Replication Transcription Translation
... • A gene is a segment of DNA • A gene is a sequence of nucleotides that codes for a functional product (usually a protein) • 1 gene = 1000’s of base pairs • 41000 possibilities of combinations ...
... • A gene is a segment of DNA • A gene is a sequence of nucleotides that codes for a functional product (usually a protein) • 1 gene = 1000’s of base pairs • 41000 possibilities of combinations ...
3/27
... • Goal: to measure RNA levels of all genes in genome • RNA levels vary with the following: – Cell type – Developmental stage – External stimuli ...
... • Goal: to measure RNA levels of all genes in genome • RNA levels vary with the following: – Cell type – Developmental stage – External stimuli ...
I - Nutley Public Schools
... ________________ to tyrosine. ii. In albinism, tyrosine cannot be converted to melanin skin pigment. o b. Evolution of gene -- product concepts: i. Early experiments with bread mold ________________ led to "one gene -________________" hypothesis. ii. This was broadened to one gene -- one prote ...
... ________________ to tyrosine. ii. In albinism, tyrosine cannot be converted to melanin skin pigment. o b. Evolution of gene -- product concepts: i. Early experiments with bread mold ________________ led to "one gene -________________" hypothesis. ii. This was broadened to one gene -- one prote ...
PDF
... domain protein 2) and a co-factor [MBD3L1 (methyl-CpG binding domain protein 3-like 1)] to enrich for doublestranded methylated DNA that might have as few as two methyl groups. It should be noted that both of these techniques have been commercialized as kits, which might be useful to the novice user ...
... domain protein 2) and a co-factor [MBD3L1 (methyl-CpG binding domain protein 3-like 1)] to enrich for doublestranded methylated DNA that might have as few as two methyl groups. It should be noted that both of these techniques have been commercialized as kits, which might be useful to the novice user ...
Genetics Session 5b_2016
... phenotype and a genetic predictor is h, the square root of the heritability (h2). Imagine if we had a perfect genetic predictor for height (e.g. all causal variants known without error) then the prediction error for any individual would be 7*√(10.8) = 3.1cm, assuming that h2=0.8 and that the standar ...
... phenotype and a genetic predictor is h, the square root of the heritability (h2). Imagine if we had a perfect genetic predictor for height (e.g. all causal variants known without error) then the prediction error for any individual would be 7*√(10.8) = 3.1cm, assuming that h2=0.8 and that the standar ...
Lesson 3
... Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) • RNA is made in the nucleus from DNA • RNA is a single strand • RNA has the nitrogen bases A, G, C, and U (uracil) • The sugar-phospate backbone contains the sugar ribose ...
... Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) • RNA is made in the nucleus from DNA • RNA is a single strand • RNA has the nitrogen bases A, G, C, and U (uracil) • The sugar-phospate backbone contains the sugar ribose ...
Microarray Analysis & Functional Genomics
... From NSF Program Announcement: Environmental Genomics ...
... From NSF Program Announcement: Environmental Genomics ...
CH 16 and 17 PowerPoint
... • Unlike the human's seemingly random distribution of gene-rich areas, many other organisms' genomes are more uniform, with genes evenly spaced throughout. • Humans have on average three times as many kinds of proteins as the fly or worm because of mRNA transcript "alternative splicing" and chemical ...
... • Unlike the human's seemingly random distribution of gene-rich areas, many other organisms' genomes are more uniform, with genes evenly spaced throughout. • Humans have on average three times as many kinds of proteins as the fly or worm because of mRNA transcript "alternative splicing" and chemical ...
Name - PSUSDscienceresources
... and put in their place the genes for hemoglobin, the molecule in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Mulligan hoped that the genetically modified virus would no longer tell the cell it had entered to make more virus particles. It would just order hemoglobin proteins. Mulligan assembled his fleet of ...
... and put in their place the genes for hemoglobin, the molecule in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Mulligan hoped that the genetically modified virus would no longer tell the cell it had entered to make more virus particles. It would just order hemoglobin proteins. Mulligan assembled his fleet of ...
GEN2MHG – MOLECULAR AND HUMAN GENETICS DNA is made
... ▪ generally right-handed helix ▪ two grooves, major (22A wide) and minor (12A) of different sizes are present -> major groove is more accessible to transcription factors Alternative DNA structures; ▪ B-DNA – most common and biologically significant -> right handed and 10 base pairs per turn ▪ A-DNA ...
... ▪ generally right-handed helix ▪ two grooves, major (22A wide) and minor (12A) of different sizes are present -> major groove is more accessible to transcription factors Alternative DNA structures; ▪ B-DNA – most common and biologically significant -> right handed and 10 base pairs per turn ▪ A-DNA ...
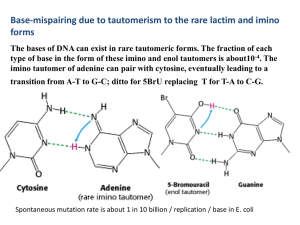
4 . The imino tautomer of adenine can pair with cytosine
... Deamination of bases: Chemical mutagenesis and possibly carcinogenesis Nitrous acid (HNO2) hydrolyzes amino groups on bases via diazotization. Adenine is deaminated to hypoxanthine, cytosine to uracil, and guanine to xanthine. Hypoxanthine pairs with cytosine, inducing a mutation of A-T to G-C. It ...
