* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pre-septal cellulitis
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Acute pancreatitis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis signs and symptoms wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
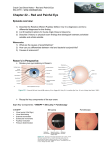
Version 7 (xy.02.10) Condition Aetiology Predisposing factors Symptoms Signs Cellulitis: preseptal and orbital Preseptal cellulitis: bacterial infection of tissues lying anterior to the orbital septum (therefore not an orbital condition) in young children, high risk of extension into the orbit Orbital cellulitis bacterial infection of tissues lying posterior to the orbital septum (within the orbit) severe sight- and life-threatening emergency For both conditions, the usual causative organisms are Staphylococcus, Streptococcus and Haemophilus species Preseptal cellulitis: upper respiratory tract infection dacryocystitis hordeolum impetigo (skin infection) insect bite or sting trauma, sharp or blunt, around eye recent surgery around eye Orbital cellulitis: acute sinusitis (especially ethmoid sinusitis) trauma dacryocystitis preseptal cellulitis dental abscess Preseptal cellulitis: Acute onset of swelling, redness and tenderness of lids fever malaise irritability in children Orbital cellulitis: sudden onset of unilateral swelling of conjunctiva and lids pain on ocular movement blurred vision and reduced visual acuity diplopia fever severe malaise Preseptal cellulitis: erythema of skin (can extend beyond orbital rim) lid oedema, warmth, tenderness ptosis pyrexia (fever greater than 38°C, normal temperature ranges from 3637.5°C) Orbital cellulitis: proptosis restriction of extraocular motility pain with eye movement visual acuity may be reduced pupil reactions may be abnormal (RAPD) Version 7 (xy.02.10) pyrexia Feature proptosis Ocular motility Visual acuity RAPD Preseptal cellulitis absent normal normal normal Orbital cellulitis present painful, restricted reduced present (Modified from a table in Denniston AKO and Murray PI: Oxford Handbook of Ophthalmology. OUP 2008) Differential diagnosis Preseptal cellulitis: orbital cellulitis hordeolum (external or internal) acute blepharitis viral conjunctivitis with eyelid swelling allergic conjunctivitis with eyelid swelling Orbital cellulitis: cavernous sinus thrombosis mucormycosis (fungal infection) sarcoidosis dysthyroid exophthalmos neoplasia with inflammation Management by Optometrist NonCheck and record patient’s temperature pharmacological Preseptal cellulitis: cold compress for symptomatic relief Pharmacological Preseptal cellulitis: analgesia as required Management Preseptal cellulitis: A2: initial management and emergency referral to Ophthalmologist. category Telephone on-call Ophthalmologist Orbital cellulitis: A1: emergency referral to Ophthalmologist, no intervention. Telephone oncall Ophthalmologist Possible management by Ophthalmologist Preseptal cellulitis: confirmation of diagnosis CT or MRI scan children may require admission to hospital for observation systemic antibiotics (oral and/or parenteral) Orbital cellulitis: confirmation of diagnosis CT or MRI scan blood tests, possibly including microbial culture admission to hospital systemic antibiotics (parenteral and/or oral) drainage of orbital abscess co-management with ENT specialist colleague Evidence base Botting AM, McIntosh D, Mahadevan M. Paediatric pre- and post-septal periorbital infections are different diseases. A retrospective review of 262 cases. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2008; 72(3): 377-83 Version 7 (xy.02.10) Centre for Evidence-based Medicine Level of Evidence = 4