Chapter 16 Cholinesterase Inhibitors
... May be bacterial, viral, or both Usually starts as viral infection of the nasopharynx Diagnosis (must have all three of the following) ...
... May be bacterial, viral, or both Usually starts as viral infection of the nasopharynx Diagnosis (must have all three of the following) ...
Urinary Tract Infection Adult Genito-Urinary Infections Epidemiology, Etiology, and
... • ~20 to 1 ratio in patients with recurrent UTI • Not as well defined as UTI • Typical presentation: • Cystitis + flank pain and fevers • Septic shock is uncommon → important to consider an obstructive etiology • E. coli in 90% • Unique virulence characteristics ...
... • ~20 to 1 ratio in patients with recurrent UTI • Not as well defined as UTI • Typical presentation: • Cystitis + flank pain and fevers • Septic shock is uncommon → important to consider an obstructive etiology • E. coli in 90% • Unique virulence characteristics ...
Infections of the Chest Wall
... 1. These necrotizing infections are usually at the chest tube or thoracotomy site. 2. Infections of the head and neck as well as dental manipulation are the source of necrotizing infections of chest wall. ...
... 1. These necrotizing infections are usually at the chest tube or thoracotomy site. 2. Infections of the head and neck as well as dental manipulation are the source of necrotizing infections of chest wall. ...
Hepatitis B Prevention
... World Health Organization concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Dotted lines on maps represent approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement. ...
... World Health Organization concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Dotted lines on maps represent approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement. ...
Correspondence: A.M. Jones, Manchester Adult Cystic
... monitoring and supportive measures, or commencement of preemptive antibiotic therapy to prevent clinical deterioration from an accompanying bacterial exacerbation, particularly for those patients with known chronic bacterial infection. In addition, infection control measures may require prompt diagn ...
... monitoring and supportive measures, or commencement of preemptive antibiotic therapy to prevent clinical deterioration from an accompanying bacterial exacerbation, particularly for those patients with known chronic bacterial infection. In addition, infection control measures may require prompt diagn ...
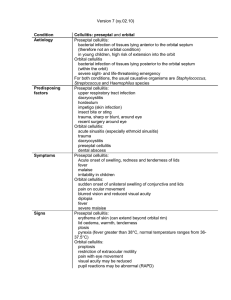
Pre-septal cellulitis
... (therefore not an orbital condition) in young children, high risk of extension into the orbit Orbital cellulitis bacterial infection of tissues lying posterior to the orbital septum (within the orbit) severe sight- and life-threatening emergency For both conditions, the usual causative organisms are ...
... (therefore not an orbital condition) in young children, high risk of extension into the orbit Orbital cellulitis bacterial infection of tissues lying posterior to the orbital septum (within the orbit) severe sight- and life-threatening emergency For both conditions, the usual causative organisms are ...
Whooping cough - Wamberal Surgery
... Initial pertussis symptoms, about 2–3 weeks after airways infection, are those of a cold. The afflicted person is highly infectious during this catarrhal phase of runny nose, dry cough and sneezing. The cough gets worse over 2–3 days with associated symptoms of fever and tiredness. Infected airways ...
... Initial pertussis symptoms, about 2–3 weeks after airways infection, are those of a cold. The afflicted person is highly infectious during this catarrhal phase of runny nose, dry cough and sneezing. The cough gets worse over 2–3 days with associated symptoms of fever and tiredness. Infected airways ...
Right Lung Apical Cavity with Bilateral Pleural Effusion
... immunocompetent hosts without significant prior exposure to the health care system. Pneumonia in these patients is frequently preceded by extra-pulmonary staphylococcal infection, particularly skin infection. This patient had no prodrome of viral pneumonia, and right-sided endocarditis was not suppo ...
... immunocompetent hosts without significant prior exposure to the health care system. Pneumonia in these patients is frequently preceded by extra-pulmonary staphylococcal infection, particularly skin infection. This patient had no prodrome of viral pneumonia, and right-sided endocarditis was not suppo ...
