* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Consultant Urological Surgeon Benenden Hospital Tunbridge Wells
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Signs and symptoms of Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatoid arthritis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myasthenia gravis wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Management of multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
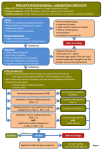
LUTS Shawket Alkhayal Consultant Urological Surgeon Benenden Hospital Tunbridge Wells Nuffield Hospital LUTS are a major burden for the ageing male population. Age is an important risk factor for LUTS and the prevalence of LUTS increases as men get older. Bothersome LUTS can occur in up to 30% of men older than 65 years. Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) It can comprise voiding or storage urinary symptoms and can arise from any of the following organ problem: Prostate: benign prostate enlargement (BPH), prostate cancer, prostatitis Urethra: strictures, inflammation Bladder: Cystitis, Detrusor muscle weakness or overactivity, Bladder pain Syndrome Neurological disease Voiding Symptoms Weak or intermittent urinary stream Hesitancy Straining Sense of incomplete emptying Terminal dribbling Storage Symptoms Frequency Urgency Urge incontinence Nocturia Enuresis Assessment Medical history Associated co-morbidities Review current medication, to identify drugs that may be contributing to the problem Specific questionnaire (IPSS) Urinary frequency volume chart (Bladder Diary) Examination General examination Examination of the abdomen External genitalia Digital Rectal Examination (DRE) Tests Urine dipstick test blood glucose protein leucocytes nitrites Offer men PSA test after counseling Serum creatinine test (plus estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] calculation) if you suspect renal impairment palpable bladder nocturnal enuresis recurrent urinary tract infections history of renal stones Conservative Management Storage Symptoms Bladder training for OAB symptoms Advice on fluid intake Lifestyle advice Containment products if they are incontinent Drug Therapy for mild to moderate symptoms For predominantly voiding symptoms-offer an alpha blocker For predominantly storage symptoms offer an anticholinergic For mixed symptoms offer an alpha blocker first then add anticholinergic after 4 weeks if no improvement Referral for Specialist Assessment If bothersome LUTS that have not responded to conservative management or drug treatment LUTS complicated by recurrent or persistent urinary tract infection or Urinary retention or Renal impairment you suspect is caused by lower urinary tract dysfunction or Suspected urological cancer Specialist Assessment History review Examination including DRE Bladder diary IPSS Flow test and check residual volumes Alpha blockers if not been tried for voiding Symptoms with low flow rate and high residuals Add 5 alpha reductase inhibitors for men with prostates estimated to be larger than 30 g or a PSA level greater than 1.4 ng/ml Anticholinegics for OAB symptoms with good flow test and minimal residuals Late afternoon loop diuretic for nocturnal polyuria. Oral desmopressin for nocturnal polyuria if other medical causes have been excluded and other treatments failed Urodynamic Assessment Predominantly storage symptoms Men under 40 or over 85 Previous pelvic surgery Neurological disease Cystoscopy Recurrent infection Sterile pyuria Haematuria New storage symptoms Bladder pain Dysuria Imaging of the Upper Urinary Tract Chronic retention Haematuria Recurrent infection Sterile pyuria Profound symptoms or pain Surgical Management of BPH If voiding symptoms are severe, or If drug treatment and conservative management options have been unsuccessful or are not appropriate Discuss the alternatives to and outcomes from surgery TURP, Bipolar TURP, HOLEP All other surgical treatments should be in the context of audit or research Management of OAB if symptoms have not responded to conservative management and drug treatments Botox Bladder injections for men with detrusor over activity, and is willing and able to self-catheterise Sacral nerve stimulation Cystoplasty Urinary Diversion New treatments PDE5-inhibitors (Tadalafil 5mg) for patients with LUTS and ED Beta 3 agonist (Mirabegron) for OAB PTNS- for OAB symptoms