Loci sarA and/or agr by the Genes Regulated Staphylococcus
... mutant cells during various phases of growth (early-, mid-, and late-log and stationary phases). agr regulation by SarA. To validate the transcription profiling methodology used, we first investigated whether the agr locus transcripts, RNAII and RNAIII, produced expression patterns mimicking previou ...
... mutant cells during various phases of growth (early-, mid-, and late-log and stationary phases). agr regulation by SarA. To validate the transcription profiling methodology used, we first investigated whether the agr locus transcripts, RNAII and RNAIII, produced expression patterns mimicking previou ...
Parental Legacy Determines Methylation and Expression of an
... intron. On Northern analysis only a single transcript of 2.3 kb is detected (data not shown), suggesting that transcription initiation starts within the immunoglobulin-derived DNA segment. But transcription at a cryptic promoter in the first intron of c-myc might be indistinguishable from transcript ...
... intron. On Northern analysis only a single transcript of 2.3 kb is detected (data not shown), suggesting that transcription initiation starts within the immunoglobulin-derived DNA segment. But transcription at a cryptic promoter in the first intron of c-myc might be indistinguishable from transcript ...
Cloning and expression analysis of follicle
... (7TM) helices and a carboxy-terminal intracellular tail (Hsu et al. 2000). The cDNA and sequences of the GTHs receptor have been determined for a number of fish species, such as Oncorhynchus masou rhodurus (Oba et al. 1999b) and later from many other teleost species such as Clarias gariepinus (Boger ...
... (7TM) helices and a carboxy-terminal intracellular tail (Hsu et al. 2000). The cDNA and sequences of the GTHs receptor have been determined for a number of fish species, such as Oncorhynchus masou rhodurus (Oba et al. 1999b) and later from many other teleost species such as Clarias gariepinus (Boger ...
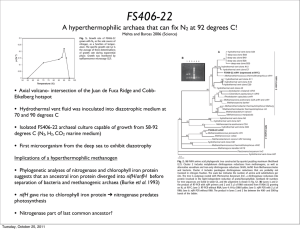
FS406-22
... and 95°C (Fig. 1). Agitation of the culture was nec(12). Cluster 2 includes molybdenum dinitrogenase reductases from methanogens, as well as essary for growth on N2, and clusters of two or more alternative vanadium and iron-only dinitrogenase reductases (VnfH, AnfH) from Methanosarcinales cocci were ...
... and 95°C (Fig. 1). Agitation of the culture was nec(12). Cluster 2 includes molybdenum dinitrogenase reductases from methanogens, as well as essary for growth on N2, and clusters of two or more alternative vanadium and iron-only dinitrogenase reductases (VnfH, AnfH) from Methanosarcinales cocci were ...
Motif Mining from Gene Regulatory Networks
... with distinct sets of nodes is at least U = 4. – The number of appearances in the real network is significantly larger than in the randomized networks: Nreal – Nrand > 0.1Nrand (Why??). ...
... with distinct sets of nodes is at least U = 4. – The number of appearances in the real network is significantly larger than in the randomized networks: Nreal – Nrand > 0.1Nrand (Why??). ...
The importance of alternative splicing in the drug discovery process
... Antisense oligonucleotides can be designed to inhibit study the function of the gene. However, it turned out that abnormal, disease-causing splicing. Such an approach was not all the gene is shut down and a residual binding activused to correct an aberrant splicing of the cystic fibrosis ity remains ...
... Antisense oligonucleotides can be designed to inhibit study the function of the gene. However, it turned out that abnormal, disease-causing splicing. Such an approach was not all the gene is shut down and a residual binding activused to correct an aberrant splicing of the cystic fibrosis ity remains ...
Higher order structural effects stabilizing the
... The first triplet is a CGC tWW/tSW motif, where an additional cytosine, uses its ‘Watson–Crick’ edge to pair with the ‘Sugar’ edge of the guanine and the N4 atom of the cytosine in the G:C pair. We found nine instances of this motif, all in tRNA molecules. The second triplet is a CGU tWW/Intermediate ...
... The first triplet is a CGC tWW/tSW motif, where an additional cytosine, uses its ‘Watson–Crick’ edge to pair with the ‘Sugar’ edge of the guanine and the N4 atom of the cytosine in the G:C pair. We found nine instances of this motif, all in tRNA molecules. The second triplet is a CGU tWW/Intermediate ...
1030examII
... May be caused by an addition of any number of nucleotides (bases) not in multiples of three May be caused by a deletion of any number of nucleotides (bases) not in multiples of three Disrupts the reading frame of a gene Usually destroys a protein's ability to function All of the above are co ...
