Biol-1406_Ch10Notes.ppt
... • 10.2 How Is Information in a Gene Transcribed into RNA? • 10.3 How Is the Base Sequence of a Messenger RNA Molecule Translated into Protein? • 10.4 How Do Mutations in DNA Affect the Function of Genes? • 10.5 How Are Genes Regulated? ...
... • 10.2 How Is Information in a Gene Transcribed into RNA? • 10.3 How Is the Base Sequence of a Messenger RNA Molecule Translated into Protein? • 10.4 How Do Mutations in DNA Affect the Function of Genes? • 10.5 How Are Genes Regulated? ...
Study Guide for DNA Structure and Replication
... 1.2.6 Understand cellular structures, their functions, and how specific genes regulate these functions. Describe how DNA molecules are long chains linking four kinds of smaller molecules, whose sequence encodes genetic information. To be successful a student should be able to check off the followi ...
... 1.2.6 Understand cellular structures, their functions, and how specific genes regulate these functions. Describe how DNA molecules are long chains linking four kinds of smaller molecules, whose sequence encodes genetic information. To be successful a student should be able to check off the followi ...
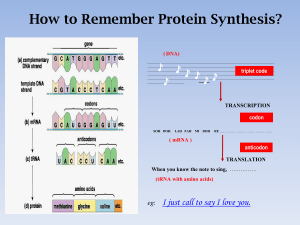
How to remember Protein Synthesis
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
Avian Systematics
... chromosomes. Again, should be most similar between closely related species. • Ectoparasites = external parasites are often specific for a particular species of bird. Closely related birds should have similar ectoparasites since they evolved along with the birds. • TAKE HOME = systematics is not a st ...
... chromosomes. Again, should be most similar between closely related species. • Ectoparasites = external parasites are often specific for a particular species of bird. Closely related birds should have similar ectoparasites since they evolved along with the birds. • TAKE HOME = systematics is not a st ...
How Can A Mutation in DNA Affect an Organism
... 4. How many bases are different in sickle hemoglobin DNA compared with normal hemoglobin DNA? ________________ 5. How many genes are needed to code one amino acid into a protein such as hemoglobin? ____________ 6. Define the word mutation a. by using the word "gene" _________________________________ ...
... 4. How many bases are different in sickle hemoglobin DNA compared with normal hemoglobin DNA? ________________ 5. How many genes are needed to code one amino acid into a protein such as hemoglobin? ____________ 6. Define the word mutation a. by using the word "gene" _________________________________ ...
Microarrays - Computational Bioscience Program
... Gene levels at the borderline of differential expression – Their measurability reduce by random error For highly differentially expressed genes, having sufficient replicates would serve as validation. ...
... Gene levels at the borderline of differential expression – Their measurability reduce by random error For highly differentially expressed genes, having sufficient replicates would serve as validation. ...
6 genetics no test
... – Favorable genes from one organism are recombined with other pieces of DNA in another organism – The genetic makeup of various plant & animals is changed! – Examples: ...
... – Favorable genes from one organism are recombined with other pieces of DNA in another organism – The genetic makeup of various plant & animals is changed! – Examples: ...
A) Describe and/or predict observed patterns of
... 12. A scientist uses enzymes to splice genetic DNA into a plasmid, and then inserts the plasmid into a cell. Which of the following is most likely an application of this process? A. producing an exact genetic clone of prized racehorse B. producing a vaccine against the human papillomavirus C. determ ...
... 12. A scientist uses enzymes to splice genetic DNA into a plasmid, and then inserts the plasmid into a cell. Which of the following is most likely an application of this process? A. producing an exact genetic clone of prized racehorse B. producing a vaccine against the human papillomavirus C. determ ...
DNA - Wsfcs
... Adenine pairs with Thymine Guanine pairs with Cytosine The nitrogen bases are held together by hydrogen bonds. Due to the base pairing the two strands are complementary to each other ...
... Adenine pairs with Thymine Guanine pairs with Cytosine The nitrogen bases are held together by hydrogen bonds. Due to the base pairing the two strands are complementary to each other ...
DNA Notes.pps
... Replication Quiz 1. Why is replication necessary? So both new cells will have the correct DNA 2. When does replication occur? During interphase (S phase). 3. Describe how replication works. Enzymes unzip DNA and complementary nucleotides join each original strand. 4. Use the complementary rule to c ...
... Replication Quiz 1. Why is replication necessary? So both new cells will have the correct DNA 2. When does replication occur? During interphase (S phase). 3. Describe how replication works. Enzymes unzip DNA and complementary nucleotides join each original strand. 4. Use the complementary rule to c ...
F plasmid
... Host proteins are involved in antitermination. N causes antitermination at both r-dependent and r-independent terminators by restricting the pause time at the terminator. ...
... Host proteins are involved in antitermination. N causes antitermination at both r-dependent and r-independent terminators by restricting the pause time at the terminator. ...
Functions of Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids
... • One mRNA may code for more than one protein • Together with transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers genetic information from DNA to proteins ...
... • One mRNA may code for more than one protein • Together with transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers genetic information from DNA to proteins ...
DNA STRUCTURE AND REPLICATION Nucleotides: 1. 5 carbon
... determine where the location of the 35S in the mixture. Where was the 35S located in the centrifuged mixture?________________ What conclusion did they reach based on these results? ___________________________________________________________ ...
