Proteins - RHS AP Biology
... Nucleotides: molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. Amino acids: A group of 20 different kinds of small molecules that link together in long chains to form proteins; building blocks of protein. RNA: a nucleic molecule similar to DNA that delivers DNA's gen ...
... Nucleotides: molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. Amino acids: A group of 20 different kinds of small molecules that link together in long chains to form proteins; building blocks of protein. RNA: a nucleic molecule similar to DNA that delivers DNA's gen ...
Unit Three “Cell Proliferation and Genetics”
... which is the DNA in the nucleus, enables the efficient operation of the remainder of the cell is via Protein Synthesis • Recall that proteins maintain the proper function of the cell by acting as enzyme that regulate the vital chemical reactions of the cell • In essence, DNA makes RNA makes Protein ...
... which is the DNA in the nucleus, enables the efficient operation of the remainder of the cell is via Protein Synthesis • Recall that proteins maintain the proper function of the cell by acting as enzyme that regulate the vital chemical reactions of the cell • In essence, DNA makes RNA makes Protein ...
Effects of diet on genes for cholesterol and lipid metabolism
... NOTE: Changes in biochemistry and gene expression in the liver are a MAJOR topic in nutrition..but we usually can’t measure that directly by getting ...
... NOTE: Changes in biochemistry and gene expression in the liver are a MAJOR topic in nutrition..but we usually can’t measure that directly by getting ...
BIS2A TM Murphy Page 1 PROBLEMS ON MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
... chains coded by the two messengers. Why don’t different messages always give different polypeptides? c). List the differences in base sequences between mRNA 1 and mRNA 3. List the differences in amino acid sequences in the polypeptide chains coded by the two messengers. What is the relationship betw ...
... chains coded by the two messengers. Why don’t different messages always give different polypeptides? c). List the differences in base sequences between mRNA 1 and mRNA 3. List the differences in amino acid sequences in the polypeptide chains coded by the two messengers. What is the relationship betw ...
Protein synthesis - Teachnet UK-home
... 1. An annotated flow chart showing the stages of protein synthesis. 2. Publish you work on your own website pages! (to go on school site ) Two sites below will help ...
... 1. An annotated flow chart showing the stages of protein synthesis. 2. Publish you work on your own website pages! (to go on school site ) Two sites below will help ...
chapter12
... They remove two phosphates as the subunits are covalently linked to the 3’ end of the growing RNA molecule. These reactions are strongly exergonic. Messenger RNA contains the base sequence that codes for proteins. ...
... They remove two phosphates as the subunits are covalently linked to the 3’ end of the growing RNA molecule. These reactions are strongly exergonic. Messenger RNA contains the base sequence that codes for proteins. ...
Protein Synthesis – Part 3
... C. This process needs the assistance of tRNA (transfer RNA) to transfer free amino acids from the cytoplasm to the construction site of the Ribosome. a. Remember, that the ANTICODON is found on the tRNA molecule, NOT the mRNA. 2. The Anticodon “matches” the codon on the mRNA molecule ensuring the pr ...
... C. This process needs the assistance of tRNA (transfer RNA) to transfer free amino acids from the cytoplasm to the construction site of the Ribosome. a. Remember, that the ANTICODON is found on the tRNA molecule, NOT the mRNA. 2. The Anticodon “matches” the codon on the mRNA molecule ensuring the pr ...
Plant Molecular Biology
... gene expression in living cells, found in bacteria and invertebrates CAT – chloramphenicol acetyltransferase, used as an early reporter in plants, assay with radioactive substrate, bacterial gene 26. (10 pts) What is the general phenotype of the Det/COP/Fus mutants of Arabidopsis? What is the role o ...
... gene expression in living cells, found in bacteria and invertebrates CAT – chloramphenicol acetyltransferase, used as an early reporter in plants, assay with radioactive substrate, bacterial gene 26. (10 pts) What is the general phenotype of the Det/COP/Fus mutants of Arabidopsis? What is the role o ...
