module 1: introduction to the genome browser: what is a gene?
... You can use the buttons in the "Navigation control" section to navigate to different parts of the genome. You can zoom in to a region by clicking on one of the buttons next to the "zoom in" label (i.e. 1.5x, 3x, 10x, base). Similarly, you can zoom out by clicking on the buttons next to the "zoom out ...
... You can use the buttons in the "Navigation control" section to navigate to different parts of the genome. You can zoom in to a region by clicking on one of the buttons next to the "zoom in" label (i.e. 1.5x, 3x, 10x, base). Similarly, you can zoom out by clicking on the buttons next to the "zoom out ...
A Survey of Intron Research in Genetics
... The existence of the intron-exon structure has been particularly intriguing. Introns are only found in eukaryotic genomes and make up a large portion of the DNA in eukaryotic genomes. In humans, for example, approximately 30% of the human genome is made up of introns [1]. Only about 3% consists of c ...
... The existence of the intron-exon structure has been particularly intriguing. Introns are only found in eukaryotic genomes and make up a large portion of the DNA in eukaryotic genomes. In humans, for example, approximately 30% of the human genome is made up of introns [1]. Only about 3% consists of c ...
Biomolecular chemistry 3. Translating the genetic code
... In bacteria there is a specific tRNA, known as the initiator tRNA, that carries fMet. This fMet-tRNA recognizes the first codon AUG following a purine-rich sequence, known as the Shine-Delgarno sequence (or box), that base-pairs with a complementary sequence in the ribosome. This is essentially the ...
... In bacteria there is a specific tRNA, known as the initiator tRNA, that carries fMet. This fMet-tRNA recognizes the first codon AUG following a purine-rich sequence, known as the Shine-Delgarno sequence (or box), that base-pairs with a complementary sequence in the ribosome. This is essentially the ...
FOUR la INVARIANT CHAIN FORMS DERIVE
... lymphoid lines, revealed three clusters of protected fragments, lying at approximately -5, -10, and -32 by upstream of the first ATG codon of the open reading frame (Fig. 3) . The 2-3 by difference in length among fragments within a cluster may be due either to ragged ends generated by the S 1 diges ...
... lymphoid lines, revealed three clusters of protected fragments, lying at approximately -5, -10, and -32 by upstream of the first ATG codon of the open reading frame (Fig. 3) . The 2-3 by difference in length among fragments within a cluster may be due either to ragged ends generated by the S 1 diges ...
Nucleoside Phosphoramidate Monoesters: Potential
... tRNA Formation in E. Coli • 60 genes for tRNA are clustered in 25 transcription units • tRNA Precursors containing several tRNAs are cleaved with RNases: ...
... tRNA Formation in E. Coli • 60 genes for tRNA are clustered in 25 transcription units • tRNA Precursors containing several tRNAs are cleaved with RNases: ...
Activity of ribosomes and tmRNA of Streptomyces aureofaciens
... It is known that tetracycline blocks binding of ternary complex to A-site by sterically interfering with accommodation of the aminoacyl-tRNA [22]. To demonstrate whether ribosomes of S. aureofaciens are resistant to tetracycline, we examined binding of [14C]Phe-tRNA.EFTu.GTP to ribosomes. These expe ...
... It is known that tetracycline blocks binding of ternary complex to A-site by sterically interfering with accommodation of the aminoacyl-tRNA [22]. To demonstrate whether ribosomes of S. aureofaciens are resistant to tetracycline, we examined binding of [14C]Phe-tRNA.EFTu.GTP to ribosomes. These expe ...
Stockholm University
... levels [19]. In the human dopamine receptor D2, a synonymous codon change lowered the mRNA stability and caused a reduction in protein levels [20]. Furthermore, synonymous codon changes in the E. coli outer membrane protein OmpA resulted in a 10-fold lowering of both mRNA and protein levels [21]. In ...
... levels [19]. In the human dopamine receptor D2, a synonymous codon change lowered the mRNA stability and caused a reduction in protein levels [20]. Furthermore, synonymous codon changes in the E. coli outer membrane protein OmpA resulted in a 10-fold lowering of both mRNA and protein levels [21]. In ...
Let`s see How Dramatic Effect can be drawn by Point Mutation with
... which signals termination of translation. Result in an incomplete, short polypeptide. ...
... which signals termination of translation. Result in an incomplete, short polypeptide. ...
Creation/Evolution - Geoscience Research Institute
... meanings for the 64 codons, so many codons are synonyms. The fact that many amino acids are coded for by several codons is called degeneracy ©1998 Timothy G. Standish ...
