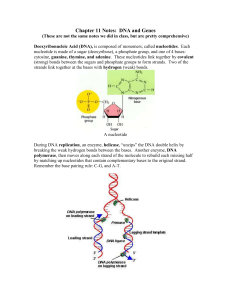
Chapter 11 Notes: DNA and Genes
... In transcription, a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA, by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. In this case, however, thymine is replaced with uracil, so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA i ...
... In transcription, a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA, by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. In this case, however, thymine is replaced with uracil, so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA i ...
Mutation or polymorphism?
... mutations. However, not all mutations cause diseases. Any new sequence variant, even if neutral or beneficial in effect, will start off as a rare mutation. Polymorphic sequence variants usually do not cause overt debilitating diseases. Many are found outside of genes and are completely neutral in ef ...
... mutations. However, not all mutations cause diseases. Any new sequence variant, even if neutral or beneficial in effect, will start off as a rare mutation. Polymorphic sequence variants usually do not cause overt debilitating diseases. Many are found outside of genes and are completely neutral in ef ...
DNA Replication - Texas Tech University
... transferases) Histone acetylation increases accessibility ...
... transferases) Histone acetylation increases accessibility ...
Molecular genetics (cloning)
... with the wanted gene? • Cultivate the transformed culture • Spread the culture on a nutrient plate and select for transformants! ...
... with the wanted gene? • Cultivate the transformed culture • Spread the culture on a nutrient plate and select for transformants! ...
DNA Discovery, Structure, Replication, Transcription, Translation
... Match the letter with the corresponding phrase: 5. Identify a nucleotide of DNA. 6. Identify the labeled deoxyribose sugar. 7. Identify all of the labeled nitrogen bases. 8. Identify a labeled phosphate group. 9. Identify all of the labeled purines. 10. Identify the labeled hydrogen bonds. ...
... Match the letter with the corresponding phrase: 5. Identify a nucleotide of DNA. 6. Identify the labeled deoxyribose sugar. 7. Identify all of the labeled nitrogen bases. 8. Identify a labeled phosphate group. 9. Identify all of the labeled purines. 10. Identify the labeled hydrogen bonds. ...
Bioinformatics: One Minute and One Hour at a Time
... • Distance from one gene to a set of genes is minimum of all distances from the gene to the individual members (Single Linkage) • Repeat until all genes have been joined ...
... • Distance from one gene to a set of genes is minimum of all distances from the gene to the individual members (Single Linkage) • Repeat until all genes have been joined ...
Chromosomes, Alleles, Genes, Mutations
... chromosomes that have the same genes as each other, arranged in the same sequence, but not necessarily the same alleles of those genes ...
... chromosomes that have the same genes as each other, arranged in the same sequence, but not necessarily the same alleles of those genes ...
GENETIC TRANSFER AND RECOMBINATION (Chapter 8):
... Vertical gene transfer: between parent and offspring Horizontal gene transfer: between other organisms in the same generation Three types: 1. Transformation 2. Conjugation 3. Transduction All types: Involve unidirectional transfer of information (donor to recipient—recipient called recombinant cell) ...
... Vertical gene transfer: between parent and offspring Horizontal gene transfer: between other organisms in the same generation Three types: 1. Transformation 2. Conjugation 3. Transduction All types: Involve unidirectional transfer of information (donor to recipient—recipient called recombinant cell) ...
DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis Notes Part 1
... (proteins) Two phases: Transcription & Translation mRNA must be processed before it leaves the nucleus of eukaryotic cells ...
... (proteins) Two phases: Transcription & Translation mRNA must be processed before it leaves the nucleus of eukaryotic cells ...
Social media policy
... The process of helping people understand and adapt to the genetic, medical, psychological and familial implications of genetic contributions to disease. Genetic recombination The exchange of genetic material either between or within chromosomes which occurs during meiosis. Genetic/genomic variation ...
... The process of helping people understand and adapt to the genetic, medical, psychological and familial implications of genetic contributions to disease. Genetic recombination The exchange of genetic material either between or within chromosomes which occurs during meiosis. Genetic/genomic variation ...
Genetic terms, punnett squares
... » Plasmids - circular DNA molecules found in bacteria, separate from other bacterial DNA » Sticky ends - matching or complimentary segments of DNA that are produced by restriction enzymes » Human genes can be inserted into bacterial plasmids so the bacteria can produce human enzymes or proteins = re ...
