Transcription
... Eukaryotic transcription initiation require a variety of transcription factor because of the indirectly binding of Eukaryotic RNA-pol to DNA ...
... Eukaryotic transcription initiation require a variety of transcription factor because of the indirectly binding of Eukaryotic RNA-pol to DNA ...
Ensembl. Going beyond A,T, G and C
... Signal peptides, TM Helices • 1097 protein transcripts from 487 loci – 219 have signal peptides (107 loci) – 12 loci have an isoform without the signal peptide – 41 transcripts have a gain or loss of a tansmembrane helix (sometimes up to 8!) ...
... Signal peptides, TM Helices • 1097 protein transcripts from 487 loci – 219 have signal peptides (107 loci) – 12 loci have an isoform without the signal peptide – 41 transcripts have a gain or loss of a tansmembrane helix (sometimes up to 8!) ...
Combined pharmacophore based small molecule design for direct
... suppressed human GBM in vitro and suppressed OLIG2 target genes ...
... suppressed human GBM in vitro and suppressed OLIG2 target genes ...
Leukaemia Section t(13;19)(q14;p13) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Martineau M, Strefford JC, Moorman AV. Molecular cytogenetic characterization of TCF3 (E2A)/19p13.3 rearrangements in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2007 May;46(5):47886 ...
... Martineau M, Strefford JC, Moorman AV. Molecular cytogenetic characterization of TCF3 (E2A)/19p13.3 rearrangements in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2007 May;46(5):47886 ...
GENE REGULATION IN HIGHER ORGANSIMS Although eukaryotes
... A clear case of developmental regulation can be seen in our genes for hemoglobin; the molecule in red blood cells that function to transport oxygen. All hemoglobins are made of four polypeptide chains, which almost always occur in two pairs. The 4 chains of amino acids - globinssurround the iron-co ...
... A clear case of developmental regulation can be seen in our genes for hemoglobin; the molecule in red blood cells that function to transport oxygen. All hemoglobins are made of four polypeptide chains, which almost always occur in two pairs. The 4 chains of amino acids - globinssurround the iron-co ...
Photo Album
... current model of CREB-mediated transcription. Under basal conditions, unphosphorylated CREB is bound to the CRE element in the promoter of its target genes. Upon neural activity, CREB is phosphorylated at Ser-133 by various kinases within the KID domain. The KIX domain of CBP can then bind to CREB a ...
... current model of CREB-mediated transcription. Under basal conditions, unphosphorylated CREB is bound to the CRE element in the promoter of its target genes. Upon neural activity, CREB is phosphorylated at Ser-133 by various kinases within the KID domain. The KIX domain of CBP can then bind to CREB a ...
Eukaryotic Genes
... complexes, making it possible for three independently regulated families of promoters. – The eukaryotic RNA polymerases require more transcription factors to initiate RNA synthesis. – These transcription factors play many different roles including recognizing other transcription factors, removing ch ...
... complexes, making it possible for three independently regulated families of promoters. – The eukaryotic RNA polymerases require more transcription factors to initiate RNA synthesis. – These transcription factors play many different roles including recognizing other transcription factors, removing ch ...
Introduction to Biology
... throwing the virus into a predesigned protein soup that contained all the polymerases and other enzymatic ingredients necessary for RNA transcription and translation. The synthetic virus was able to successfully replicate itself from this mixture.” ...
... throwing the virus into a predesigned protein soup that contained all the polymerases and other enzymatic ingredients necessary for RNA transcription and translation. The synthetic virus was able to successfully replicate itself from this mixture.” ...
English Version Full Professor of General Botany at Sapienza
... same University. Chief of the laboratory of "in vitro morphogenesis and differentiation" in the Department of Plant Biology of Sapienza University since 1987. Specific experience in cytology, histology, in vitro culture systems, electron and confocal microscopy, flow cytometry, epifluorescence. Spec ...
... same University. Chief of the laboratory of "in vitro morphogenesis and differentiation" in the Department of Plant Biology of Sapienza University since 1987. Specific experience in cytology, histology, in vitro culture systems, electron and confocal microscopy, flow cytometry, epifluorescence. Spec ...
Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives)
... Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Compare and contrast chromatin and chromosome: composition, proteins involved and level of packing. Explain the structure and function of nucleosome, histones, scaffold proteins (metaphase chromosomes) 2. Explain the role of chemical mod ...
... Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Compare and contrast chromatin and chromosome: composition, proteins involved and level of packing. Explain the structure and function of nucleosome, histones, scaffold proteins (metaphase chromosomes) 2. Explain the role of chemical mod ...
Indezine Template
... Overview: The Flow of Genetic Information • The information content of DNA is in the form of specific sequences of nucleotides • The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of proteins • Proteins are the links between genotype and ...
... Overview: The Flow of Genetic Information • The information content of DNA is in the form of specific sequences of nucleotides • The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of proteins • Proteins are the links between genotype and ...
Worksheet for videos below
... DNA Replication 1. During which cell cycle phase do eukaryotes copy their DNA? ____________________________________ 2. Which theory of DNA replication is the correct theory as determined by the Meselson-Stahl experiment? _______________________________________________________________________________ ...
... DNA Replication 1. During which cell cycle phase do eukaryotes copy their DNA? ____________________________________ 2. Which theory of DNA replication is the correct theory as determined by the Meselson-Stahl experiment? _______________________________________________________________________________ ...
