Practicing Protein Synthesis
... Below are two partial sequences of DNA bases. Sequence 1 is from a human and sequence 2 is from a cow. In both humans and cows, the sequence contains the gene to make the protein insulin. Insulin is necessary for the uptake of sugar from the blood. Without insulin, a person (or a cow) cannot digest ...
... Below are two partial sequences of DNA bases. Sequence 1 is from a human and sequence 2 is from a cow. In both humans and cows, the sequence contains the gene to make the protein insulin. Insulin is necessary for the uptake of sugar from the blood. Without insulin, a person (or a cow) cannot digest ...
BIO S - Chapter 13 RNA
... Proteins are made by joining amino acids together into long chains, called polypeptides. As many as 20 different amino acids are commonly found in polypeptides. ...
... Proteins are made by joining amino acids together into long chains, called polypeptides. As many as 20 different amino acids are commonly found in polypeptides. ...
Chapter 7 Review
... including that transcription and translation can occur in the same location; no 5′ cap must be added; prokaryotes have a higher rate of protein synthesis; and polysomes can transcribe almost simultaneously with transcription. 41. The effects of the poly(A) tail include increased translation time. 42 ...
... including that transcription and translation can occur in the same location; no 5′ cap must be added; prokaryotes have a higher rate of protein synthesis; and polysomes can transcribe almost simultaneously with transcription. 41. The effects of the poly(A) tail include increased translation time. 42 ...
Document
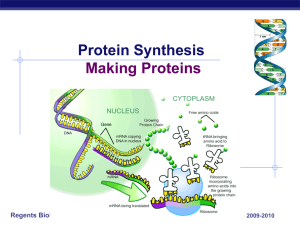
... How does mRNA code for proteins mRNA leaves nucleus mRNA goes to ribosomes in cytoplasm ...
... How does mRNA code for proteins mRNA leaves nucleus mRNA goes to ribosomes in cytoplasm ...
What is a protein
... Exon is identified by the START codon (AUG) Intron is discarded tRNA reads each codon (three nucleotide set code for amino acid) and transfers the correct amino acid accordingly. 5. The amino acids are linked together in the codon order. 6. tRNA will read the mRNA until it reaches a TERMINATOR or ST ...
... Exon is identified by the START codon (AUG) Intron is discarded tRNA reads each codon (three nucleotide set code for amino acid) and transfers the correct amino acid accordingly. 5. The amino acids are linked together in the codon order. 6. tRNA will read the mRNA until it reaches a TERMINATOR or ST ...
Plate 32 - Viral Replication
... 1. Union Phase (Adsorption) • Capsid proteins only bind with specific receptors on the host cell’s surface – This gives viruses their host range (which type of organism it may infect) ...
... 1. Union Phase (Adsorption) • Capsid proteins only bind with specific receptors on the host cell’s surface – This gives viruses their host range (which type of organism it may infect) ...
Lecture 17 Protein synthesis pp101-110
... 3.13 A protein’s specific shape determines its function • A polypeptide chain contains hundreds or thousands of amino acids linked by peptide ...
... 3.13 A protein’s specific shape determines its function • A polypeptide chain contains hundreds or thousands of amino acids linked by peptide ...
The unfolded protein response: an intracellular
... full-length protein is produced. According to the ‘direct’ model (b), the first ribosome stalls upon directly encountering the intron, presumably at a region of tight secondary structure. Further ribosomes and associated nascent chains stack behind it. If the intron is localized in the 3’-untranslat ...
... full-length protein is produced. According to the ‘direct’ model (b), the first ribosome stalls upon directly encountering the intron, presumably at a region of tight secondary structure. Further ribosomes and associated nascent chains stack behind it. If the intron is localized in the 3’-untranslat ...
II. The Steps of Translation
... been chemically-modified following synthesis of the molecule. At least one kind of tRNA is present for each of the 20 amino acids used in protein synthesis. Some amino acids employ the services of two or three different tRNAs, so most cells contain as many as 32 different kinds of tRNA. The amino ac ...
