David A. Banks David A. Banks DNA Rockstar: Using Interactive
... animated illustration in the background); 5) reformulating pre-DNA replication/transcription/translation gameplay such that it utilizes open-ended, inquiry-based pedagogies. It is this final improvement that is most crucial. As James Paul Gee has said, “good games give information ‘on demand’ and ‘j ...
... animated illustration in the background); 5) reformulating pre-DNA replication/transcription/translation gameplay such that it utilizes open-ended, inquiry-based pedagogies. It is this final improvement that is most crucial. As James Paul Gee has said, “good games give information ‘on demand’ and ‘j ...
BI 200 - Exam #4
... be more than one correct answer, and you may use an answer more than once, but put only one answer for each. ...
... be more than one correct answer, and you may use an answer more than once, but put only one answer for each. ...
Power Point Notes
... Each old strand serves as the template for complementary new strand Figure 13.10 Page 223 ...
... Each old strand serves as the template for complementary new strand Figure 13.10 Page 223 ...
CH 11 Study Guide: DNA, RNA, and Proteins
... mRNA: carries the DNA message from the nucleus to the cytoplasm rRNA: combines with proteins to form the ribosome tRNA: carries amino acids to the ribosome so that proteins can be made 5. Who discovered the structure of DNA? Watson & Crick 6. IF a sequence of codons on a DNA strand is AAC TAG GGT, w ...
... mRNA: carries the DNA message from the nucleus to the cytoplasm rRNA: combines with proteins to form the ribosome tRNA: carries amino acids to the ribosome so that proteins can be made 5. Who discovered the structure of DNA? Watson & Crick 6. IF a sequence of codons on a DNA strand is AAC TAG GGT, w ...
$doc.title
... Cul]va]on : No degrada]ve-‐lindane bacteria. PCR : No Amplifica]on Metagenomic DNA analysis: Gene]c and phenotypic screening : Nega]ve ...
... Cul]va]on : No degrada]ve-‐lindane bacteria. PCR : No Amplifica]on Metagenomic DNA analysis: Gene]c and phenotypic screening : Nega]ve ...
Summary - Ruhr-Universität Bochum
... DNA, RNA-free calf thymus DNA was treated with N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea, using either single stranded or double stranded DNA. Unfortunately, no specific binding to the anti DNA adduct antibodies was observed with any kind of DNA-fragments. In the second approach, the DNA-analogue – peptid nucleic acids ...
... DNA, RNA-free calf thymus DNA was treated with N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea, using either single stranded or double stranded DNA. Unfortunately, no specific binding to the anti DNA adduct antibodies was observed with any kind of DNA-fragments. In the second approach, the DNA-analogue – peptid nucleic acids ...
Unit 4 Review KEY File
... 5. What type of mutation does this represent?frameshift 6. What is the result of such a mutation?All amino acids after the deletion or insertion will be different 7. DNA and RNA are both what type of biomolecule? Nucleic Acids ...
... 5. What type of mutation does this represent?frameshift 6. What is the result of such a mutation?All amino acids after the deletion or insertion will be different 7. DNA and RNA are both what type of biomolecule? Nucleic Acids ...
P.324doc
... of proteins, because of the redundant nature of the genetic code. Introns are regions are cut out of the mRNA in the process of transcription, thus preventing the mutation from manifesting itself in the organism. Silent mutations that do occur in coding regions, exons, do not affect the translation ...
... of proteins, because of the redundant nature of the genetic code. Introns are regions are cut out of the mRNA in the process of transcription, thus preventing the mutation from manifesting itself in the organism. Silent mutations that do occur in coding regions, exons, do not affect the translation ...
DNA Discovery, Structure, Replication, Transcription, Translation
... 14.Explain the replication of DNA. Include the role of DNA polymerase, replication bubbles, and the replication fork. ...
... 14.Explain the replication of DNA. Include the role of DNA polymerase, replication bubbles, and the replication fork. ...
B2 Topic 1 Can Do Sheet
... 1.20 Recall that stem cells in the embryo can differentiate into all other types of cells, but that cells lose this ability as the animal matures 1.21 Demonstrate an understanding of the advantages, disadvantages and risks arising from adult and embryonic stem cell research 1.22 Describe how the ord ...
