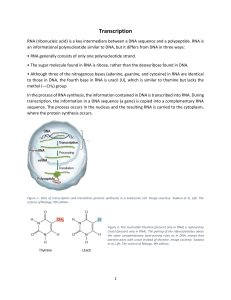
Transcription and RNA processing
... prokaryotic and eukaryotic genes, transcription begins at a DNA sequence that is upstream (to the “left” on the DNA) of the first codon (i.e., at the promoter), and ends downstream (to the “right” on the DNA) of the termination codon. In eukaryotes, there is usually a “polyadenylation” sequence (AAU ...
... prokaryotic and eukaryotic genes, transcription begins at a DNA sequence that is upstream (to the “left” on the DNA) of the first codon (i.e., at the promoter), and ends downstream (to the “right” on the DNA) of the termination codon. In eukaryotes, there is usually a “polyadenylation” sequence (AAU ...
DNA
... From these numbers, we can begin to appreciate the diversity of DNA and hence the diversity of living organism consisting of the alphabet ...
... From these numbers, we can begin to appreciate the diversity of DNA and hence the diversity of living organism consisting of the alphabet ...
What are transcription factors?
... luckily there are 2 tall people living at your house. It is also a difficult light switch to turn on, so 2 people need to work together to turn it on. In order to make light/gene product, you need the STAT to exist as a dimer (two STATs bound together). In our analogy, that means we need two peo ...
... luckily there are 2 tall people living at your house. It is also a difficult light switch to turn on, so 2 people need to work together to turn it on. In order to make light/gene product, you need the STAT to exist as a dimer (two STATs bound together). In our analogy, that means we need two peo ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... recombinant molecule into a bacterial host • Cloning can also be done in eukaryotic cells such as yeast • One can then produce large quantities of the gene or piece of DNA in pure form ...
... recombinant molecule into a bacterial host • Cloning can also be done in eukaryotic cells such as yeast • One can then produce large quantities of the gene or piece of DNA in pure form ...
Epigenetic regulation of gene transcription. Publications
... cell and is repressive to any process which requires access to the DNA including DNA repair, replication, recombination and gene transcription. Understanding how these processes occur in the context of chromatin is important since defective chromatin has been associated with developmental disorders ...
... cell and is repressive to any process which requires access to the DNA including DNA repair, replication, recombination and gene transcription. Understanding how these processes occur in the context of chromatin is important since defective chromatin has been associated with developmental disorders ...
Final Review: 2nd Semester Biology Answer Key
... amino acid encoded by a codon in the mRNA to the protein produced during translation. 35. Transcription is the production of an mRNA copy of a gene. It occurs in the nucleus. The enzyme RNA polymerase unwinds a section of DNA at the start of a gene, and adds the complementary RNA nucleotides to the ...
... amino acid encoded by a codon in the mRNA to the protein produced during translation. 35. Transcription is the production of an mRNA copy of a gene. It occurs in the nucleus. The enzyme RNA polymerase unwinds a section of DNA at the start of a gene, and adds the complementary RNA nucleotides to the ...
PPT2
... Writhe W is a measure of the coiling of the axis of the double helix. A right-handed coil is assigned a negative number (negative supercoiling) and a lefthanded coil is assigned a positive number (positive ...
... Writhe W is a measure of the coiling of the axis of the double helix. A right-handed coil is assigned a negative number (negative supercoiling) and a lefthanded coil is assigned a positive number (positive ...
THE FUNCTION OF DNA AND GENETIC ENGINEERING By
... guidelines. By the end of my investigation and the end of my research I wanted to have these questions answered to the best of my ability, and understand the topics fully. I had one main, over- arching question, however beneath those were several, more specific ones to narrow down my areas of resear ...
... guidelines. By the end of my investigation and the end of my research I wanted to have these questions answered to the best of my ability, and understand the topics fully. I had one main, over- arching question, however beneath those were several, more specific ones to narrow down my areas of resear ...
DNA (Gene) Mutations
... more) missing, added, or incorrect A mistake in the genetic code Wrong instructions wrong building materials wrong structure. ...
... more) missing, added, or incorrect A mistake in the genetic code Wrong instructions wrong building materials wrong structure. ...
Biotechnology
... Examples • EcoRI binds & cuts DNA at the following sequence: – 5 ... GAATTC ... 3 – 3... CTTAAG ... 5 • The sequence is palindromic: – reads the same 5-to-3 on both strands. ...
... Examples • EcoRI binds & cuts DNA at the following sequence: – 5 ... GAATTC ... 3 – 3... CTTAAG ... 5 • The sequence is palindromic: – reads the same 5-to-3 on both strands. ...
Chapter 18 – Gene Mutations and DNA Repair
... • Slippage of new strand can result in expanded number of repeats in offspring cells • Cause of anticipation ...
... • Slippage of new strand can result in expanded number of repeats in offspring cells • Cause of anticipation ...
Constructing a Model of Protein Synthesis
... messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA’s nucleotide sequence into the form of a complementary RNA molecule. Then the mRNA carries this code out to the ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized (assembled). The code, DNA or mRNA, specifies the order in which the amino acids are joined together ...
... messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA’s nucleotide sequence into the form of a complementary RNA molecule. Then the mRNA carries this code out to the ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized (assembled). The code, DNA or mRNA, specifies the order in which the amino acids are joined together ...