... May be caused by an addition of any number of nucleotides (bases) not in multiples of three May be caused by a deletion of any number of nucleotides (bases) not in multiples of three Disrupts the reading frame of a gene Usually destroys a protein's ability to function All of the above are co ...
The microRNAs of Caenorhabditis elegans
... lin-4 was the natural candidate to coordinate the temporally graded expression of LIN-14. Genetic epistasis analysis showed that a wild type copy of lin-14 was required to mediate the lin-4 heterochronic phenotype, indicating lin-4 lay upstream of lin-14 [27]. Moreover, the temporally graded protein ...
... lin-4 was the natural candidate to coordinate the temporally graded expression of LIN-14. Genetic epistasis analysis showed that a wild type copy of lin-14 was required to mediate the lin-4 heterochronic phenotype, indicating lin-4 lay upstream of lin-14 [27]. Moreover, the temporally graded protein ...
The murine homologue of HIRA, a DiGeorge
... acids 510 and 607 or 608. Our Hira sequence is 99% identical to the recently reported mouse Hira sequence (35) and 100% identical to the mouse Tuple1 cDNA clone MF2 (26). In addition to homology with yeast Hir1p and Hir2p, BlastP and BEAUTY database searches with our mouse Hira sequence reveal high ...
... acids 510 and 607 or 608. Our Hira sequence is 99% identical to the recently reported mouse Hira sequence (35) and 100% identical to the mouse Tuple1 cDNA clone MF2 (26). In addition to homology with yeast Hir1p and Hir2p, BlastP and BEAUTY database searches with our mouse Hira sequence reveal high ...
how to analyze a splicing mutation - Stamm revision
... 3’ splice sites are responsible for approx 15% of the genetic diseases that are caused by point mutations [1]. Furthermore, for some genes this is much higher for example in NF1 and ATM, it has been shown that mutations that cause splicing alterations occur in approximately 50% of the affected patie ...
... 3’ splice sites are responsible for approx 15% of the genetic diseases that are caused by point mutations [1]. Furthermore, for some genes this is much higher for example in NF1 and ATM, it has been shown that mutations that cause splicing alterations occur in approximately 50% of the affected patie ...
A mixed group ll/group III twintron in the Euglena
... and wx gene. Introns are also known to be mobile genetic elements (7). Some group I introns, the best known being the co+ intron, are transmitted from intron+ alleles to intron" alleles. Intron insertion occurs by DNA site-specific recombination catalyzed by enzyme(s) encoded within the intron. Ther ...
... and wx gene. Introns are also known to be mobile genetic elements (7). Some group I introns, the best known being the co+ intron, are transmitted from intron+ alleles to intron" alleles. Intron insertion occurs by DNA site-specific recombination catalyzed by enzyme(s) encoded within the intron. Ther ...
In-class assignment: Fukuda et al. (2016) paper
... 7. Xist and Tsix have antagonistic functions.Are the results in 5a consistent with this? Why or why not? Explain. The results in Fig 5a indicate that Xist and Tsix are regulated similarly by Oct4. When Oct4 is knocked out, both transcript levels drop, suggesting that Oct4 is a positive regulator of ...
... 7. Xist and Tsix have antagonistic functions.Are the results in 5a consistent with this? Why or why not? Explain. The results in Fig 5a indicate that Xist and Tsix are regulated similarly by Oct4. When Oct4 is knocked out, both transcript levels drop, suggesting that Oct4 is a positive regulator of ...
Characterization of Chicken MMP13 Expression and Genetic Effect
... follicles of sexually immature chicken ovaries, in the theca cell layers of all sized follicles of sexually mature chicken ovaries. Furthermore, we identified a positive element (positions –1863 to –1036) controlling chicken MMP13 transcription, and, in this region, six single nucleotide polymorphism ...
... follicles of sexually immature chicken ovaries, in the theca cell layers of all sized follicles of sexually mature chicken ovaries. Furthermore, we identified a positive element (positions –1863 to –1036) controlling chicken MMP13 transcription, and, in this region, six single nucleotide polymorphism ...
Module 7 – Microbial Molecular Biology and Genetics
... DNA is a long polymer made from repeating units called nucleotides. As first discovered by James D. Watson and Francis Crick, the structure of DNA of all species comprises two helical chains each coiled round the same axis, and each with a pitch of 34 Ångströms (3.4 nanometres) and a radius of 10 Ån ...
... DNA is a long polymer made from repeating units called nucleotides. As first discovered by James D. Watson and Francis Crick, the structure of DNA of all species comprises two helical chains each coiled round the same axis, and each with a pitch of 34 Ångströms (3.4 nanometres) and a radius of 10 Ån ...
