzymes to build substance. (negative feedback) (see page 353 fig. 18.20) 2. (Pro. & Euk) Adjust the amount being made of certain enzymes by regulating expression of genes coding for enzymes Prokaryotes only - structural genes ("SG"): code for enzymes, structural proteins - regulatory genes: con ...
Cloning Genes
... DNA fragments by size In electric field with positive and negative poles, which pole will DNA be attracted to? Why? ...
... DNA fragments by size In electric field with positive and negative poles, which pole will DNA be attracted to? Why? ...
Biology EOCT Review
... DNA and Genetics RNA - Ribonucleic Acid Nucleic acid 3 differences from DNA Sugar is ribose instead of deoxyribose Nitrogen bases: adenine, uracil, guanine, and cytosine Single stranded 3 types of RNA Messenger RNA – carries DNA nucleotide sequence out of the nucleus to the ribosome ...
... DNA and Genetics RNA - Ribonucleic Acid Nucleic acid 3 differences from DNA Sugar is ribose instead of deoxyribose Nitrogen bases: adenine, uracil, guanine, and cytosine Single stranded 3 types of RNA Messenger RNA – carries DNA nucleotide sequence out of the nucleus to the ribosome ...
Nerve activates contraction
... – Loosely packed areas are being actively transcribed. (Euchromatin) -- during Interphase ...
... – Loosely packed areas are being actively transcribed. (Euchromatin) -- during Interphase ...
lab- where`s the CAT palffy 2010-1
... your scissors to act as a restriction enzyme, cut across that strip between the center G and C. You will be forming a fragment that ends with GG and another that begins with CC. (HINT: each sample should have 5 of these sites, giving 6 fragments, with the exception of the standard DNA.) Count the nu ...
... your scissors to act as a restriction enzyme, cut across that strip between the center G and C. You will be forming a fragment that ends with GG and another that begins with CC. (HINT: each sample should have 5 of these sites, giving 6 fragments, with the exception of the standard DNA.) Count the nu ...
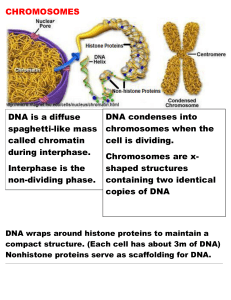
Chromosomes Notes
... DNA wraps around histone proteins to maintain a compact structure. (Each cell has about 3m of DNA) Nonhistone proteins serve as scaffolding for DNA. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... DNA wraps around histone proteins to maintain a compact structure. (Each cell has about 3m of DNA) Nonhistone proteins serve as scaffolding for DNA. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Human Genome Project
... mediocre at best. Humans, especially those who are experts in the field, do a much better job of evaluating evidence and deciding what a given gene’s function is. There is a big problem of too much information not uniformly coded or maintained. The scientific literature contains numerous examples of ...
... mediocre at best. Humans, especially those who are experts in the field, do a much better job of evaluating evidence and deciding what a given gene’s function is. There is a big problem of too much information not uniformly coded or maintained. The scientific literature contains numerous examples of ...
(Genetics).
... Many people are allergic to substances in the environment. Of the many foods that contain allergens (allergyinducing substances), peanuts cause some of the most severe reactions. Mildly allergic people may only get hives. Highly allergic people can go into a form of shock. Some people die each year ...
... Many people are allergic to substances in the environment. Of the many foods that contain allergens (allergyinducing substances), peanuts cause some of the most severe reactions. Mildly allergic people may only get hives. Highly allergic people can go into a form of shock. Some people die each year ...
Gene Regulation - Eukaryotic Cells
... Epigenetics • Epigenetics refers to processes that influence gene expression or function without changing the underlying DNA sequence. 1. Acetylation 2. Methylation ...
... Epigenetics • Epigenetics refers to processes that influence gene expression or function without changing the underlying DNA sequence. 1. Acetylation 2. Methylation ...
The Bioinformatics Institute
... • DNA polymerase has primase activity generates RNA primers. • DNA polymerase is the main replicating enzyme. • Eukaryotic DNA polymerases appear to lack 5’ 3’ exonuclease activity needed to remove RNA primer from each Okazaki fragment. • ‘Flap endonuclease’ (FEN1) initiates primer degradatio ...