CHAPTER 10 - Protein Synthesis The DNA genotype is expressed
... of the cell or exported out of the cell Figure 10.20 • Summary of transcription and translation Review: The flow of genetic information in the cell is DNA→RNA→protein • The sequence of codons in DNA spells out the primary structure of a polypeptide – Polypeptides form proteins that cells and organis ...
... of the cell or exported out of the cell Figure 10.20 • Summary of transcription and translation Review: The flow of genetic information in the cell is DNA→RNA→protein • The sequence of codons in DNA spells out the primary structure of a polypeptide – Polypeptides form proteins that cells and organis ...
DNA and proteins
... • The part of the DNA molecule to be transcribed unwinds and ‘unzips’ as DNA helicase breaks the H bonds between the bases • RNA polymerase catalyses the binding of activated free RNA nucleotides to the template • Uracil binds to adenine NOT thymine • The nucleotides condense together forming ...
... • The part of the DNA molecule to be transcribed unwinds and ‘unzips’ as DNA helicase breaks the H bonds between the bases • RNA polymerase catalyses the binding of activated free RNA nucleotides to the template • Uracil binds to adenine NOT thymine • The nucleotides condense together forming ...
Sample Exam #2 ( file)
... Codons are: A. responsible for making sure DNA replication does not produce mutations. B. used to translate an mRNA into the amino acid sequence of a protein. C. the code geneticists use to let A stand for adenine, G for guanine, C for cytosine, and T for thymidine. D. sequences of one, two or three ...
... Codons are: A. responsible for making sure DNA replication does not produce mutations. B. used to translate an mRNA into the amino acid sequence of a protein. C. the code geneticists use to let A stand for adenine, G for guanine, C for cytosine, and T for thymidine. D. sequences of one, two or three ...
From DNA to Protein synthesis lab
... construction must be packaged and transferred out of the DNA "library." First, the specific sequence of DNA that codes for the protein is transcribed into a complementary strand of mRNA. In eukaryotic cells, the mRNA then leaves the nucleus and enters the cl.toplasm. In all cells, the mRNA molecule ...
... construction must be packaged and transferred out of the DNA "library." First, the specific sequence of DNA that codes for the protein is transcribed into a complementary strand of mRNA. In eukaryotic cells, the mRNA then leaves the nucleus and enters the cl.toplasm. In all cells, the mRNA molecule ...
Exam 2 Review Key - Iowa State University
... -accessory proteins -GTP (energy source) d. What are the three RNA binding sites and what are their purposes? -A: acceptor: charged tRNA enter here; peptide bond forms between aa’s in A and P -P: growing peptide chain attached here: tRNA releases amino acid -E: exit e. What kind of bonds are found i ...
... -accessory proteins -GTP (energy source) d. What are the three RNA binding sites and what are their purposes? -A: acceptor: charged tRNA enter here; peptide bond forms between aa’s in A and P -P: growing peptide chain attached here: tRNA releases amino acid -E: exit e. What kind of bonds are found i ...
1) Lecture notes: effects of bile salts on cholesterol metabolism
... NOTE: Changes in biochemistry and gene expression in the liver are a MAJOR topic in nutrition..but we usually can’t measure that directly by getting ...
... NOTE: Changes in biochemistry and gene expression in the liver are a MAJOR topic in nutrition..but we usually can’t measure that directly by getting ...
Document
... c.) in the promoter? Ask yourself—What acts at the promoter?! RNA Polymerase…Okay, there are some critical regions in the promoter (namely –10 and –35) that serve as binding sites for RNA Polymerase. If those were mutated, could that possibly result inproduction of a non-functional protein? YES! Mut ...
... c.) in the promoter? Ask yourself—What acts at the promoter?! RNA Polymerase…Okay, there are some critical regions in the promoter (namely –10 and –35) that serve as binding sites for RNA Polymerase. If those were mutated, could that possibly result inproduction of a non-functional protein? YES! Mut ...
In_Vitro_Translation
... germ extracts, use RNA as a template; whereas "coupled" and "linked" systems start with DNA templates, which are transcribed into RNA then translated. ...
