DNA Unit Study Guide
... 1. Describe how mRNA codons are translated into amino acids. 2. Summarize the process of protein synthesis, or translation, step by step. 3. How many nucleotides make up a codon? Is the stop codon an amino acid? 4. What is the responsibility of tRNA? What is an anticodon? Suppose AGU was the anti ...
... 1. Describe how mRNA codons are translated into amino acids. 2. Summarize the process of protein synthesis, or translation, step by step. 3. How many nucleotides make up a codon? Is the stop codon an amino acid? 4. What is the responsibility of tRNA? What is an anticodon? Suppose AGU was the anti ...
Gene Section CBFb (subunit b of core binding factor)
... Transcription Alternate splicing at cDNA positions 495 (in exon 5) and 526. ...
... Transcription Alternate splicing at cDNA positions 495 (in exon 5) and 526. ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis Study Guide
... use a codon chart (the circle one will be provided). Describe the relationship between amino acids and proteins. List some functions of proteins in the human body. ...
... use a codon chart (the circle one will be provided). Describe the relationship between amino acids and proteins. List some functions of proteins in the human body. ...
Human gene expression and genomic imprinting
... Pathogenic gene expression Genetic changes in the regulatory mechanism of the control elements of gene expression – examples • 1. mutations within the promoter region • 2. mutation within enhancers, silencers and response elements • 3.non-physiological gene expression – control of inappropriate enh ...
... Pathogenic gene expression Genetic changes in the regulatory mechanism of the control elements of gene expression – examples • 1. mutations within the promoter region • 2. mutation within enhancers, silencers and response elements • 3.non-physiological gene expression – control of inappropriate enh ...
Proteins are macromolecules that serve specific purposes in all
... it can assume many distinct yet potentially valid conformations). The conformation common to all members of the set is called the pharmacophore and is responsible for the drug activity. Having isolated the pharmacophore, the pharmaceutical drug activity can be improved, side effects reduced, etc. An ...
... it can assume many distinct yet potentially valid conformations). The conformation common to all members of the set is called the pharmacophore and is responsible for the drug activity. Having isolated the pharmacophore, the pharmaceutical drug activity can be improved, side effects reduced, etc. An ...
1 Exam 2 CSS/Hort 430/530 2010 1. The concept of “one gene: one
... 29. In a PCR reaction, the highest temperature step (typically ~ 95oC) is necessary for a. DNA replication b. Primer annealing c. Denaturing double stranded DNA 30. Which of the following properties make TAQ polymerase particularly useful for PCR? a. It is very cheap b. It cuts double stranded DNA c ...
... 29. In a PCR reaction, the highest temperature step (typically ~ 95oC) is necessary for a. DNA replication b. Primer annealing c. Denaturing double stranded DNA 30. Which of the following properties make TAQ polymerase particularly useful for PCR? a. It is very cheap b. It cuts double stranded DNA c ...
Investigation of the role of expanded gene families
... In addition to the InterPro data, complete protein sequences from each individual organism were clustered into related sets by running BlastClust at different percentage identities over varying lengths of the sequences. The proteins common to both InterPro duplicate gene clusters and sequence based ...
... In addition to the InterPro data, complete protein sequences from each individual organism were clustered into related sets by running BlastClust at different percentage identities over varying lengths of the sequences. The proteins common to both InterPro duplicate gene clusters and sequence based ...
File
... The gene structure contains regulatory regions, transcribed regions, and other functional sequence regions A regulatory region called promoter usually present at the beginning of the gene which can initiate the starting of gene expression (mRNA transcription) from 5' to 3' direction.. Some genes hav ...
... The gene structure contains regulatory regions, transcribed regions, and other functional sequence regions A regulatory region called promoter usually present at the beginning of the gene which can initiate the starting of gene expression (mRNA transcription) from 5' to 3' direction.. Some genes hav ...
Cloning and PCR File
... Gene cloning is the process of isolating and making copies of a gene. This is useful for many purposes. For example, gene cloning might be used to isolate and make copies of a normal gene for gene therapy. Gene cloning involves four steps: isolation, ligation, transformation, and selection. You can ...
... Gene cloning is the process of isolating and making copies of a gene. This is useful for many purposes. For example, gene cloning might be used to isolate and make copies of a normal gene for gene therapy. Gene cloning involves four steps: isolation, ligation, transformation, and selection. You can ...
Aliens? - Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health
... • Discovered in a C. elegans screen • Alter gene expression at the posttranscriptional level (precise mechanism unknown) • Tend to be high-level regulators (>100 targets each) • Percentage of human genes under miRNA control is unknown but possibly 20-30% • Often are developmental or cell state ...
... • Discovered in a C. elegans screen • Alter gene expression at the posttranscriptional level (precise mechanism unknown) • Tend to be high-level regulators (>100 targets each) • Percentage of human genes under miRNA control is unknown but possibly 20-30% • Often are developmental or cell state ...
