DNA Transcription and Protein synthesis
... RNA polymerase I : it synthesizes the precursor of the 28s ,18s, and 5.8s r-RNA in the nucleolus RNA polymerase II : it synthesizes the precursor of m-RNA in addition to srRNA RNA polymerase III : it produces the small RNA including tRNA 5s ribosomal RNA and some snRNA ...
... RNA polymerase I : it synthesizes the precursor of the 28s ,18s, and 5.8s r-RNA in the nucleolus RNA polymerase II : it synthesizes the precursor of m-RNA in addition to srRNA RNA polymerase III : it produces the small RNA including tRNA 5s ribosomal RNA and some snRNA ...
No Slide Title
... • Longer time to accumulate introns? • Genomes are more recombinogenic due to repeated sequences? • Selection for increased protein complexity – Gene number does not correlate with complexity – Ergo, it must come from somewhere ...
... • Longer time to accumulate introns? • Genomes are more recombinogenic due to repeated sequences? • Selection for increased protein complexity – Gene number does not correlate with complexity – Ergo, it must come from somewhere ...
Poster
... to create a model of the T7 RNA Polymerase (T7 RNAP) using data from the Protein Data Bank and a visualization program called RasMol. T7 is virus that infects bacteria, but its RNA Polymerase is a very important molecule to scientists. Scientists can use T7 RNAP to create large amounts of a specific ...
... to create a model of the T7 RNA Polymerase (T7 RNAP) using data from the Protein Data Bank and a visualization program called RasMol. T7 is virus that infects bacteria, but its RNA Polymerase is a very important molecule to scientists. Scientists can use T7 RNAP to create large amounts of a specific ...
Chapter 12 Learning Objectives
... 23. Explain what gel electrophoresis is generally, and how it can be used to separate molecules (including both DNA and food coloring). Explain how size and charge affect this separation. 24. Explain how DNA gel electrophoresis can be used to compare different DNA samples generally 25. Explain what ...
... 23. Explain what gel electrophoresis is generally, and how it can be used to separate molecules (including both DNA and food coloring). Explain how size and charge affect this separation. 24. Explain how DNA gel electrophoresis can be used to compare different DNA samples generally 25. Explain what ...
Restriction Enzymes
... short DNA sequences. They can range from 2 bases to 30+ bases long. In some regions of the genome, the number of repeats varies highly from individual to ...
... short DNA sequences. They can range from 2 bases to 30+ bases long. In some regions of the genome, the number of repeats varies highly from individual to ...
Office Hours
... estimated to be only a few billion years, you should now be wondering… What is the origin of our information? ...
... estimated to be only a few billion years, you should now be wondering… What is the origin of our information? ...
Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
... Position of the course Every student must know the basic principles of biochemistry and molecular biology. Part Biochemistry This course provides a fundamental base for the study (structure, organisation and function) and optimal control of living matter (animal, plant and microorganism). After a su ...
... Position of the course Every student must know the basic principles of biochemistry and molecular biology. Part Biochemistry This course provides a fundamental base for the study (structure, organisation and function) and optimal control of living matter (animal, plant and microorganism). After a su ...
You Light Up My Life
... assembly is provided by removal of two phosphate groups from free nucleotides ...
... assembly is provided by removal of two phosphate groups from free nucleotides ...
Genetic Engineering Powerpoint
... Prasher took a gel in which restriction fragments from the jellyfish genome had been separated and found that one of the fragments bound tightly to the mRNA That fragment contained the actual gene for GFP ...
... Prasher took a gel in which restriction fragments from the jellyfish genome had been separated and found that one of the fragments bound tightly to the mRNA That fragment contained the actual gene for GFP ...
DNA review worksheet.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 38. What is the error rate in DNA replication? What helps lower this error rate to 1 in 1 billion nucleotides? 39. What is a mutation? 40. Name several things that can cause DNA mutations. ...
... 38. What is the error rate in DNA replication? What helps lower this error rate to 1 in 1 billion nucleotides? 39. What is a mutation? 40. Name several things that can cause DNA mutations. ...
Summary notes on Genetics and Gene expression
... A nonsense mutation –base substitution results in a stop codon being transcribed on to mRNA so polypeptide chain is stopped prematurely and will often not function A mis-sense mutation –base substitution results in a different amino acid being coded for which could change the tertiary structure A Si ...
... A nonsense mutation –base substitution results in a stop codon being transcribed on to mRNA so polypeptide chain is stopped prematurely and will often not function A mis-sense mutation –base substitution results in a different amino acid being coded for which could change the tertiary structure A Si ...