PDF
... which is implicated in the terminal differentiation and function of neurons, is inappropriately expressed in REST-depleted cells, suggesting that REST might serve to regulate neuronal differentiation programmes rather than the initial stages of neuronal lineage commitment. ...
... which is implicated in the terminal differentiation and function of neurons, is inappropriately expressed in REST-depleted cells, suggesting that REST might serve to regulate neuronal differentiation programmes rather than the initial stages of neuronal lineage commitment. ...
Chapter 26 - RNA Metabolism
... • Pause sites - regions of the gene where the rate of elongation slows down (10 to 100-fold) or stops temporarily • Transcription termination often occurs here • G-C- rich regions are more difficult to separate than A-T rich regions and may be pause sites • Pause is exaggerated when newly transcribe ...
... • Pause sites - regions of the gene where the rate of elongation slows down (10 to 100-fold) or stops temporarily • Transcription termination often occurs here • G-C- rich regions are more difficult to separate than A-T rich regions and may be pause sites • Pause is exaggerated when newly transcribe ...
Week 3 Pre-Lecture Slides
... • What would happen to transcription if the -10 and -35 boxes were switched? What if the +1 was a different base? What if the termination sequence was lost? • There are four channels in the RNA polymerase protein leading from the core to the outside. Name each of these channels usefully based on t ...
... • What would happen to transcription if the -10 and -35 boxes were switched? What if the +1 was a different base? What if the termination sequence was lost? • There are four channels in the RNA polymerase protein leading from the core to the outside. Name each of these channels usefully based on t ...
notes File - selu moodle
... snRNA recognizes intron exon junction and form a splicesome (introns are tagged by their sequence) Cleavage occurs at 5’ end of intron and a lariat is formed Free 3’ end of exon is used to displace the intron and join exon to exon Alternate splicing allows a single transcript to be translated into ...
... snRNA recognizes intron exon junction and form a splicesome (introns are tagged by their sequence) Cleavage occurs at 5’ end of intron and a lariat is formed Free 3’ end of exon is used to displace the intron and join exon to exon Alternate splicing allows a single transcript to be translated into ...
Cancer Prone Disease Section Trichothiodystrophy (TTD) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... The DNA repair defect is found in 3 classes: Patient with TTD-A group (low level of the TFIIH transcription factor), Patients mutated in the XPB gene (TTD/XPB), involving XPB, also called ERCC3, located in 2q21; and All the other patients mutated in the XPD gene (TTD/XPD), involving XPD, also called ...
... The DNA repair defect is found in 3 classes: Patient with TTD-A group (low level of the TFIIH transcription factor), Patients mutated in the XPB gene (TTD/XPB), involving XPB, also called ERCC3, located in 2q21; and All the other patients mutated in the XPD gene (TTD/XPD), involving XPD, also called ...
Access Slides
... • Provide a marker for recognition by other proteins. For example, a conserved “bromo” domain found in SWI/SNF and other transcription factors recognizes this marker. ...
... • Provide a marker for recognition by other proteins. For example, a conserved “bromo” domain found in SWI/SNF and other transcription factors recognizes this marker. ...
Leukaemia Section t(4;21)(q31;q22) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... transactivation domain; forms heterodimers; widely expressed; nuclear localisation; transcription factor (activator) for various hematopoietic-specific genes. ...
... transactivation domain; forms heterodimers; widely expressed; nuclear localisation; transcription factor (activator) for various hematopoietic-specific genes. ...
No Slide Title
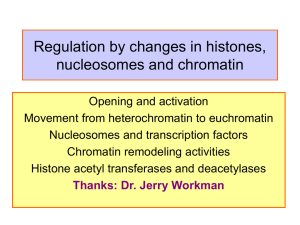
... • Destabilize histone/DNA interactions. • Bound transcription factors can thus participate in nucleosome displacement and/or rearrangement. • Provides sequence specificity to the formation of DNAse hypersensitive sites. • DNAse hypersensitive sites may be – nucleosome free regions or – factor bound, ...
... • Destabilize histone/DNA interactions. • Bound transcription factors can thus participate in nucleosome displacement and/or rearrangement. • Provides sequence specificity to the formation of DNAse hypersensitive sites. • DNAse hypersensitive sites may be – nucleosome free regions or – factor bound, ...
CS374 - Stanford University
... throwing the virus into a predesigned protein soup that contained all the polymerases and other enzymatic ingredients necessary for RNA transcription and translation. The synthetic virus was able to successfully replicate itself from this mixture.” ...
... throwing the virus into a predesigned protein soup that contained all the polymerases and other enzymatic ingredients necessary for RNA transcription and translation. The synthetic virus was able to successfully replicate itself from this mixture.” ...
Les 6b RNA Transcription and Translation
... A.A. allow the protein molecule to form its necessary structure Proteins have many structures/shapes ...
... A.A. allow the protein molecule to form its necessary structure Proteins have many structures/shapes ...
Transcription factor
In molecular biology and genetics, a transcription factor (sometimes called a sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA. Transcription factors perform this function alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA polymerase (the enzyme that performs the transcription of genetic information from DNA to RNA) to specific genes.A defining feature of transcription factors is that they contain one or more DNA-binding domains (DBDs), which attach to specific sequences of DNA adjacent to the genes that they regulate. Additional proteins such as coactivators, chromatin remodelers, histone acetylases, deacetylases, kinases, and methylases, while also playing crucial roles in gene regulation, lack DNA-binding domains, and, therefore, are not classified as transcription factors.