... meanings for the 64 codons, so many codons are synonyms. The fact that many amino acids are coded for by several codons is called degeneracy ©1998 Timothy G. Standish ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
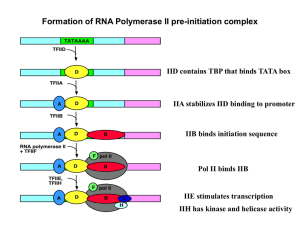
... • Crystal structure of T. aquaticus RNA polymerase holoenzyme shows an extensive interface between s and b- and b’-subunits of the core • Structure also predicts s region 1.1 helps open the main channel of the enzyme to admit dsDNA template to form the closed promoter complex • After helping to open ...
... • Crystal structure of T. aquaticus RNA polymerase holoenzyme shows an extensive interface between s and b- and b’-subunits of the core • Structure also predicts s region 1.1 helps open the main channel of the enzyme to admit dsDNA template to form the closed promoter complex • After helping to open ...
PBI 6 Features on Teacher`s Map 2-08.qxp
... for the protein shifts to the b reading frame, since 16 is not a multiple of 3. As a result, 29 amino acids are added to those coded by the truncated Exon I before protein synthesis is terminated by a STOP codon. The 29 amino acids are totally unrelated to β-globin and the truncated protein is compl ...
... for the protein shifts to the b reading frame, since 16 is not a multiple of 3. As a result, 29 amino acids are added to those coded by the truncated Exon I before protein synthesis is terminated by a STOP codon. The 29 amino acids are totally unrelated to β-globin and the truncated protein is compl ...
HUMAN PRIMARY CELLS RNA PRODUCTS Total RNA
... allows us to observe the 18s and 28s ribosomal RNA bands, which are another indicator of good RNA quality. Q. Why does my RNA product come in DEPC-treated water? A. AllCells stores and ships RNA products in DEPC-treated water which is nuclease-free, and can maintain quality and integrity of the RNA ...
... allows us to observe the 18s and 28s ribosomal RNA bands, which are another indicator of good RNA quality. Q. Why does my RNA product come in DEPC-treated water? A. AllCells stores and ships RNA products in DEPC-treated water which is nuclease-free, and can maintain quality and integrity of the RNA ...
Pipecleaner Proteins Lab
... Because proteins are smaller than microscopic, we would have a pretty hard time doing a hands-on lab on this topic. However, we can explore proteins in an indirect way through modeling. Everything in science is done with models – the scientific method itself is about modeling complex ideas into simp ...
... Because proteins are smaller than microscopic, we would have a pretty hard time doing a hands-on lab on this topic. However, we can explore proteins in an indirect way through modeling. Everything in science is done with models – the scientific method itself is about modeling complex ideas into simp ...
The Panicum mosaic virus-like 3` cap
... eIF4B, and possibly PABP) work to unwind the secondary structure naturally present in most 5’ untranslated regions (UTRs) of RNAs (33,73). In order for the ribosome to scan to the start codon, the mRNA secondary structures must be unwound (33,73-75). eIF4G serves as a scaffolding protein, simultaneo ...
... eIF4B, and possibly PABP) work to unwind the secondary structure naturally present in most 5’ untranslated regions (UTRs) of RNAs (33,73). In order for the ribosome to scan to the start codon, the mRNA secondary structures must be unwound (33,73-75). eIF4G serves as a scaffolding protein, simultaneo ...
How and why does β-actin mRNA target?
... a KH-domain RNA-binding protein, that bind βactin mRNA act as dominant negative for localization, presumably because the RNA-binding region blocks the full-length endogenous protein from assembling a transport particle around the RNA (Farina et al., 2003). Significantly, this dominant-negative fragm ...
... a KH-domain RNA-binding protein, that bind βactin mRNA act as dominant negative for localization, presumably because the RNA-binding region blocks the full-length endogenous protein from assembling a transport particle around the RNA (Farina et al., 2003). Significantly, this dominant-negative fragm ...
Unraveling the mechanisms of RNA
... associations with a range of different RNA-binding proteins. These interactions are highly dynamic in nature and the balance between binding and dissociation events is likely to play a pivotal role in the function of RNA-binding proteins. Biacore™ systems are ideally suited to the detailed kinetic a ...
... associations with a range of different RNA-binding proteins. These interactions are highly dynamic in nature and the balance between binding and dissociation events is likely to play a pivotal role in the function of RNA-binding proteins. Biacore™ systems are ideally suited to the detailed kinetic a ...