... been chemically-modified following synthesis of the molecule. At least one kind of tRNA is present for each of the 20 amino acids used in protein synthesis. Some amino acids employ the services of two or three different tRNAs, so most cells contain as many as 32 different kinds of tRNA. The amino ac ...
SECTION D What Does DNA Do?
... 3. What is the molecule that carries the information from a gene to the place where a protein will be made? _____________________________________________ 4. What is the process by which such a molecule is made? _________________________ 5. What is the enzyme that mediates the process named above? __ ...
... 3. What is the molecule that carries the information from a gene to the place where a protein will be made? _____________________________________________ 4. What is the process by which such a molecule is made? _________________________ 5. What is the enzyme that mediates the process named above? __ ...
BIOL 1406 - Ch. 16-18 Review
... of nucleotides in the DNA that codes for the amino acid sequence of this protein (hint: codon)? A. 3 B. 100 C. 300 D. 900 E. none of the above ...
... of nucleotides in the DNA that codes for the amino acid sequence of this protein (hint: codon)? A. 3 B. 100 C. 300 D. 900 E. none of the above ...
ANSWERS TO CHAPTER 3
... of smooth endoplasmic reticulum, and protein secretion is unlikely with the small amount of rough endoplasmic reticulum. Few vesicles also suggest that exocytosis is not occurring. ...
... of smooth endoplasmic reticulum, and protein secretion is unlikely with the small amount of rough endoplasmic reticulum. Few vesicles also suggest that exocytosis is not occurring. ...
DNA - Wiley
... An intron (intervening sequence) is a segment of DNA which is transcribed into mRNA but not actually used when a protein is expressed An exon (expressed sequence) in the part of the DNA gene which is expressed Each gene usually contains a number of introns and exons ...
... An intron (intervening sequence) is a segment of DNA which is transcribed into mRNA but not actually used when a protein is expressed An exon (expressed sequence) in the part of the DNA gene which is expressed Each gene usually contains a number of introns and exons ...
Honors_Genetics_B_Student_Notes
... transcription factor: a molecule that controls the transcription of DNA into mRNA transcription activator: turns a gene “on”, specific protein is produced (DNA → mRNA → protein) transcription repressor: blocks the process of transcription, turns a gene “off”, protein is not being ...
... transcription factor: a molecule that controls the transcription of DNA into mRNA transcription activator: turns a gene “on”, specific protein is produced (DNA → mRNA → protein) transcription repressor: blocks the process of transcription, turns a gene “off”, protein is not being ...
Handout
... The process repeats so that one amino acid is added at a time to the growing polypeptide (which is always anchored to a tRNA bound within the ribosome) The polypeptide continues to grow until the ribosome reaches a stop codon At the stop codon, the polypeptide chain is released from the last tRNA an ...
... The process repeats so that one amino acid is added at a time to the growing polypeptide (which is always anchored to a tRNA bound within the ribosome) The polypeptide continues to grow until the ribosome reaches a stop codon At the stop codon, the polypeptide chain is released from the last tRNA an ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... polydeoxyribonucleotide chain determines the specificity of amino acids sequence along the polypeptide chain to be synthesized. What is the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain synthesized by the portion of the DNA with nucleotides TTTCGACCC? Lys-Ala-Gly ...
... polydeoxyribonucleotide chain determines the specificity of amino acids sequence along the polypeptide chain to be synthesized. What is the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain synthesized by the portion of the DNA with nucleotides TTTCGACCC? Lys-Ala-Gly ...
TNA: Transcription and Triplet Code
... • It is synthesized in the nucleus, is sent to the cytosol of the cell and binds with ribosomes. • It makes up less than 5% of the RNA's as it doesn't "survive" long enough to make up much of the RNA's. • It has a half-life (t½) of 4-24 hours. • mRNA is around only long enough to drive the synthesis ...