Fig 16.12a - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Three types of RNA polymerases in eukaryotes • RNA pol I – transcribes rRNA genes • RNA pol II – transcribes all protein-coding genes (mRNAs) and micro-RNAs • RNA pol III – transcribes tRNA genes and some small regulatory RNAs ...
... Three types of RNA polymerases in eukaryotes • RNA pol I – transcribes rRNA genes • RNA pol II – transcribes all protein-coding genes (mRNAs) and micro-RNAs • RNA pol III – transcribes tRNA genes and some small regulatory RNAs ...
The biased nucleotide composition of the HIV genome: a constant
... (LTRs) are available for these groups (Table 1). As the LTR is relatively A-poor [5], calculations based upon the coding regions only will result in higher A-levels. Interestingly, HIV-1 group M subtypes A, B, C and D have significantly different nucleotide compositions concerning the A- and G-perce ...
... (LTRs) are available for these groups (Table 1). As the LTR is relatively A-poor [5], calculations based upon the coding regions only will result in higher A-levels. Interestingly, HIV-1 group M subtypes A, B, C and D have significantly different nucleotide compositions concerning the A- and G-perce ...
An accessible database for mouse and human whole transcriptome
... between exons 2 and 3 is amplified (intron 4800 bp), whereas between 3 and 4, it is not. (B) View from the UCSC genome browser track ...
... between exons 2 and 3 is amplified (intron 4800 bp), whereas between 3 and 4, it is not. (B) View from the UCSC genome browser track ...
Amino acid specificity in translation
... were deliberately mutated such that they were aminoacylated by a different aaRS, and the resulting ‘identityswapped’ tRNAs were shown to insert the new amino acid into protein [7,8]. In addition, suppressor tRNAs esterified with O30 different unnatural amino acids have been successfully incorporated ...
... were deliberately mutated such that they were aminoacylated by a different aaRS, and the resulting ‘identityswapped’ tRNAs were shown to insert the new amino acid into protein [7,8]. In addition, suppressor tRNAs esterified with O30 different unnatural amino acids have been successfully incorporated ...
BioBank CDNA - Primerdesign Ltd
... The BioBank a high quality source of cDNA validated for use in real-time PCR experiments. The cDNA is reverse transcribed from high quality DNAse treated RNA from a variety of sources using an optimised blend of Oligo-dT and random nonamer primers. BioBank cDNA is therefore essentially free of genom ...
... The BioBank a high quality source of cDNA validated for use in real-time PCR experiments. The cDNA is reverse transcribed from high quality DNAse treated RNA from a variety of sources using an optimised blend of Oligo-dT and random nonamer primers. BioBank cDNA is therefore essentially free of genom ...
From bedside to bench: how to analyze a splicing
... genetic diseases that are caused by point mutations [1]. Furthermore, for some genes this is much higher for example in NF1 and ATM, it has been shown that mutations that cause splicing alterations occur in approximately 50% of the affected patients [2,3]. Of these mutations, 24% would have been mis ...
... genetic diseases that are caused by point mutations [1]. Furthermore, for some genes this is much higher for example in NF1 and ATM, it has been shown that mutations that cause splicing alterations occur in approximately 50% of the affected patients [2,3]. Of these mutations, 24% would have been mis ...
Evolutionary dynamics of RNA-like replicator systems
... serves as the precursor of DNA (i.e., DNA monomers are synthesized from RNA monomers [15]); the other functions of RNA include gene regulation, metabolite sensing, and defense against viruses [16]. The above observations can be summarized in two points: the functional equivalence (at least in princi ...
... serves as the precursor of DNA (i.e., DNA monomers are synthesized from RNA monomers [15]); the other functions of RNA include gene regulation, metabolite sensing, and defense against viruses [16]. The above observations can be summarized in two points: the functional equivalence (at least in princi ...
localization of histone gene transcripts in newt lampbrush
... The recent availability of short DNA sequences cloned in plasmid or bacteriophage vectors has made possible the production, by nick-translation, of labelled probes of great sequence purity. Such probes, after denaturation, are ideally suited for hybridizing to RNA transcripts on lampbrush chromosome ...
... The recent availability of short DNA sequences cloned in plasmid or bacteriophage vectors has made possible the production, by nick-translation, of labelled probes of great sequence purity. Such probes, after denaturation, are ideally suited for hybridizing to RNA transcripts on lampbrush chromosome ...
Regulatory Genes Controlling MPG7 Expression
... glutamine or ammonium, are utilized preferentially over amino acids, nucleotides, or more complex nitrogen sources. This ...
... glutamine or ammonium, are utilized preferentially over amino acids, nucleotides, or more complex nitrogen sources. This ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.