... 1.20 Recall that stem cells in the embryo can differentiate into all other types of cells, but that cells lose this ability as the animal matures 1.21 Demonstrate an understanding of the advantages, disadvantages and risks arising from adult and embryonic stem cell research 1.22 Describe how the ord ...
Genetics Review
... • Translation: In the cytoplasm, on the ribosome, the mRNA codon matches tRNA anticodon to bring the proper amino acid in for bonding. Once the whole mRNA is read by the ribosome, the stop codon ends the production of the peptide chain; the protein is complete! ...
... • Translation: In the cytoplasm, on the ribosome, the mRNA codon matches tRNA anticodon to bring the proper amino acid in for bonding. Once the whole mRNA is read by the ribosome, the stop codon ends the production of the peptide chain; the protein is complete! ...
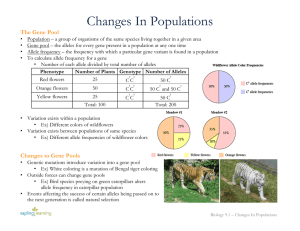
Changes In Populations
... Changes to Gene Pools • Genetic mutations introduce variation into a gene pool • Ex) White coloring is a mutation of Bengal tiger coloring • Outside forces can change gene pools • Ex) Bird species preying on green caterpillars alters allele frequency in caterpillar population • Events affecting the ...
... Changes to Gene Pools • Genetic mutations introduce variation into a gene pool • Ex) White coloring is a mutation of Bengal tiger coloring • Outside forces can change gene pools • Ex) Bird species preying on green caterpillars alters allele frequency in caterpillar population • Events affecting the ...
made from DNA aptamers核酸适配体, which are short
... when encountering diseased cells,” comments Jorgen Kjems, a DNA origami expert at the University of Aarhus, in Denmark. “This will inevitably lower the toxicity and thereby the side effects of therapeutic drugs carried by the device. The next step will be to harness DNA nanorobots to withstand the h ...
... when encountering diseased cells,” comments Jorgen Kjems, a DNA origami expert at the University of Aarhus, in Denmark. “This will inevitably lower the toxicity and thereby the side effects of therapeutic drugs carried by the device. The next step will be to harness DNA nanorobots to withstand the h ...
The MOLECULES of LIFE
... stable than the natural DNA and RNA double helices with the same sequence of bases. Explain why such helices can form, and why they can be more stable. b. Given the increased stability of such modified nucleotides, why has nature not used them to build the genetic material? Provide two different re ...
... stable than the natural DNA and RNA double helices with the same sequence of bases. Explain why such helices can form, and why they can be more stable. b. Given the increased stability of such modified nucleotides, why has nature not used them to build the genetic material? Provide two different re ...
The nucleotide sequence of the tnpA gene completes the sequence
... functions sufficiently related to those of Tn501 that complementation of mutants in the transposition genes can occur (4,5), and models for the evolutionary relationship between these transposons have been proposed (6-9). Several other transposons have been identified which appear to be closely rela ...
... functions sufficiently related to those of Tn501 that complementation of mutants in the transposition genes can occur (4,5), and models for the evolutionary relationship between these transposons have been proposed (6-9). Several other transposons have been identified which appear to be closely rela ...
Lecture 3: More Transmission Genetics
... The diseased individuals are present in every generation (indicates a dominant disease) and males and females are both about equally affected (indicates autosomal inheritance) ...
... The diseased individuals are present in every generation (indicates a dominant disease) and males and females are both about equally affected (indicates autosomal inheritance) ...
genetics
... inheritance of each trait is determined by "units" or "factors" (now called genes ) that are passed on to descendents unchanged an individual inherits one such unit from each parent for each trait that a trait may not show up in an individual but can still be passed on to the next generation. ...
... inheritance of each trait is determined by "units" or "factors" (now called genes ) that are passed on to descendents unchanged an individual inherits one such unit from each parent for each trait that a trait may not show up in an individual but can still be passed on to the next generation. ...