Tools of Genetic Engineering 2
... fragment expresses normally as in parental cell. Thus, the foreign DNA fragments can be procured from a variety of sources depending on the aims and scope of cloning experiments. • Identification and characterization of DNA sequences are rather more difficult on its genome than using mRNA, if it is ...
... fragment expresses normally as in parental cell. Thus, the foreign DNA fragments can be procured from a variety of sources depending on the aims and scope of cloning experiments. • Identification and characterization of DNA sequences are rather more difficult on its genome than using mRNA, if it is ...
Chapter 4 BSCS Green Sections 4.7
... and illustrate the digestion of a lactose sugar molecule. Color and label each molecule based upon the reading above. ...
... and illustrate the digestion of a lactose sugar molecule. Color and label each molecule based upon the reading above. ...
TF binding
... changes in gene activity that are not caused by changes in the DNA sequence • The study of stable, long-term alterations in the transcriptional potential of a cell that are not necessarily heritable • Functionally relevant changes to the genome that do not involve a change in the nucleotide sequence ...
... changes in gene activity that are not caused by changes in the DNA sequence • The study of stable, long-term alterations in the transcriptional potential of a cell that are not necessarily heritable • Functionally relevant changes to the genome that do not involve a change in the nucleotide sequence ...
I. Microbial Genetics (Chapter 7) A. Overview 1. all of the information
... a. useful for tracking genetic events, determining genetic organization, mapping genes b. detected by replica plating or biochemical indicators c. many mutations are neutral (no phenotypic change) (1) usually single nucleotide substitution, "corrected" by degeneracy of the genetic code (2) mutation ...
... a. useful for tracking genetic events, determining genetic organization, mapping genes b. detected by replica plating or biochemical indicators c. many mutations are neutral (no phenotypic change) (1) usually single nucleotide substitution, "corrected" by degeneracy of the genetic code (2) mutation ...
Highlight Review – Common Assessment #4 Multiple Choice
... In guinea pigs, the allele for rough coat (R) is dominant over the allele for smooth coat (r). A heterozygous guinea pig and a homozygous recessive guinea pig are mated. Which of the following would be the phenotypes of the offspring? a. all rough coat c. 2 rough coat and 2 smooth coat b. all smooth ...
... In guinea pigs, the allele for rough coat (R) is dominant over the allele for smooth coat (r). A heterozygous guinea pig and a homozygous recessive guinea pig are mated. Which of the following would be the phenotypes of the offspring? a. all rough coat c. 2 rough coat and 2 smooth coat b. all smooth ...
Chapter 14 - The Biology Corner
... If a person with type AB is married to someone with type O blood, what blood types are possible in their children? ...
... If a person with type AB is married to someone with type O blood, what blood types are possible in their children? ...
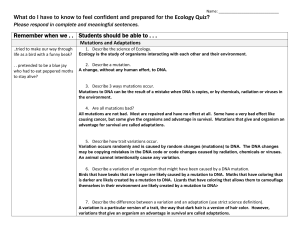
Remember when we . . Students should be able to
... Ecology is the study of organisms interacting with each other and their environment. ...
... Ecology is the study of organisms interacting with each other and their environment. ...
Protein Synthesis Analogy
... 3. The teacher’s desk will be the nucleus. The nucleus will have DNA strands. 4. Students will be mRNA molecules. The mRNA molecule (one student from each group) will transcribe a copy of a DNA message at the teacher’s desk (the DNA never leaves the nucleus). 5. The students’ desk will be the riboso ...
... 3. The teacher’s desk will be the nucleus. The nucleus will have DNA strands. 4. Students will be mRNA molecules. The mRNA molecule (one student from each group) will transcribe a copy of a DNA message at the teacher’s desk (the DNA never leaves the nucleus). 5. The students’ desk will be the riboso ...
doc
... 11. What is a Principle Component Analysis? A. A way to visualize n-dimensional protein space by breaking projecting it onto a 2-dimensional screen. B. BLAST is used to identify common motifs that together using domain shuffling make up the components of a large number of proteins. C. A measure of h ...
... 11. What is a Principle Component Analysis? A. A way to visualize n-dimensional protein space by breaking projecting it onto a 2-dimensional screen. B. BLAST is used to identify common motifs that together using domain shuffling make up the components of a large number of proteins. C. A measure of h ...
12-4 Mutations - Lincoln Park High School
... because it changes all codons after the point of the mutation. The result is all of the amino acids will be changed which can affect the proper formation of a protein. ...
... because it changes all codons after the point of the mutation. The result is all of the amino acids will be changed which can affect the proper formation of a protein. ...