Contextual Genetic Algorithms: Evolving Developmental Rules
... in the cell might be responsible for posttranscriptional alteration of genetic information; this mechanism was called 'RNA Editing' [2, 1986]. "It was coined to illustrate that the alterations of the RNA sequence (i) occur in the protein-coding region and (ii) are most likely the result of a posttra ...
... in the cell might be responsible for posttranscriptional alteration of genetic information; this mechanism was called 'RNA Editing' [2, 1986]. "It was coined to illustrate that the alterations of the RNA sequence (i) occur in the protein-coding region and (ii) are most likely the result of a posttra ...
Minireview Shifty Ciliates: Frequent Programmed
... gene occasionally shift reading frames and continue synthesis into pol, producing a Gag-Pol fusion protein. The frequency of this frameshift is as much as 10,000fold greater than the estimated rate of spontaneous translational frameshifting. The sequence of the region in and around the site of frame ...
... gene occasionally shift reading frames and continue synthesis into pol, producing a Gag-Pol fusion protein. The frequency of this frameshift is as much as 10,000fold greater than the estimated rate of spontaneous translational frameshifting. The sequence of the region in and around the site of frame ...
In Vitro Translation Systems – Protein expression
... Express up to 0.75mg per mL of functional protein in less than 16 hours. The 1-Step Human High-Yield In Vitro Translation (IVT) Kits enable the expression of functional proteins with 10 to 100 times greater yield per mL than other mammalian IVT systems. The 1-Step High-Yield IVT System uses modified ...
... Express up to 0.75mg per mL of functional protein in less than 16 hours. The 1-Step Human High-Yield In Vitro Translation (IVT) Kits enable the expression of functional proteins with 10 to 100 times greater yield per mL than other mammalian IVT systems. The 1-Step High-Yield IVT System uses modified ...
DNA Replication
... 9. Termination occurs when the ribosome encounters one of the three “stop” codons (see the Figure). At termination, the completed polypeptide, the last tRNA, and the two ribosomal subunits are released. The ribosomal subunits can now attach to the same or another mRNA and repeat the process. ...
... 9. Termination occurs when the ribosome encounters one of the three “stop” codons (see the Figure). At termination, the completed polypeptide, the last tRNA, and the two ribosomal subunits are released. The ribosomal subunits can now attach to the same or another mRNA and repeat the process. ...
Isr J Chem (2010) - Weizmann Institute of Science
... formation. We aim to define the minimal ribosomal component required for maintaining PTC structure and function, in order to shed light on the evolution of the ribosome. Since the discovery made in the 1960 s that the ribosome can catalyze peptide bond formation between minimal substrates, e. g. pur ...
... formation. We aim to define the minimal ribosomal component required for maintaining PTC structure and function, in order to shed light on the evolution of the ribosome. Since the discovery made in the 1960 s that the ribosome can catalyze peptide bond formation between minimal substrates, e. g. pur ...
Aberrant mRNA Transcripts and the Nonsense
... The eukaryotic nucleolus is multifunctional and involved in the metabolism and assembly of many different RNAs and ribonucleoprotein particles as well as in cellular functions, such as cell division and transcriptional silencing in plants. We previously showed that Arabidopsis thaliana exon junction ...
... The eukaryotic nucleolus is multifunctional and involved in the metabolism and assembly of many different RNAs and ribonucleoprotein particles as well as in cellular functions, such as cell division and transcriptional silencing in plants. We previously showed that Arabidopsis thaliana exon junction ...
Transcription
... region to build off. Instead, RNA polymerase starts transcription at a single stranded promoter site. • RNA polymerase is more error-prone than DNA polymerase: 1 mistake in 104 bases, as opposed to 1 base in 109 for DNA polymerase ...
... region to build off. Instead, RNA polymerase starts transcription at a single stranded promoter site. • RNA polymerase is more error-prone than DNA polymerase: 1 mistake in 104 bases, as opposed to 1 base in 109 for DNA polymerase ...
Computational Biology - Bioinformatik
... play a variety of roles in biology. Most notably, siRNA is involved in the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway, where it interferes with the expression of a specific gene. In addition to their role in the RNAi pathway, siRNAs also act in RNAi-related pathways, e.g., as an antiviral mechanism or in shapi ...
... play a variety of roles in biology. Most notably, siRNA is involved in the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway, where it interferes with the expression of a specific gene. In addition to their role in the RNAi pathway, siRNAs also act in RNAi-related pathways, e.g., as an antiviral mechanism or in shapi ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.