Whooping Cough (Pertussis) Information Leaflet for Patients What is
... Whooping Cough is most contagious 2 to 4 days before the cough starts so the most effective prevention is through immunization. Vaccine is given to babies at 2, 4, 6 months of age and later at 45 year preschool children. A booster dose is recommended at 11-14 years. Doctor may prescribe antibiotics ...
... Whooping Cough is most contagious 2 to 4 days before the cough starts so the most effective prevention is through immunization. Vaccine is given to babies at 2, 4, 6 months of age and later at 45 year preschool children. A booster dose is recommended at 11-14 years. Doctor may prescribe antibiotics ...
- European Medical Journal
... Viruses are responsible for the vast majority of respiratory tract infections (RTIs; ≥80%). Common causal agents include human rhinovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, adenoviruses, and influenza virus.5 Bacteria spp. also represent aetiological agents, both alone and as bacterial superinfections, c ...
... Viruses are responsible for the vast majority of respiratory tract infections (RTIs; ≥80%). Common causal agents include human rhinovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, adenoviruses, and influenza virus.5 Bacteria spp. also represent aetiological agents, both alone and as bacterial superinfections, c ...
Consultant Urological Surgeon Benenden Hospital Tunbridge Wells
... Sterile pyuria Haematuria New storage symptoms Bladder pain Dysuria ...
... Sterile pyuria Haematuria New storage symptoms Bladder pain Dysuria ...
a cauliflower ear: an unusual complication of tmj surgery
... infection secondary to insinuation of pus between the auricular cartilage and its perichondrium from nearby focus. This infection eventually leads to rapid melting of the avascular cartilage and if treated improperly, necrosis of the cartilage will take place resulting in considerable morbidity and ...
... infection secondary to insinuation of pus between the auricular cartilage and its perichondrium from nearby focus. This infection eventually leads to rapid melting of the avascular cartilage and if treated improperly, necrosis of the cartilage will take place resulting in considerable morbidity and ...
Schistosomiasis
... Allergic reaction:urticaria, angioneuroedema, enlargement of lymph nodes and eosinophilia Digestive syndromes: abdominal pain, diarrhea with pus and blood, constipation or diarrhea Hepatosplenomegaly ...
... Allergic reaction:urticaria, angioneuroedema, enlargement of lymph nodes and eosinophilia Digestive syndromes: abdominal pain, diarrhea with pus and blood, constipation or diarrhea Hepatosplenomegaly ...
Safe Use of Antibiotics – Frequently Asked Questions
... the antibiotics which they are previously sensitive to, i.e. the previous effective treatment is no longer capable of controlling the same infection. When the bacteria become resistant to most commonly used antibiotics, they are commonly referred as “superbugs” or “MDROs”. 7. What are multi-drug res ...
... the antibiotics which they are previously sensitive to, i.e. the previous effective treatment is no longer capable of controlling the same infection. When the bacteria become resistant to most commonly used antibiotics, they are commonly referred as “superbugs” or “MDROs”. 7. What are multi-drug res ...
Side Effects Of Osteoporosis Drugs
... Other less common: Constipation; diarrhea; full or bloated feeling; gas; headache; nausea ...
... Other less common: Constipation; diarrhea; full or bloated feeling; gas; headache; nausea ...
Lateral Canthotomy
... 2) Lube your Two x Fr 14 foleys, and tie your large gynae tampon with 2.0 silk in the middle 3) Under direct vision (with laryngoscope) – pass both foleys into each nare along the floor on the nose – watch passage into oro-pharynx 4) Retrieve through the mouth with magils forceps 5) Tie tampon to th ...
... 2) Lube your Two x Fr 14 foleys, and tie your large gynae tampon with 2.0 silk in the middle 3) Under direct vision (with laryngoscope) – pass both foleys into each nare along the floor on the nose – watch passage into oro-pharynx 4) Retrieve through the mouth with magils forceps 5) Tie tampon to th ...
emesyl - Itonis Holdings
... Stop use and ask a doctor if symptoms persist. If pregnant or breast feeding, ask a health professional before use. Keep out of reach of children. If swallowed, get medical help or contact a ...