... • DNA polymerase has primase activity generates RNA primers. • DNA polymerase is the main replicating enzyme. • Eukaryotic DNA polymerases appear to lack 5’ 3’ exonuclease activity needed to remove RNA primer from each Okazaki fragment. • ‘Flap endonuclease’ (FEN1) initiates primer degradatio ...
Basic Genetics
... 2. What sex chromosomes do females have? 3. What sex chromosomes do males have? 4. What sex chromosomes do birds and reptiles have? 5. What chromosomes do birds and reptile males have? 6. What chromosomes do birds and reptile females have? 7. What determines the sex of alligators, crocodiles and mos ...
... 2. What sex chromosomes do females have? 3. What sex chromosomes do males have? 4. What sex chromosomes do birds and reptiles have? 5. What chromosomes do birds and reptile males have? 6. What chromosomes do birds and reptile females have? 7. What determines the sex of alligators, crocodiles and mos ...
Recombinant Biotechnology
... • Like other enzymes restriction enzymes show specificity for certain substrates, and will only digest DNA within specific sequences of bases - called recognition sequence or a restriction site. • Some restriction enzymes cut DNA into overhanging single stranded ends. • Others will generate fragmen ...
... • Like other enzymes restriction enzymes show specificity for certain substrates, and will only digest DNA within specific sequences of bases - called recognition sequence or a restriction site. • Some restriction enzymes cut DNA into overhanging single stranded ends. • Others will generate fragmen ...
Protein Synthesis (Transcription and Translation) Really Think about
... 9. What does it mean to “transcribe” DNA? ______________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Transcribe this DNA sequence GGACCATAGACCATA 11. What happens during translation? __________________________ ...
... 9. What does it mean to “transcribe” DNA? ______________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Transcribe this DNA sequence GGACCATAGACCATA 11. What happens during translation? __________________________ ...
D. Cell Specialization: Regulation of Transcription Cell
... DNA can also control expression from genes in the euchromatin ...
... DNA can also control expression from genes in the euchromatin ...
Eukaryotic Gene Control
... “base” rate of transcription distant control sequences on DNA binding of activator proteins “enhanced” rate (high level) of transcription ...
... “base” rate of transcription distant control sequences on DNA binding of activator proteins “enhanced” rate (high level) of transcription ...
Poster
... Our enzyme, yHst2, belongs to an important family of enzymes called sirtuins. yHst2 is the yeast homologue of human Sir two 2. All Sir2 deacetylases have amino acid sequences that are very similar in all organisms from bacteria to humans. They all remove acetyl groups from acetyllysine sidechains on ...
... Our enzyme, yHst2, belongs to an important family of enzymes called sirtuins. yHst2 is the yeast homologue of human Sir two 2. All Sir2 deacetylases have amino acid sequences that are very similar in all organisms from bacteria to humans. They all remove acetyl groups from acetyllysine sidechains on ...
three possibile models for replication
... 16) They can cause the release of digestive (hydrolytic) enzymes from lysosomes, which break down the host cell and eventually kill it 17) They can cause infected cells to produce toxins that lead to disease symptoms 18) Vaccines = harmless derivatives of viruses that stimulate the immune system to ...
... 16) They can cause the release of digestive (hydrolytic) enzymes from lysosomes, which break down the host cell and eventually kill it 17) They can cause infected cells to produce toxins that lead to disease symptoms 18) Vaccines = harmless derivatives of viruses that stimulate the immune system to ...
DNA Technology - wvhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... **Junk DNA (introns) will be cut at different places for different people, therefore producing different size fragments ...
... **Junk DNA (introns) will be cut at different places for different people, therefore producing different size fragments ...
DNA
... discover the “transforming factor” They did this by using extracts from the heatkilled cells and digesting specific classes of molecules with enzymes Enzyme ...
... discover the “transforming factor” They did this by using extracts from the heatkilled cells and digesting specific classes of molecules with enzymes Enzyme ...