Binary fission and viral reproduction
... • This does not lead to an increase in variation. • Asexual reproduction also means that the DNA is not altered (as it is via sexual reproduction). • Offspring are genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell. ...
... • This does not lead to an increase in variation. • Asexual reproduction also means that the DNA is not altered (as it is via sexual reproduction). • Offspring are genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell. ...
oncogenes-and-tumour-suppressor
... MAPKK via phosphorylation on both threonine and tyrosine residues in the TXY sequence The MAPK family consists of four members, ERK1/2 (also known as classical MAPK), JNK/SAPK, p38 and ERK5/BMK1. Each molecule is activated by distinct pathways and transmits signals either independently or co-ord ...
... MAPKK via phosphorylation on both threonine and tyrosine residues in the TXY sequence The MAPK family consists of four members, ERK1/2 (also known as classical MAPK), JNK/SAPK, p38 and ERK5/BMK1. Each molecule is activated by distinct pathways and transmits signals either independently or co-ord ...
tumour Suppressor Genes
... MAPKK via phosphorylation on both threonine and tyrosine residues in the TXY sequence The MAPK family consists of four members, ERK1/2 (also known as classical MAPK), JNK/SAPK, p38 and ERK5/BMK1. Each molecule is activated by distinct pathways and transmits signals either independently or co-ord ...
... MAPKK via phosphorylation on both threonine and tyrosine residues in the TXY sequence The MAPK family consists of four members, ERK1/2 (also known as classical MAPK), JNK/SAPK, p38 and ERK5/BMK1. Each molecule is activated by distinct pathways and transmits signals either independently or co-ord ...
Can You Divide - Cell Reproduction Notes
... – Cell grows and develops – Chromosomes duplicate themselves – Centrioles appear ...
... – Cell grows and develops – Chromosomes duplicate themselves – Centrioles appear ...
SOL-Life Science Review
... Cells and Genetics • Hooke was 1st person to observe cells • Cells – Basic Unit of structure and function of life – Prokaryote: bacteria/no nucleus – Eukaryote: membrane structures; everything but bacteria – Unicellular: only one cell (has structures to carry out functions) – Multicellular: many ce ...
... Cells and Genetics • Hooke was 1st person to observe cells • Cells – Basic Unit of structure and function of life – Prokaryote: bacteria/no nucleus – Eukaryote: membrane structures; everything but bacteria – Unicellular: only one cell (has structures to carry out functions) – Multicellular: many ce ...
Rally Coach for Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
... 2. Explain in one sentence: How did you know which was the prokaryo'c cell? ____________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 3. Explain in one sentence: How did you know which was the eukaryo'c ...
... 2. Explain in one sentence: How did you know which was the prokaryo'c cell? ____________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 3. Explain in one sentence: How did you know which was the eukaryo'c ...
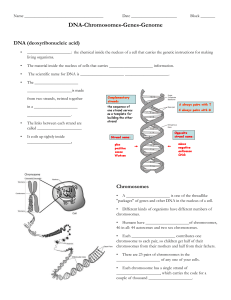
DNA-Chromosomes-Genes-Genome student notesheet
... _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
... _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
lec#18
... • Because epigenetic modifications regulate gene expression.. They might affect the response of one gene in different cells. • E.g NOTCH1 gene in oncogenic in T cell leukemia but is tumor suppressor in squamous cell carcinoma • As if NOTCH is Spiderman : you have the red Spiderman and the black one ...
... • Because epigenetic modifications regulate gene expression.. They might affect the response of one gene in different cells. • E.g NOTCH1 gene in oncogenic in T cell leukemia but is tumor suppressor in squamous cell carcinoma • As if NOTCH is Spiderman : you have the red Spiderman and the black one ...
Cell Division
... Meiosis Definition cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms; the nucleus divides into four nuclei each containing half the chromosome number leading to gametes. ...
... Meiosis Definition cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms; the nucleus divides into four nuclei each containing half the chromosome number leading to gametes. ...
Gene Section TGFBR3 (transforming growth factor, beta receptor III)
... accumulation of this complex in the nucleus, where along with co-activators and co-repressors they regulate the transcription of genes involved in proliferation, angiogenesis, apoptosis, and differen-tiation. In addition to regulating receptor mediated Smad signaling, TbetaRIII also mediates ligand ...
... accumulation of this complex in the nucleus, where along with co-activators and co-repressors they regulate the transcription of genes involved in proliferation, angiogenesis, apoptosis, and differen-tiation. In addition to regulating receptor mediated Smad signaling, TbetaRIII also mediates ligand ...
FALL EOC Questions
... 2. Describe two major differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Give examples of each. 3. For each process, indicate the cell organelle where it occurs: a. protein synthesis, b. photosynthesis, c. DNA replication, d. water storage, e. aerobic ATP production. 4. What are three major diffe ...