... Stop use and ask a doctor if symptoms persist. If pregnant or breast feeding, ask a health professional before use. Keep out of reach of children. If swallowed, get medical help or contact a ...
Slide 1
... pop/snap in R knee and immediate swelling/pain. Eased with ice and rest within a week. Improved by 75% at first appointment and after full compliance with rehab, better but unable to fully extend knee (-10 degree). ...
... pop/snap in R knee and immediate swelling/pain. Eased with ice and rest within a week. Improved by 75% at first appointment and after full compliance with rehab, better but unable to fully extend knee (-10 degree). ...
MRSA -- Information for Patients Who May Be Carriers
... Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) is a special type of Staphylococcus or Staph bacteria that is unaffected by the antibiotic drugs used to treat normal Staph infections. MRSA cannot spread through the air, but it is contagious by contact, either by touching an infected person direct ...
... Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) is a special type of Staphylococcus or Staph bacteria that is unaffected by the antibiotic drugs used to treat normal Staph infections. MRSA cannot spread through the air, but it is contagious by contact, either by touching an infected person direct ...
Acute Otitis Media
... Otitis Media with Effusion: presence of nonpurulent fluid within the middle ear cavity ...
... Otitis Media with Effusion: presence of nonpurulent fluid within the middle ear cavity ...
brain abscess - Melbourne Neurosurgery
... People who are sick or run down have a higher chance. If you are taking immunosuppressive drugs. If you have chronic respiratory disease. ...
... People who are sick or run down have a higher chance. If you are taking immunosuppressive drugs. If you have chronic respiratory disease. ...
ADULT CELLULITIS DEFINITION
... Known methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) positive (family or household member) ...
... Known methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) positive (family or household member) ...
Bacterial Skin Infections
... *Carbuncle is usually single and located on the back and lower side of the neck and on other hairy areas. *Carbuncles are composed of furuncles joined together in the subcutaneous area and when sloughing shows multiple openings on the surface of the skin. *Suppuration is deeply seated than in the fu ...
... *Carbuncle is usually single and located on the back and lower side of the neck and on other hairy areas. *Carbuncles are composed of furuncles joined together in the subcutaneous area and when sloughing shows multiple openings on the surface of the skin. *Suppuration is deeply seated than in the fu ...
Sinusitis

Sinusitis, also known as a sinus infection or rhinosinusitis, is inflammation of the sinuses resulting in symptoms. Common signs and symptoms include thick nasal mucous, a plugged nose, and pain in the face. Other signs and symptoms may include fever, headaches, poor sense of smell, sore throat, and cough. The cough is often worse at night. Serious complications are rare. It is defined as acute rhinosinusitis (ARS) if it lasts less than 4 weeks, and as chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) if it lasts for more than 12 weeks.It can be due to infection, allergies, air pollution, or structural problems in the nose. Most cases are due to a viral infection. A bacterial infection may be present if symptoms last more than ten days or if a person worsens after starting to improve. Recurrent episodes are more likely in people with asthma, cystic fibrosis, and poor immune function. X-rays are not typically needed unless complications are suspected. In chronic cases confirmatory testing is recommended by either direct visualization or computed tomography.Some cases may be prevented by hand washing, avoiding smoking, and immunization. Pain killers such as naproxen, nasal steroids, and nasal irrigation may be used to help with symptoms. Treating ARS with or without an antibiotic is reasonable for uncomplicated bacterial cases. If after a further seven days there is still no improvement antibiotics may either be recommended or changed. In those in whom antibiotics are used, either amoxicillin or amoxicillin/clavulanate is recommended first line. Surgery may occasionally be used in people with chronic disease.Sinusitis is a common condition. It affects about between 10% and 30% of people each year in the United States and Europe. Women are more often affected than men. Chronic sinusitis affects approximately 12.5% of people. Treatment of sinusitis in the United States results in more than 11 billion USD in costs.