Chapter 13: Genetic Engineering
... Combining DNA from two different sources by cutting with the same restriction enzymes creates DNA that has ...
... Combining DNA from two different sources by cutting with the same restriction enzymes creates DNA that has ...
DNA Structure and Replication
... Directions: Below are check lists of things you should know and things you should be able to do by the end of the unit. Use this tool to help you prepare for the unit assessment. By the conclusion of this unit, you should know the following: 1. Watson, Crick, Franklin and Wilkins are generally cred ...
... Directions: Below are check lists of things you should know and things you should be able to do by the end of the unit. Use this tool to help you prepare for the unit assessment. By the conclusion of this unit, you should know the following: 1. Watson, Crick, Franklin and Wilkins are generally cred ...
Document
... Departures from strand symmetry or Chargaff asymmetries can be expressed by differences: (A-T)/(A+T) and (C-G)/(C+G) for each strand Strand symmetry originates from identical mutation/substitution processes affecting each strand ...
... Departures from strand symmetry or Chargaff asymmetries can be expressed by differences: (A-T)/(A+T) and (C-G)/(C+G) for each strand Strand symmetry originates from identical mutation/substitution processes affecting each strand ...
幻灯片 1 - TUST
... 1. Viruses are simple, acellular entities consisting of one or more molecules of either DNA or RNA enclosed in a coat of protein (and sometimes, in addition, substances such as lipids and carbohydrates). They can reproduce only within living cells and are obligately intracellular parasites. 2. Virus ...
... 1. Viruses are simple, acellular entities consisting of one or more molecules of either DNA or RNA enclosed in a coat of protein (and sometimes, in addition, substances such as lipids and carbohydrates). They can reproduce only within living cells and are obligately intracellular parasites. 2. Virus ...
“Cowboy Glossary” of Genetic Terms
... Low Density Genomic Profile – a DNA test that uses 30,000 SNP markers; these 30K markers are then imputed up to 50K for GE-EPDs High Density Genomic Profile – a DNA test that uses 150,000 SNP markers, providing more genomic information; GE-EPDs are created by extracting 50K of these markers Genetic ...
... Low Density Genomic Profile – a DNA test that uses 30,000 SNP markers; these 30K markers are then imputed up to 50K for GE-EPDs High Density Genomic Profile – a DNA test that uses 150,000 SNP markers, providing more genomic information; GE-EPDs are created by extracting 50K of these markers Genetic ...
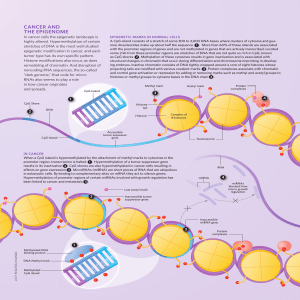
CaNCer aND THe ePIGeNOMe
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
Mutational Genetic Load: Can the Human
... Because genomes are products of natural processes rather than “intelligent design,” all genomes should contain functional and nonfunctional parts. The nonfunctional fraction of the genome consists mostly of junk DNA, which is useless as well as harmless and on which selection does not operate. In th ...
... Because genomes are products of natural processes rather than “intelligent design,” all genomes should contain functional and nonfunctional parts. The nonfunctional fraction of the genome consists mostly of junk DNA, which is useless as well as harmless and on which selection does not operate. In th ...
Homework Assignment #7
... 1c) What are HbA and HbS (note the italics!) and how do they differ from each other? Focus on the molecules! (10 Points) ...
... 1c) What are HbA and HbS (note the italics!) and how do they differ from each other? Focus on the molecules! (10 Points) ...
Slide 1
... base substitution that removes a MstII site. – Different banding pattern on gel indicates whether fetus will be a carrier or have disease (homozygous) ...
... base substitution that removes a MstII site. – Different banding pattern on gel indicates whether fetus will be a carrier or have disease (homozygous) ...
nitrogen bases
... 1. Label boxes a-d using the terms: Nitrogen base, Nucleotide, Deoxyribose (sugar), and Phosphate. Use your DNA Guided Notes. c. Deoxyribose (Sugar) a. Nitrogen base ...
... 1. Label boxes a-d using the terms: Nitrogen base, Nucleotide, Deoxyribose (sugar), and Phosphate. Use your DNA Guided Notes. c. Deoxyribose (Sugar) a. Nitrogen base ...
ThreeAimsIn3Days 50.5 KB - d
... -Cladistics (the building of evolutionary trees) can be done with shapes/body forms OR molecular similarities OR both. Both are best, and both should agree. -Analysis of skull data shows that we come from bipedal organisms. That is, after the monkeys left the trees, lost the tails, and became apes l ...
... -Cladistics (the building of evolutionary trees) can be done with shapes/body forms OR molecular similarities OR both. Both are best, and both should agree. -Analysis of skull data shows that we come from bipedal organisms. That is, after the monkeys left the trees, lost the tails, and became apes l ...