Anatomy of the Gene - University of Missouri
... How Does DNA Carry Information? To answer this question we must take a closer look at DNA. DNA is a biopolymer •Polymers are molecules made of repeating units or building blocks •DNA has four chemical building blocks symbolized by the letters A,G,C,& T •The letters of your DNA are in a specific ord ...
... How Does DNA Carry Information? To answer this question we must take a closer look at DNA. DNA is a biopolymer •Polymers are molecules made of repeating units or building blocks •DNA has four chemical building blocks symbolized by the letters A,G,C,& T •The letters of your DNA are in a specific ord ...
Chapter 5 - Biology 210A - Introduction to the Biological Sciences
... • A DNA molecule has two polynucleotides spiraling around an imaginary axis, forming a double helix • In the DNA double helix, the two backbones run in opposite 5 → 3 directions from each other, an arrangement referred to as antiparallel • One DNA molecule includes many genes • The nitrogenous bas ...
... • A DNA molecule has two polynucleotides spiraling around an imaginary axis, forming a double helix • In the DNA double helix, the two backbones run in opposite 5 → 3 directions from each other, an arrangement referred to as antiparallel • One DNA molecule includes many genes • The nitrogenous bas ...
Applications of RNA minimum free energy computations
... by exploiting the nucleotide bias present in a succession of codons, such signals are less apparent in noncoding RNA genes. Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) (Eddy, 2001; Eddy, 2002) is transcribed from genomic DNA and plays a biologically important role, although it is not translated into protein. Examples in ...
... by exploiting the nucleotide bias present in a succession of codons, such signals are less apparent in noncoding RNA genes. Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) (Eddy, 2001; Eddy, 2002) is transcribed from genomic DNA and plays a biologically important role, although it is not translated into protein. Examples in ...
Solution structure of the Drosha double-stranded RNA-binding domain Open Access
... to produce hairpin precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA) [3]. Pre-miRNA are transported to the cytoplasm [4-7] and further processed by Dicer enzymes to produce mature miRNA [8-13]. Drosha contains two RNase III domains that form the enzyme’s catalytic center. At the C-terminus is a double-stranded RNA-bindin ...
... to produce hairpin precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA) [3]. Pre-miRNA are transported to the cytoplasm [4-7] and further processed by Dicer enzymes to produce mature miRNA [8-13]. Drosha contains two RNase III domains that form the enzyme’s catalytic center. At the C-terminus is a double-stranded RNA-bindin ...
Whole-genome expression analysis of snf swi mutants of
... required for nucleosome remodeling activity in vivo or for other unknown aspects of Snf兾Swi activity, such as response to signals or interactions with transcriptional regulators. The factors that determine the dependence of a gene on Snf兾Swi are not understood. Several studies have indicated that Sn ...
... required for nucleosome remodeling activity in vivo or for other unknown aspects of Snf兾Swi activity, such as response to signals or interactions with transcriptional regulators. The factors that determine the dependence of a gene on Snf兾Swi are not understood. Several studies have indicated that Sn ...
Handouts
... The Yoneda lemma allows the embedding of any category into a category of functors defined on that category. It suggests that instead of studying the (small) category C, one should study the category o ...
... The Yoneda lemma allows the embedding of any category into a category of functors defined on that category. It suggests that instead of studying the (small) category C, one should study the category o ...
Formation and nuclear export of tRNA, rRNA and mRNA is regulated
... and pre-tRNA processing. A high-throughput proteomic analysis recently identified many potentially ubiquitinated proteins in yeast (Peng et al., 2003), including several ribosome synthesis factors and tRNA processing enzymes. Which of these ubiquitin residues are added directly by Rsp5p remains to b ...
... and pre-tRNA processing. A high-throughput proteomic analysis recently identified many potentially ubiquitinated proteins in yeast (Peng et al., 2003), including several ribosome synthesis factors and tRNA processing enzymes. Which of these ubiquitin residues are added directly by Rsp5p remains to b ...
chapt 8
... The order of bases in the DNA molecules is the genetic information that codes for proteins. – The sequence of nucleotides forms words that are like a recipe for proteins. Each word contains three base letters. – ATGC are the four letters that are used to make the words. – Each three-letter word code ...
... The order of bases in the DNA molecules is the genetic information that codes for proteins. – The sequence of nucleotides forms words that are like a recipe for proteins. Each word contains three base letters. – ATGC are the four letters that are used to make the words. – Each three-letter word code ...