... » Plasmids - circular DNA molecules found in bacteria, separate from other bacterial DNA » Sticky ends - matching or complimentary segments of DNA that are produced by restriction enzymes » Human genes can be inserted into bacterial plasmids so the bacteria can produce human enzymes or proteins = re ...
Ch 5.3 Lecture #1
... • The bases attract each other because of hydrogen bonds. • Hydrogen bonds are weak but there are millions and millions of them in a single molecule of DNA. ...
... • The bases attract each other because of hydrogen bonds. • Hydrogen bonds are weak but there are millions and millions of them in a single molecule of DNA. ...
Chapter 16
... • Protein called the lac repressor can bind to the operator, but only when lactose is absent. If operator is bound, promoter region is partially blocked-genes can not be transcribed. • This two switch control mechanism thus causes the cell to produce only what the cell needs, when it needs it. ...
... • Protein called the lac repressor can bind to the operator, but only when lactose is absent. If operator is bound, promoter region is partially blocked-genes can not be transcribed. • This two switch control mechanism thus causes the cell to produce only what the cell needs, when it needs it. ...
Bioinformatics Tools and Genomes to Life
... -- the multiprotein complexes that execute cellular functions and govern cell form. • Characterize gene regulatory networks. • Characterize the functional repertoire of complex microbial communities in their natural environments at the molecular level. • Develop the computational methods and capabil ...
... -- the multiprotein complexes that execute cellular functions and govern cell form. • Characterize gene regulatory networks. • Characterize the functional repertoire of complex microbial communities in their natural environments at the molecular level. • Develop the computational methods and capabil ...
File
... • Chromosomes contain genes which code for proteins • We are making a combination of proteins that our mom & dad have! – for hair and eye color – for height and weight – that make dimples, freckles, etc. ...
... • Chromosomes contain genes which code for proteins • We are making a combination of proteins that our mom & dad have! – for hair and eye color – for height and weight – that make dimples, freckles, etc. ...
Trends in Biotechnology
... Compare the how different vectors can carry different sizes of DNA into the bacteria. 5. List the types of vectors that can be used to transform yeast, mammalian cells and plants, and why they are effective in those organisms. 6. List the methods of transformation of cells. ...
... Compare the how different vectors can carry different sizes of DNA into the bacteria. 5. List the types of vectors that can be used to transform yeast, mammalian cells and plants, and why they are effective in those organisms. 6. List the methods of transformation of cells. ...
Basic Medical College of Fudan University
... A. Mitochondria are believed to have evolved from free living bacteria-like organisms during the last ~1.5 billion years. B. The mitochondrial “Eve” is thought to have lived in Africa ~ 200 million years ago. C. Analysis of mitochondria DNA has provided crucial evidence for the “Out of Africa”theory ...
... A. Mitochondria are believed to have evolved from free living bacteria-like organisms during the last ~1.5 billion years. B. The mitochondrial “Eve” is thought to have lived in Africa ~ 200 million years ago. C. Analysis of mitochondria DNA has provided crucial evidence for the “Out of Africa”theory ...
11.2 Reading Guide - Lewis Center for Educational Research
... Since the “original code” found along the ______________ molecule can’t leave the nucleus, it must first be ______________ (meaning to write or make a copy). The “copy” is “written” as a molecule of ____________ that differs from the original on three counts, they are… RNA is ______________ stranded ...
... Since the “original code” found along the ______________ molecule can’t leave the nucleus, it must first be ______________ (meaning to write or make a copy). The “copy” is “written” as a molecule of ____________ that differs from the original on three counts, they are… RNA is ______________ stranded ...
learning objectives
... 4. When cool, the primers are bound to their complementary sequences near the desired gene. 5. The enzyme, DNA polymerase, then begins at a primer and replicates the single-stranded DNA. 6. Many copies of the desired gene can be made in this manner. B. Formation of cDNA 1. Prokaryotes do not have ex ...
... 4. When cool, the primers are bound to their complementary sequences near the desired gene. 5. The enzyme, DNA polymerase, then begins at a primer and replicates the single-stranded DNA. 6. Many copies of the desired gene can be made in this manner. B. Formation of cDNA 1. Prokaryotes do not have ex ...