... Deamination of bases: Chemical mutagenesis and possibly carcinogenesis Nitrous acid (HNO2) hydrolyzes amino groups on bases via diazotization. Adenine is deaminated to hypoxanthine, cytosine to uracil, and guanine to xanthine. Hypoxanthine pairs with cytosine, inducing a mutation of A-T to G-C. It ...
DNA
... alteration. Tumor-Suppressor Genes : inhibit expression of tumor phenotype. When are inactivated or lost abnormal proliferation Oncogenes :Genes which can potentially induce neoplastic transformation. They include genes for growth factors, growth factor receptors, protein ...
... alteration. Tumor-Suppressor Genes : inhibit expression of tumor phenotype. When are inactivated or lost abnormal proliferation Oncogenes :Genes which can potentially induce neoplastic transformation. They include genes for growth factors, growth factor receptors, protein ...
DNA, RNA and Protein
... – How does DNA replication differ in prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells? – Replication in most prokaryotic cells starts from a single point and proceeds in two directions until the entire chromosome is copied. ...
... – How does DNA replication differ in prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells? – Replication in most prokaryotic cells starts from a single point and proceeds in two directions until the entire chromosome is copied. ...
Option B: Biotechnology and Bioinformatics AHL
... 9. EST is an expressed sequence tag that can be used to identify potential genes. 429-431; Handout Applications and Skills: Application: Use of knockout technology in mice to determine gene function. Online. Application: Discovery of genes by EST data mining. Online. Skill: Explore chromosome 21 in ...
... 9. EST is an expressed sequence tag that can be used to identify potential genes. 429-431; Handout Applications and Skills: Application: Use of knockout technology in mice to determine gene function. Online. Application: Discovery of genes by EST data mining. Online. Skill: Explore chromosome 21 in ...
STANDARD 10: THE CENTRAL DOGMA
... which matches mRNA’s codon. Another tRNA lands and the amino acids are connected with a ______________ bond. The first tRNA _________ and the ribosome shifts to the _________. A new tRNA lands and the amino acids connect again. The process continues and now the amino acid chain is called a _________ ...
... which matches mRNA’s codon. Another tRNA lands and the amino acids are connected with a ______________ bond. The first tRNA _________ and the ribosome shifts to the _________. A new tRNA lands and the amino acids connect again. The process continues and now the amino acid chain is called a _________ ...
Manipulating and Analyzing DNA
... recombinant DNA. You will use two different websites to understand both topics. By the end of today you should be able answer the flooring questions: What are restriction enzymes? How and why are they used in biotechnology? How do restriction enzymes play a role in recombinant DNA? Restriction Enzym ...
... recombinant DNA. You will use two different websites to understand both topics. By the end of today you should be able answer the flooring questions: What are restriction enzymes? How and why are they used in biotechnology? How do restriction enzymes play a role in recombinant DNA? Restriction Enzym ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... a. A copy of the information found in DNA. b. Carries instructions to the ribosomes on how to make a specific protein. ...
... a. A copy of the information found in DNA. b. Carries instructions to the ribosomes on how to make a specific protein. ...
Types/Sources of Genetic Data Mendelian Genetics
... Problem of “blending inheritance” ² Darwin: “I have lately been inclined to speculate very crudely & indistinctly, that propagation by true fertilisation, will turn out to be a sort of mixture & not true fusion, of two distinct individuals, or rather of innumerable individuals, as each parent ha ...
... Problem of “blending inheritance” ² Darwin: “I have lately been inclined to speculate very crudely & indistinctly, that propagation by true fertilisation, will turn out to be a sort of mixture & not true fusion, of two distinct individuals, or rather of innumerable individuals, as each parent ha ...
I. Comparing genome sequences
... • Homologous sequences = derived from a common ancestor • Orthologous sequences = homologous sequences separated by a speciation event (e.g., human HOXA and mouse Hoxa) • Paralogous sequences = homologous sequences separated by gene duplication (e.g., human HOXA and human HOXB) ...
... • Homologous sequences = derived from a common ancestor • Orthologous sequences = homologous sequences separated by a speciation event (e.g., human HOXA and mouse Hoxa) • Paralogous sequences = homologous sequences separated by gene duplication (e.g., human HOXA and human HOXB) ...
Athena, Jen and Natalie`s Powerpt
... And so the template strand gets complimented Into a single strand of mRNA, There’s no thymine in it But uracil takes its place Polymerase then adds nucleotides In the direction of mRNA’s 5 to 3 prime Just like DNA replication It’s the direction of all genetic creation The DNA strand that is read is ...
... And so the template strand gets complimented Into a single strand of mRNA, There’s no thymine in it But uracil takes its place Polymerase then adds nucleotides In the direction of mRNA’s 5 to 3 prime Just like DNA replication It’s the direction of all genetic creation The DNA strand that is read is ...