Chapter 10: Nucleic Acids And Protein Synthesis
... 2. 3.2 billion base pairs in the 23 human chromosomes 3. Now scientists need to understand what the DNA sequences encode 4. Bioinformatics: used computers to compare different DNA sequences 5. Will help to diagnose, treat, and prevent genetic disorders, cancer and infectious diseases in the future. ...
... 2. 3.2 billion base pairs in the 23 human chromosomes 3. Now scientists need to understand what the DNA sequences encode 4. Bioinformatics: used computers to compare different DNA sequences 5. Will help to diagnose, treat, and prevent genetic disorders, cancer and infectious diseases in the future. ...
Chapter 18 – Gene Mutations and DNA Repair
... • Slippage of new strand can result in expanded number of repeats in offspring cells • Cause of anticipation ...
... • Slippage of new strand can result in expanded number of repeats in offspring cells • Cause of anticipation ...
Bio Unit 7b DNA packet
... What do we do if there is a change? • Some changes cause _______________ • ____________ are non-lethal - Important for diversity (survival of the fittest) How many genes do this? • Any gene has the _________________ to mutate • Can happen anywhere (______________________________________________) • O ...
... What do we do if there is a change? • Some changes cause _______________ • ____________ are non-lethal - Important for diversity (survival of the fittest) How many genes do this? • Any gene has the _________________ to mutate • Can happen anywhere (______________________________________________) • O ...
Genetic Notes - Biloxi Public Schools
... Before a cell divides, it makes a copy of its DNA. This ensures that both new cells have all the genetic information they need. A genome is the complete sequence of an organism’s DNA. ...
... Before a cell divides, it makes a copy of its DNA. This ensures that both new cells have all the genetic information they need. A genome is the complete sequence of an organism’s DNA. ...
How are animal proteins made from DNA?
... What is “transcription?” • A part of the DNA double helix within the nucleus is ________, cut by _______, and then copied onto a new ______ ______, called mRNA. This process is called ___________.” • Once the DNA is transcribed, the single strand moves from the ______ to a ________ in the _________ ...
... What is “transcription?” • A part of the DNA double helix within the nucleus is ________, cut by _______, and then copied onto a new ______ ______, called mRNA. This process is called ___________.” • Once the DNA is transcribed, the single strand moves from the ______ to a ________ in the _________ ...
DNA_Technology_part2
... • The plasmids must be reintroduced into the host cell e.g. bacteria • This process is called transformation. • The bacteria, plasmids and calcium are mixed together. • By altering the temperature the bacteria become permeable and the plasmid can pass through the cell membrane. ...
... • The plasmids must be reintroduced into the host cell e.g. bacteria • This process is called transformation. • The bacteria, plasmids and calcium are mixed together. • By altering the temperature the bacteria become permeable and the plasmid can pass through the cell membrane. ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
... The DNA strands separate as weak hydrogen bonds between the bases are breaking at stage 2 Free RNA nucleotides join up with exposed bases on one of the DNA Strands at stage 3. Uracil joins with Adenine, Cytosine with Guanine Weak hydrogen bonds are forming between the new base pairs at stage 4 The n ...
... The DNA strands separate as weak hydrogen bonds between the bases are breaking at stage 2 Free RNA nucleotides join up with exposed bases on one of the DNA Strands at stage 3. Uracil joins with Adenine, Cytosine with Guanine Weak hydrogen bonds are forming between the new base pairs at stage 4 The n ...
DNA: the Molecule of Heredity
... sequence that also changes the protein it codes for • Mutations can happen in reproductive cells and in body cells (cancer) ...
... sequence that also changes the protein it codes for • Mutations can happen in reproductive cells and in body cells (cancer) ...
Transposable Elements
... Molecular Analysis of Transposons • Transposons isolated by first cloning a gene that they invaded. A number have been cloned this way, via "Transposon trapping“. • Some common molecular features: – Exist as multiple copies in the genome – Insertion site of element does not have extensive homology ...
... Molecular Analysis of Transposons • Transposons isolated by first cloning a gene that they invaded. A number have been cloned this way, via "Transposon trapping“. • Some common molecular features: – Exist as multiple copies in the genome – Insertion site of element does not have extensive homology ...
DNA
... • Complementary base pairing occurs along different portions than DNA." • Hairpin: secondary structure formed by a stem-loop." ...
... • Complementary base pairing occurs along different portions than DNA." • Hairpin: secondary structure formed by a stem-loop." ...
chromosome
... • Different kinds of organisms have different numbers of chromosomes. • Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, 46 in all: 44 autosomes and two sex chromosomes. • Each parent contributes one chromosome to each pair, so children get half of their chromosomes from their mothers and half from their father ...
... • Different kinds of organisms have different numbers of chromosomes. • Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, 46 in all: 44 autosomes and two sex chromosomes. • Each parent contributes one chromosome to each pair, so children get half of their chromosomes from their mothers and half from their father ...
Exam Procedures: this isBMB 526 Exam #1 11/5/12 this is form A
... producing the primary transcript (the 7-minute old RNA) from the collagen α1(II) gene? A) E. coli RNA polymerase B) RNA polymerase I C) RNA polymerase II D) RNA polymerase III E) reverse transcriptase 31. In splicing the primary transcript to form the functional RNA, which of the following component ...
... producing the primary transcript (the 7-minute old RNA) from the collagen α1(II) gene? A) E. coli RNA polymerase B) RNA polymerase I C) RNA polymerase II D) RNA polymerase III E) reverse transcriptase 31. In splicing the primary transcript to form the functional RNA, which of the following component ...