GHW#11-Questions$Slides
... 22.15 Recombinant DNA and Genetic Engineering, 834 22.16 The Polymerase Chain Reaction, 838 ...
... 22.15 Recombinant DNA and Genetic Engineering, 834 22.16 The Polymerase Chain Reaction, 838 ...
File
... a. producing two new strands. b. separating the strands. c. producing DNA polymerase. d. correctly pairing bases. Q: The first step in DNA replication is a. producing two new strands. b. separating the strands. c. producing DNA polymerase. d. correctly pairing bases. Q: In addition to carrying out t ...
... a. producing two new strands. b. separating the strands. c. producing DNA polymerase. d. correctly pairing bases. Q: The first step in DNA replication is a. producing two new strands. b. separating the strands. c. producing DNA polymerase. d. correctly pairing bases. Q: In addition to carrying out t ...
Chapter 11
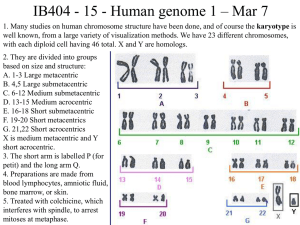
... c. The ends of eukaryotic chromosomes, the telomeres, present problems in replication V. DNA in chromosomes is packaged in a highly organized way A. The genome of E. Coli consists of about 4 x 106 base pairs – about 1.35 mm in length B. The haploid DNA of a human cell is made of 3 x 109 base pairs – ...
... c. The ends of eukaryotic chromosomes, the telomeres, present problems in replication V. DNA in chromosomes is packaged in a highly organized way A. The genome of E. Coli consists of about 4 x 106 base pairs – about 1.35 mm in length B. The haploid DNA of a human cell is made of 3 x 109 base pairs – ...
BioRad #166-0007EDU: Forensic DNA Fingerprinting Checklist PREP
... Restriction enzymes (endonucleases) are natural defense mechanisms of bacteria against invading bacteria. Restriction enzymes act like molecular scissors, making cuts at specific sequence of base pairs (palindromes) that it recognizes. Bacteria’s own DNA is protected by methyl groups at sites that w ...
... Restriction enzymes (endonucleases) are natural defense mechanisms of bacteria against invading bacteria. Restriction enzymes act like molecular scissors, making cuts at specific sequence of base pairs (palindromes) that it recognizes. Bacteria’s own DNA is protected by methyl groups at sites that w ...
PLANT GENETIC ENGINEERING (Genetic Transformation)
... Schleiden (1838) and Schwann (1839), which recognized the cell as the primary unit of all living organisms. The concept of cellular totipotency, which was inherent in the Cell Theory and forms the basis of plant biotechnology, was further elaborated by Haberlandt (1902), who predicted the production ...
... Schleiden (1838) and Schwann (1839), which recognized the cell as the primary unit of all living organisms. The concept of cellular totipotency, which was inherent in the Cell Theory and forms the basis of plant biotechnology, was further elaborated by Haberlandt (1902), who predicted the production ...
Protocol for T4 Polynucleotide Kinase, Cloned
... T4 Polynucleotide Kinase (T4 PNK) catalyzes the transfer of the γ-phosphate of ATP to the 5′ terminus of single- and double-stranded DNA or RNA molecules that have a 5′ hydroxyl. The enzyme also removes the 3′ phosphate from 3′-phosphoryl polynucleotides, deoxyribonucleoside 3′-monophosphates, and d ...
... T4 Polynucleotide Kinase (T4 PNK) catalyzes the transfer of the γ-phosphate of ATP to the 5′ terminus of single- and double-stranded DNA or RNA molecules that have a 5′ hydroxyl. The enzyme also removes the 3′ phosphate from 3′-phosphoryl polynucleotides, deoxyribonucleoside 3′-monophosphates, and d ...
The UCSC Human Genome Browser
... each other ever since. This schism has even led to most public projects being routinely published in Nature, with Celera and other industry papers appearing routinely in Science, until recently. 12. The public consortium insisted that Celera cheated by using the public sequence data in a way that re ...
... each other ever since. This schism has even led to most public projects being routinely published in Nature, with Celera and other industry papers appearing routinely in Science, until recently. 12. The public consortium insisted that Celera cheated by using the public sequence data in a way that re ...
DNA Function II - Complete Vocab with
... General Transcription Factors: Other enzymes/proteins that are required for RNA Polymerase to function Transcription Activators: Proteins that bind to enhancers to stimulate transcription Transcription Repressors: Proteins that bind to enhancers to shut down transcription Enhancer: A sequence of DNA ...
... General Transcription Factors: Other enzymes/proteins that are required for RNA Polymerase to function Transcription Activators: Proteins that bind to enhancers to stimulate transcription Transcription Repressors: Proteins that bind to enhancers to shut down transcription Enhancer: A sequence of DNA ...
Chapter 15
... RNA polymerases are the primary enzymes responsible for this process 1. Promoters- process starts at RNA polymerase binding sites (promoters) on the DNA template strand. Promoters are short sequences that are not transcribed by the polymerase that binds to them. Ex: TATA box25 nucleotides upstream f ...
... RNA polymerases are the primary enzymes responsible for this process 1. Promoters- process starts at RNA polymerase binding sites (promoters) on the DNA template strand. Promoters are short sequences that are not transcribed by the polymerase that binds to them. Ex: TATA box25 nucleotides upstream f ...
The Little Things About the Little Things Inside of Us The Eukaryotic
... examining mRNA sequences made in different cell types. Eukaryote genes are not organized into operons. Regulation of several genes at once requires common control elements. Eukaryotes have three RNA polymerases: I codes for rRNA; III codes for tRNA II transcribes protein-coding genes ...