Gene Technology Powerpoint
... While DNA in all humans is similar there are differences DNA fingerprinting can be used to identify a child’s parents. In this example (next page) , a family consists of a mom and dad, two daughters and two sons. The parents have one daughter and one son together, one daughter is from the mother’s p ...
... While DNA in all humans is similar there are differences DNA fingerprinting can be used to identify a child’s parents. In this example (next page) , a family consists of a mom and dad, two daughters and two sons. The parents have one daughter and one son together, one daughter is from the mother’s p ...
1 - gcisd
... a. Find the definition of both and then explain how they are related to each other 10. KNOW ABOUT MRNA’S ROLE IN REPRODUCTION a. Where is it generated or made? The nucleus b. Where does it go after it is made? The cytoplasm c. What is its main job? To make a copy of DNA’s code to build proteins d. H ...
... a. Find the definition of both and then explain how they are related to each other 10. KNOW ABOUT MRNA’S ROLE IN REPRODUCTION a. Where is it generated or made? The nucleus b. Where does it go after it is made? The cytoplasm c. What is its main job? To make a copy of DNA’s code to build proteins d. H ...
Genetics - true or false
... research could be web-based or using the print-outs of the Science Ideas and Concepts articles DNA, chromosomes and gene expression, Genotype and phenotype, Meiosis, inheritance and variation and Role of proteins in the body. © 2007–2011 The University of Waikato ...
... research could be web-based or using the print-outs of the Science Ideas and Concepts articles DNA, chromosomes and gene expression, Genotype and phenotype, Meiosis, inheritance and variation and Role of proteins in the body. © 2007–2011 The University of Waikato ...
Mutation - NIU Department of Biological Sciences
... Eukaryotes often contain very short (200-500 bp) elements that contain the ends of a longer DNA transposon and miscellaneous junk inside. They move to new locations using the transposase enzyme from a full length element. Most bacterial TEs are DNA only. In eukaryotes, DNA transposable elements occu ...
... Eukaryotes often contain very short (200-500 bp) elements that contain the ends of a longer DNA transposon and miscellaneous junk inside. They move to new locations using the transposase enzyme from a full length element. Most bacterial TEs are DNA only. In eukaryotes, DNA transposable elements occu ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... • Some RNA molecules may be cut and spliced in different ways in different tissues makes it possible for a single gene to produce several different forms of RNA. • Introns and exons may also play a role in evolution. makes it possible for very small changes in DNA sequences to have dramatic eff ...
... • Some RNA molecules may be cut and spliced in different ways in different tissues makes it possible for a single gene to produce several different forms of RNA. • Introns and exons may also play a role in evolution. makes it possible for very small changes in DNA sequences to have dramatic eff ...
Protein Synthesis PowerPoint
... Structure/Size: single strand, shorter than DNA Bases: A, U, C, G Function: read instructions and build proteins ...
... Structure/Size: single strand, shorter than DNA Bases: A, U, C, G Function: read instructions and build proteins ...
GENETIC TRANSFER AND RECOMBINATION (Chapter 8):
... Vertical gene transfer: between parent and offspring Horizontal gene transfer: between other organisms in the same generation Three types: 1. Transformation 2. Conjugation 3. Transduction All types: Involve unidirectional transfer of information (donor to recipient—recipient called recombinant cell) ...
... Vertical gene transfer: between parent and offspring Horizontal gene transfer: between other organisms in the same generation Three types: 1. Transformation 2. Conjugation 3. Transduction All types: Involve unidirectional transfer of information (donor to recipient—recipient called recombinant cell) ...
BIO520 Bioinformatics 2005 EXAM2 You may use any books, notes
... strand. Indicate which gene is least likely to be a correct prediction. Gene 1: 11 exons, plus strand. Gene 2: 5 exons, minus strand, least likely to be correct. Gene 3: 1 exon (partial gene) The polyA site and Promoter are not exons. The gene on the minus strand (12-22kb) has poor Genscan probabili ...
... strand. Indicate which gene is least likely to be a correct prediction. Gene 1: 11 exons, plus strand. Gene 2: 5 exons, minus strand, least likely to be correct. Gene 3: 1 exon (partial gene) The polyA site and Promoter are not exons. The gene on the minus strand (12-22kb) has poor Genscan probabili ...