Chpt12_RNAProcessing.doc
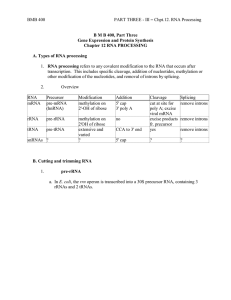
... 3. Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (or snRNPs) form the functional splicesome on pre-mRNA and catalyze splicing. a. "U" RNAs and associated proteins Small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) are about 100 to 300 nts long and can be as abundant as 105 to 106 molecules per cell. They are named U followed by an int ...
... 3. Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (or snRNPs) form the functional splicesome on pre-mRNA and catalyze splicing. a. "U" RNAs and associated proteins Small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) are about 100 to 300 nts long and can be as abundant as 105 to 106 molecules per cell. They are named U followed by an int ...
RNA EXTRACTION
... • A type of nucleic acid with only one strand - ribose instead of deoxyribose and using uracil instead of thymine (in DNA). • Provides the link between the genetic information through protein synthesis (serve as template for protein synthesis). • Total RNA= rRNA (~85%), mRNA (~2%), tRNA and other mo ...
... • A type of nucleic acid with only one strand - ribose instead of deoxyribose and using uracil instead of thymine (in DNA). • Provides the link between the genetic information through protein synthesis (serve as template for protein synthesis). • Total RNA= rRNA (~85%), mRNA (~2%), tRNA and other mo ...
Chapter 13 Chromatin Structure and its Effects on
... Chromatin is required for specificity • With DNA, RNA polymerase III transcribes both well ...
... Chromatin is required for specificity • With DNA, RNA polymerase III transcribes both well ...
Chapter 14 Lecture Notes: Nucleic Acids
... 19. Given the primary structure of DNA or mRNA, use the genetic code table to predict the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide that would be produced in translation. 20. Describe the three types of RNA and understand the role of each in translation. 21. Define the term “gene expression.” 22. D ...
... 19. Given the primary structure of DNA or mRNA, use the genetic code table to predict the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide that would be produced in translation. 20. Describe the three types of RNA and understand the role of each in translation. 21. Define the term “gene expression.” 22. D ...
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The role of yeast NAD+
... translationn than the model of cytoplasmic translation described by M. Kozak. Mitochondriall mRNAs are uncapped and predominantly possess extremely long untranslatedd leader and trailer sequences of high A+U content (>95%). These leader sequencess are likely to be difficult to scan for a ribosome, s ...
... translationn than the model of cytoplasmic translation described by M. Kozak. Mitochondriall mRNAs are uncapped and predominantly possess extremely long untranslatedd leader and trailer sequences of high A+U content (>95%). These leader sequencess are likely to be difficult to scan for a ribosome, s ...
FoldNucleus: web server for the prediction of RNA
... Received on March 23, 2015; revised on May 25, 2015; accepted on June 10, 2015 ...
... Received on March 23, 2015; revised on May 25, 2015; accepted on June 10, 2015 ...
PrimeFlow™ RNA Assay Technology Validation Paper
... PrimeFlow™ RNA Assay reveals the dynamics of RNA and protein expression within individual cells, facilitating unprecedented analysis of their correlation as the cells change over time or in response to stimulation. This novel assay uses fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) to enable simultaneous ...
... PrimeFlow™ RNA Assay reveals the dynamics of RNA and protein expression within individual cells, facilitating unprecedented analysis of their correlation as the cells change over time or in response to stimulation. This novel assay uses fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) to enable simultaneous ...
Characterization of a cDNA Clone Encoding Multiple Copies of the
... partially overlapping clones (Fig. 2A), with the longest cDNA insert 1054 base pairs (bp) (clone l), which were subcloned as EcoRI fragments in M13mp19. Sequence analysis in both directions of these cDNAs revealed a single open reading frame encoding a preprohormone of 2 I9 amino acids. cDNA clone 1 ...
... partially overlapping clones (Fig. 2A), with the longest cDNA insert 1054 base pairs (bp) (clone l), which were subcloned as EcoRI fragments in M13mp19. Sequence analysis in both directions of these cDNAs revealed a single open reading frame encoding a preprohormone of 2 I9 amino acids. cDNA clone 1 ...