... determine where the location of the 35S in the mixture. Where was the 35S located in the centrifuged mixture?________________ What conclusion did they reach based on these results? ___________________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 2 DNA to end Short Answer
... acceptable. Do not penalize if the second strand is not antiparallel and the bonding is therefore incorrect on it. (complementary) bases labelled with at least one of each of A, G, T and C correctly linked to C1; hydrogen bonds between correct complementary bases;{ Bond numbers not required. correct ...
... acceptable. Do not penalize if the second strand is not antiparallel and the bonding is therefore incorrect on it. (complementary) bases labelled with at least one of each of A, G, T and C correctly linked to C1; hydrogen bonds between correct complementary bases;{ Bond numbers not required. correct ...
DNA - The Double Helix
... Every cell in your body has the same "blueprint" or the same DNA. Like the blueprints of a house tell the builders how to construct a house, the DNA "blueprint" tells the cell how to build the organism. Yet, how can a heart be so different from a brain if all the cells contain the same instructions? ...
... Every cell in your body has the same "blueprint" or the same DNA. Like the blueprints of a house tell the builders how to construct a house, the DNA "blueprint" tells the cell how to build the organism. Yet, how can a heart be so different from a brain if all the cells contain the same instructions? ...
Unit 4 genetics part 1
... Ex in a study with type 2 diabetes take 1000 with T2D and 1000 w/o T2 d… do the T2D persons have a unique SNP in common? Recent findings are: T2D: 18 QTLs ( meaning 18 similar trait genes) T1D: 32 QLTs ( these genes found to affect the hypothalamus) Crohns disease: 32 QTL ( one gene associated with ...
... Ex in a study with type 2 diabetes take 1000 with T2D and 1000 w/o T2 d… do the T2D persons have a unique SNP in common? Recent findings are: T2D: 18 QTLs ( meaning 18 similar trait genes) T1D: 32 QLTs ( these genes found to affect the hypothalamus) Crohns disease: 32 QTL ( one gene associated with ...
2017 Wisconsin Livestock Identification Consortium Wisconsin State
... Livestock must be identified in the exhibitor’s name or in the immediate family member names. If animals are identified in the immediate family name only one form needs to be submitted along with the correct fees, however all siblings’ names MUST appear on the top of the form. Cousins are not consid ...
... Livestock must be identified in the exhibitor’s name or in the immediate family member names. If animals are identified in the immediate family name only one form needs to be submitted along with the correct fees, however all siblings’ names MUST appear on the top of the form. Cousins are not consid ...
DNA & Protein Synthesis
... • Proceeds in fragments in the other direction (called the lagging strand) in the following way • RNA primer is attached to a segment of the strand by the enzyme primase. ...
... • Proceeds in fragments in the other direction (called the lagging strand) in the following way • RNA primer is attached to a segment of the strand by the enzyme primase. ...
Ch. 12 DNA
... ~ nucleotides added according to the base-pairing rules ~ this forms 2 new DNA strands! ...
... ~ nucleotides added according to the base-pairing rules ~ this forms 2 new DNA strands! ...
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
... both protein and DNA. • If the genetic material could be tagged from the virus and then found later in the host cell, Hershey and Chase could tell if what the virus injected was protein or DNA. ...
... both protein and DNA. • If the genetic material could be tagged from the virus and then found later in the host cell, Hershey and Chase could tell if what the virus injected was protein or DNA. ...
31_operons
... – Prokaryotes• Genes transpose to/from cell’s chromosome, plasmid, or a phage chromosome. ...
... – Prokaryotes• Genes transpose to/from cell’s chromosome, plasmid, or a phage chromosome. ...
DNA Chip Analysis and Bioinformatics
... Paste the probe DNA sequence into the query box, scroll down and select “show results in a new window” and click “ BLAST”. Leave all other parameters as they are. 6. Wait until the page loads (this could take a minute or so - be patient). 7. Scroll down to “Sequences producing significant alignments ...
... Paste the probe DNA sequence into the query box, scroll down and select “show results in a new window” and click “ BLAST”. Leave all other parameters as they are. 6. Wait until the page loads (this could take a minute or so - be patient). 7. Scroll down to “Sequences producing significant alignments ...
Strawberry DNA Extraction Lab
... 9) Add 5pipette-fuls of cold Rubbing Alcohol to the test tube. BE CAREFUL: Make sure to add it down the side of the tube. DO NOT MIX! 10) Let this sit for a few minutes. You should see DNA (looks like snot) rise out of the solution. ...
... 9) Add 5pipette-fuls of cold Rubbing Alcohol to the test tube. BE CAREFUL: Make sure to add it down the side of the tube. DO NOT MIX! 10) Let this sit for a few minutes. You should see DNA (looks like snot) rise out of the solution. ...
Darwin`s finches - University of Birmingham
... Application of sequence analysis to Darwin’s finches? Using sequence data from a couple of proteins, one can propose the evolutionary process that led to today’s surviving species. One can also suggest the timescales over which these processes occurred. ...
... Application of sequence analysis to Darwin’s finches? Using sequence data from a couple of proteins, one can propose the evolutionary process that led to today’s surviving species. One can also suggest the timescales over which these processes occurred. ...