... 2. Describe two major differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Give examples of each. 3. For each process, indicate the cell organelle where it occurs: a. protein synthesis, b. photosynthesis, c. DNA replication, d. water storage, e. aerobic ATP production. 4. What are three major diffe ...
CHAPTER 3 OUTLINE File
... b. Gametes are haploid (half the number of chromosomes). c. Does not result in identical cell copies d. Errors can occur during meiosis. i. Nondisjunction, translocation 6. Producing Proteins: The Other Function of DNA a. Proteins are chemicals that make up tissues. ...
... b. Gametes are haploid (half the number of chromosomes). c. Does not result in identical cell copies d. Errors can occur during meiosis. i. Nondisjunction, translocation 6. Producing Proteins: The Other Function of DNA a. Proteins are chemicals that make up tissues. ...
Cell division and chromosomes - questions
... 9 Give two examples in each case of organs or tissues in which you would expect (a) meiosis, (b) mitosis to be taking place. ...
... 9 Give two examples in each case of organs or tissues in which you would expect (a) meiosis, (b) mitosis to be taking place. ...
Slide 1
... Cell undergoes four phases in its life cycle: G1,S,G2,M (growth, synthesis, mitosis) In S. cerevisiae, arrangement of microtubules and duplication of spindle pole bodies takes place early in the life cycle to allow for bud formation. Thus, budding S.cerevisiae lacks clear distinction between S, ...
... Cell undergoes four phases in its life cycle: G1,S,G2,M (growth, synthesis, mitosis) In S. cerevisiae, arrangement of microtubules and duplication of spindle pole bodies takes place early in the life cycle to allow for bud formation. Thus, budding S.cerevisiae lacks clear distinction between S, ...
Chapter 3 Section 1
... What are the building blocks of protein? A group of three nitrogen bases codes for a specific amino acid. The production of proteins is called protein synthesis. ...
... What are the building blocks of protein? A group of three nitrogen bases codes for a specific amino acid. The production of proteins is called protein synthesis. ...
Advanced Biology Vocabulary
... Autopolyploid An individual that has more than two chromosome sets that are all derived from a single species. ...
... Autopolyploid An individual that has more than two chromosome sets that are all derived from a single species. ...
Ecology Topics to Know
... and females are often carriers with one X affected and one normal X. Know how to read and make a pedigrees ...
... and females are often carriers with one X affected and one normal X. Know how to read and make a pedigrees ...
What happens to cells when an egg meets a sperm, then turns into
... In the very early embryo, embryonic stem cells differentiate into all the cell types that make up the organism. ...
... In the very early embryo, embryonic stem cells differentiate into all the cell types that make up the organism. ...
7th grade cell reproduction review (chapter 3 and 4-1)
... 20) In asexual reproduction, how many parents are there? 21) What term describes how a unicellular eukaryote reproduces? 22) A new organism forms by budding, but remains attached to its parent. What would start to form? 23) If a planarian is cut in two and produces two planaria, what type of asexual ...
... 20) In asexual reproduction, how many parents are there? 21) What term describes how a unicellular eukaryote reproduces? 22) A new organism forms by budding, but remains attached to its parent. What would start to form? 23) If a planarian is cut in two and produces two planaria, what type of asexual ...
“The cell cycle and other schmoos”
... iv) In the wild, they prefer to be diploid b) You can determine if an allele is dominant or recessive by mating it with another spore with a different allele c) Yeast mating is a fusion event i) Signal for mating (1) A produce a factor and alpha produce alpha factor (factors are 12-20 amino acids lo ...
... iv) In the wild, they prefer to be diploid b) You can determine if an allele is dominant or recessive by mating it with another spore with a different allele c) Yeast mating is a fusion event i) Signal for mating (1) A produce a factor and alpha produce alpha factor (factors are 12-20 amino acids lo ...
Study Guide Chapter 27 Protein Metabolism 1. Define: codon
... 2. What is the codon used to start a protein sequence? To stop a protein sequence? 3. Why is the genetic code a 3 letter code? 4. If I have a tRNA with the anticodon 3'...G-C-I...5', what possible codons on an mRNA message could it bind to? What about 3'... AUU...5'? 5. If there are 61 possible amin ...
... 2. What is the codon used to start a protein sequence? To stop a protein sequence? 3. Why is the genetic code a 3 letter code? 4. If I have a tRNA with the anticodon 3'...G-C-I...5', what possible codons on an mRNA message could it bind to? What about 3'... AUU...5'? 5. If there are 61 possible amin ...
Proto-Cells - TextAddOns.com
... Think Critically (cont’d) It is known that protocells are readily broken up by agitation and dissolved with changes in PH, heat and temperature. Are protocells likely to occur outside of a laboratory? ...
... Think Critically (cont’d) It is known that protocells are readily broken up by agitation and dissolved with changes in PH, heat and temperature. Are protocells likely to occur outside of a laboratory? ...