... • It is synthesized in the nucleus, is sent to the cytosol of the cell and binds with ribosomes. • It makes up less than 5% of the RNA's as it doesn't "survive" long enough to make up much of the RNA's. • It has a half-life (t½) of 4-24 hours. • mRNA is around only long enough to drive the synthesis ...
HOW SAGE WORKS (Reference http://www
... Each type of RNA has a unique chemical composition that is a direct transcription of information stored in a particular gene. The basic units that make up DNA and RNAs are called nucleotides. The alphabet of nucleotides is very small (with only four letters), but it suffices to spell out the unique, ...
... Each type of RNA has a unique chemical composition that is a direct transcription of information stored in a particular gene. The basic units that make up DNA and RNAs are called nucleotides. The alphabet of nucleotides is very small (with only four letters), but it suffices to spell out the unique, ...
PDF file
... The position of phosphate was determined by treating the substrate with CIP (data not shown). Asterisks indicate location of 32P label. (B) Effect of concentration of divalent cation on NTPase and RTPase activities. Immunoprecipitated PfRTH1 protein was incubated with: left panel, [g-32P]ATP-termina ...
... The position of phosphate was determined by treating the substrate with CIP (data not shown). Asterisks indicate location of 32P label. (B) Effect of concentration of divalent cation on NTPase and RTPase activities. Immunoprecipitated PfRTH1 protein was incubated with: left panel, [g-32P]ATP-termina ...
1) Two identical daughter cells result
... A two adjacent nucleotides (nitrogen bases) B two adjacent nucleotides (nitrogen bases) with an untranscribed stop sequence C three adjacent nucleotides (nitrogen bases) D three adjacent nucleotides (nitrogen bases) with an untranscribed start sequence ...
... A two adjacent nucleotides (nitrogen bases) B two adjacent nucleotides (nitrogen bases) with an untranscribed stop sequence C three adjacent nucleotides (nitrogen bases) D three adjacent nucleotides (nitrogen bases) with an untranscribed start sequence ...
SBI4U: Molecular Genetics Unit Review
... What can be found in the promoter region of DNA? TATA box: where transcription factors bind, so RNA polymerase can bind What post-transcriptional modifications occur to an mRNA before it leaves the nucleus? 5’ cap, 3’ poly-A tail, RNA splicing What are the three kinds of RNA, and what are their purp ...
... What can be found in the promoter region of DNA? TATA box: where transcription factors bind, so RNA polymerase can bind What post-transcriptional modifications occur to an mRNA before it leaves the nucleus? 5’ cap, 3’ poly-A tail, RNA splicing What are the three kinds of RNA, and what are their purp ...
lecture4(GS351)
... • Switches control transcription (which take the form of DNA sequence) - Called regulatory elements (RE’s) or enhancers - Adjoin the promoter region, but can be quite distant • Regulators, which take the form of proteins that bind the DNA, operate the switches - Called transcription factors (TF’s) • ...
... • Switches control transcription (which take the form of DNA sequence) - Called regulatory elements (RE’s) or enhancers - Adjoin the promoter region, but can be quite distant • Regulators, which take the form of proteins that bind the DNA, operate the switches - Called transcription factors (TF’s) • ...
Genetics - Mrs. Yu`s Science Classes
... (siRNAs) block mRNA transcription or translation or degrade existing mRNA. Under certain conditions, an RNA molecule will fold back and base-pair with itself, forming dsRNA. An enzyme then cuts the dsRNA into short pieces (siRNAs), which then base-pair to complementary DNA regions—those regions th ...
... (siRNAs) block mRNA transcription or translation or degrade existing mRNA. Under certain conditions, an RNA molecule will fold back and base-pair with itself, forming dsRNA. An enzyme then cuts the dsRNA into short pieces (siRNAs), which then base-pair to complementary DNA regions—those regions th ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.