... examining mRNA sequences made in different cell types. Eukaryote genes are not organized into operons. Regulation of several genes at once requires common control elements. Eukaryotes have three RNA polymerases: I codes for rRNA; III codes for tRNA II transcribes protein-coding genes ...
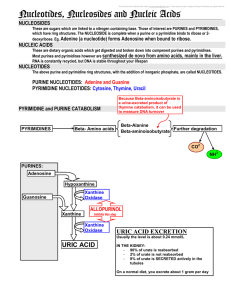
3 Nucleosides nucleotides and nucleic acids
... These are dietary organic acids which get digested and broken down into compenent purines and pyrimidines. Most purines and pyrimidines however are synthesized de novo from amino acids, mainly in the liver. RNA is constantly recycled, but DNA is stable throughout your lifespan ...
... These are dietary organic acids which get digested and broken down into compenent purines and pyrimidines. Most purines and pyrimidines however are synthesized de novo from amino acids, mainly in the liver. RNA is constantly recycled, but DNA is stable throughout your lifespan ...
notes File - selu moodle
... To detect certain cancers and genetic diseases Used in DNA fingerprinting, genetic engineering, & forensic science for tests such as: Paternity testing Personal identification Sex determination Species exclusion ...
... To detect certain cancers and genetic diseases Used in DNA fingerprinting, genetic engineering, & forensic science for tests such as: Paternity testing Personal identification Sex determination Species exclusion ...
Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives)
... sequences (proximal and distal elements) 6. Compare and contrast pre and post transcriptional and translational controls of gene expression 7. Explain interference RNA and its role play in post-transcriptional and translational regulation of gene expression 8. Define ubiquitin and proteosome and exp ...
... sequences (proximal and distal elements) 6. Compare and contrast pre and post transcriptional and translational controls of gene expression 7. Explain interference RNA and its role play in post-transcriptional and translational regulation of gene expression 8. Define ubiquitin and proteosome and exp ...
Protein Synthesis PPT
... III-1 and III-2 = Prince Albert and Queen Victoria IV-5 and IV-6 = Alice of Hesse and Ludwig IV of Hesse V-13 and V-14 = Alix and Nicholas II (Tsar of Russia) ...
... III-1 and III-2 = Prince Albert and Queen Victoria IV-5 and IV-6 = Alice of Hesse and Ludwig IV of Hesse V-13 and V-14 = Alix and Nicholas II (Tsar of Russia) ...
DNA - Community College of Rhode Island
... There are 64 different codons in the genetic code!!!! ...
... There are 64 different codons in the genetic code!!!! ...
Name - Mr. Spechts world of Science
... Which statement best describes the main function of this type of molecule? (1) It is a structural part of the cell wall. (2) It stores energy for metabolic processes. (3) It determines what traits may be inherited. (4) It transports 11. When DNA separates into two strands, the DNA would most likely ...
... Which statement best describes the main function of this type of molecule? (1) It is a structural part of the cell wall. (2) It stores energy for metabolic processes. (3) It determines what traits may be inherited. (4) It transports 11. When DNA separates into two strands, the DNA would most likely ...
Assessment
... recognizes the transcription start site of a gene? a. The polymerase strings amino acids into a polypeptide. b. Free-floating nucleotides pair up with exposed DNA bases. c. A complementary RNA strand detaches itself from the DNA. d. The DNA strand begins to unwind, separating the two strands. _____ ...
... recognizes the transcription start site of a gene? a. The polymerase strings amino acids into a polypeptide. b. Free-floating nucleotides pair up with exposed DNA bases. c. A complementary RNA strand detaches itself from the DNA. d. The DNA strand begins to unwind, separating the two strands. _____ ...
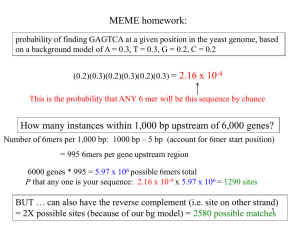
GenomicVariation_11-22
... Multiple motif finding methods now work on multiple alignments of regulatory regions of coregulated genes. Given: 1) group of regulatory regions of coregulated genes 2) orthologs of each region, in the form of multiple alignments Sinha et al. 2004 “PhyME: A probabalistic algorithm for finding motif ...
... Multiple motif finding methods now work on multiple alignments of regulatory regions of coregulated genes. Given: 1) group of regulatory regions of coregulated genes 2) orthologs of each region, in the form of multiple alignments Sinha et al. 2004 “PhyME: A probabalistic algorithm for finding motif ...
Microbiology Chapter 9
... Mutations: an inheritable change in an organisms genetic information, in its DNA 1. Can be simple as one base pair, or complex involving many bases 2. Can be natural (spontaneous - random mistakes), biological (jumping genes – transposable elements – transposons – can jump around and when inserted t ...
... Mutations: an inheritable change in an organisms genetic information, in its DNA 1. Can be simple as one base pair, or complex involving many bases 2. Can be natural (spontaneous - random mistakes), biological (jumping genes – transposable elements – transposons – can jump around and when inserted t ...
Genetics Biotech PREAP 2014
... • Drugs that prevent chromosomal separation during meiosis have been particularly useful in plant breeding. • Sometimes these drugs produce cells that have double or triple the normal number of chromosomes. • Plants grown from such cells are called polyploid because they have many sets of chromosome ...
... • Drugs that prevent chromosomal separation during meiosis have been particularly useful in plant breeding. • Sometimes these drugs produce cells that have double or triple the normal number of chromosomes. • Plants grown from such cells are called polyploid because they have many sets of chromosome ...