... germ extracts, use RNA as a template; whereas "coupled" and "linked" systems start with DNA templates, which are transcribed into RNA then translated. ...
Translation
... Two major stages involved: • The first stage is called transcription – The 2 strands of the DNA molecule unwind and mRNA copies the genetic code (letters A, C, G and T) from DNA, the master molecule. ...
... Two major stages involved: • The first stage is called transcription – The 2 strands of the DNA molecule unwind and mRNA copies the genetic code (letters A, C, G and T) from DNA, the master molecule. ...
All Living things pass on their genetic heritage by common
... Transcription of DNA sequences into RNA’s RNA polymerase makes a single stranded RNA transcript from one strand of the unwound DNA helix. Activated A, U, G and C ribonucleotide triphosphates base pair with the DNA and are linked by the RNA polymerase into RNA polynucleotides. RNA transcripts 1. rRNA ...
... Transcription of DNA sequences into RNA’s RNA polymerase makes a single stranded RNA transcript from one strand of the unwound DNA helix. Activated A, U, G and C ribonucleotide triphosphates base pair with the DNA and are linked by the RNA polymerase into RNA polynucleotides. RNA transcripts 1. rRNA ...
Document
... in your DNA? first the DNA gets transcribed into a message = mRNA the mRNA gets exported out into the cytoplasm the mRNA gets bound by a ribosome tRNA molecules bring the correct amino acid into the ribosome amino acids are linked together mRNA ...
... in your DNA? first the DNA gets transcribed into a message = mRNA the mRNA gets exported out into the cytoplasm the mRNA gets bound by a ribosome tRNA molecules bring the correct amino acid into the ribosome amino acids are linked together mRNA ...
1: How is ribonucleic acid like DNA
... 19: What is translation? By what is the mRNA message read in order to translate the proteins? ...
... 19: What is translation? By what is the mRNA message read in order to translate the proteins? ...
Document
... 2. The ribosome helps form a polypeptide bond between the amino acids. 3. The ribosome pulls the mRNA strand the length of one codon and a new tRNA binds ...
... 2. The ribosome helps form a polypeptide bond between the amino acids. 3. The ribosome pulls the mRNA strand the length of one codon and a new tRNA binds ...
Document
... Improvement was sustained for a long time - and not just while the protein levels remained low. Symptoms were still better some months after the levels of abnormal huntingtin protein had returned to pre-treatment levels. ...
... Improvement was sustained for a long time - and not just while the protein levels remained low. Symptoms were still better some months after the levels of abnormal huntingtin protein had returned to pre-treatment levels. ...
Lecture 4: DNA transcription
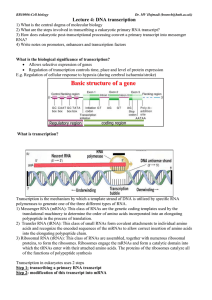
... Transcription is the mechanism by which a template strand of DNA is utilized by specific RNA polymerases to generate one of the three different types of RNA. 1) Messenger RNA (mRNA): This class of RNAs are the genetic coding templates used by the translational machinery to determine the order of ami ...
... Transcription is the mechanism by which a template strand of DNA is utilized by specific RNA polymerases to generate one of the three different types of RNA. 1) Messenger RNA (mRNA): This class of RNAs are the genetic coding templates used by the translational machinery to determine the order of ami ...
Slide 1
... zero to several because of their transient structure. • Nucleoli appear as dark, dense, irregular shaped areas of fibers and granules in the cell's nucleus. • Only plant and animal cells contain nucleoli. • They are made of proteins and ribonucleic acid, or RNA, and contain proteins, ribosomal RNA, ...
... zero to several because of their transient structure. • Nucleoli appear as dark, dense, irregular shaped areas of fibers and granules in the cell's nucleus. • Only plant and animal cells contain nucleoli. • They are made of proteins and ribonucleic acid, or RNA, and contain proteins, ribosomal RNA, ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.