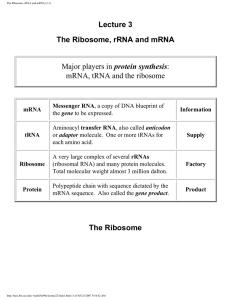
The Ribosome, rRNA and mRNA (3.1)
... determined the crystal structure of the large ribosomal subunit from Haloarcula marismortui at 2.4 angstrom resolution, and it includes 2833 of the subunit's 3045 nucleotides and 27 of its 31 proteins. The domains of its RNAs all have irregular shapes and fit together in the ribosome like the pieces ...
... determined the crystal structure of the large ribosomal subunit from Haloarcula marismortui at 2.4 angstrom resolution, and it includes 2833 of the subunit's 3045 nucleotides and 27 of its 31 proteins. The domains of its RNAs all have irregular shapes and fit together in the ribosome like the pieces ...
Gene splicing
... then curls around to form a lariat shape. which is removed from the maturing RNA. ...
... then curls around to form a lariat shape. which is removed from the maturing RNA. ...
Enhancement of the Essential Amino Acid Composition of Food
... ecosystems and crop yield through depletion of soil organic matter, mineral nutrients, and water-holding capacity of soil [15]. Integration and discrimination of diverse metabolic pathways at the mRNA level (permutation) is the biotechnological approach for doubling of crop dry matter, fatty acid, p ...
... ecosystems and crop yield through depletion of soil organic matter, mineral nutrients, and water-holding capacity of soil [15]. Integration and discrimination of diverse metabolic pathways at the mRNA level (permutation) is the biotechnological approach for doubling of crop dry matter, fatty acid, p ...
Ch. 10 Presentation
... polymerase reaches a sequence of bases in the DNA template called a terminator, which signals the end of the gene. – The polymerase molecule now detaches from the RNA molecule and the gene. ...
... polymerase reaches a sequence of bases in the DNA template called a terminator, which signals the end of the gene. – The polymerase molecule now detaches from the RNA molecule and the gene. ...
Review #3 - California Lutheran University
... What is the structure of tRNA? What is its tertiary structure? What are aminoacyl tRNA synthetases? What are the two classes of synthetases and how do they differ? If there are 61 codons and 32 or more tRNAs, why are there only 20 synthetases? What parts of the tRNA do the synthetases recognize? Why ...
... What is the structure of tRNA? What is its tertiary structure? What are aminoacyl tRNA synthetases? What are the two classes of synthetases and how do they differ? If there are 61 codons and 32 or more tRNAs, why are there only 20 synthetases? What parts of the tRNA do the synthetases recognize? Why ...
Example-Abstract
... Eukaryotic RNases H2 comprise three different subunits. In this report we determine the composition and stoichiometry of the human RNase H2 complex by biochemical analysis and find it to be the same as described before by genetic studies. Human and Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNASEH2A/Rnh201p subunits ...
... Eukaryotic RNases H2 comprise three different subunits. In this report we determine the composition and stoichiometry of the human RNase H2 complex by biochemical analysis and find it to be the same as described before by genetic studies. Human and Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNASEH2A/Rnh201p subunits ...
Figure 10.10 Deciphering the Genetic Code In 1961, Nirenberg and
... In 1961, Nirenberg and Matthaei cracked the genetic code by using an artificial mRNA in which all of the bases were uracil (poly U). In this experiment, the scientists prepared a bacterial extract that contained all of the components needed to translate proteins and then added the mRNA homopolymer. ...
... In 1961, Nirenberg and Matthaei cracked the genetic code by using an artificial mRNA in which all of the bases were uracil (poly U). In this experiment, the scientists prepared a bacterial extract that contained all of the components needed to translate proteins and then added the mRNA homopolymer. ...
CHAPTER 6
... An antiparallel double helix • diameter of 2 nm • circular in prokaryotic cells. • length of 1.6 million nm (E. coli) • Compact and folded (E. coli cell is only 2000 nm long) • The linear eukaryotic DNA is wrapped around histone proteins to form nucleosomes. • Base pairs: A-T, G-C ...
... An antiparallel double helix • diameter of 2 nm • circular in prokaryotic cells. • length of 1.6 million nm (E. coli) • Compact and folded (E. coli cell is only 2000 nm long) • The linear eukaryotic DNA is wrapped around histone proteins to form nucleosomes. • Base pairs: A-T, G-C ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.