1.5 Page 4 - csfcbiology
... controls all the activities of a cell. It is able to do this as it carries information, which controls the synthesis of proteins. An important class of proteins is enzymes that control all metabolic reactions. Therefore, by controlling which proteins are made at a particular time in a particular typ ...
... controls all the activities of a cell. It is able to do this as it carries information, which controls the synthesis of proteins. An important class of proteins is enzymes that control all metabolic reactions. Therefore, by controlling which proteins are made at a particular time in a particular typ ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... RNA specifies the sequence of amino acids in a protein by triplet codon bases. The mRNA sequence is translated into a protein sequence. Transfer RNA (tRNA) - This RNA acts as an intermediate between the mRNA and protein. Through complementary base pairing to the mRNA it delivers the amino acid coded ...
... RNA specifies the sequence of amino acids in a protein by triplet codon bases. The mRNA sequence is translated into a protein sequence. Transfer RNA (tRNA) - This RNA acts as an intermediate between the mRNA and protein. Through complementary base pairing to the mRNA it delivers the amino acid coded ...
Document
... Since RNAi degrades mRNAs and is conveniently positioned between transcription and translation, it can regulate the gene expression, i.e. the rate of the respective gene product synthesis, without changing the gene activity. Cells are using this way to achieve “fine tuning” of the expression without ...
... Since RNAi degrades mRNAs and is conveniently positioned between transcription and translation, it can regulate the gene expression, i.e. the rate of the respective gene product synthesis, without changing the gene activity. Cells are using this way to achieve “fine tuning” of the expression without ...
ap® biology 2009 scoring guidelines - AP Central
... “When tRNA attaches, it brings with it an amino acid.” The maximum of 4 points were earned in part (b). Acetylation and methylation are the mechanisms of protein regulation named. These mechanisms each earned a point for a total of 2 points. Each mechanism is also discussed: “Histone acetylation bri ...
... “When tRNA attaches, it brings with it an amino acid.” The maximum of 4 points were earned in part (b). Acetylation and methylation are the mechanisms of protein regulation named. These mechanisms each earned a point for a total of 2 points. Each mechanism is also discussed: “Histone acetylation bri ...
MS Word file
... A variety of different consensus sequences may be found in the regulatory promoters. Main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is in assembly of ...
... A variety of different consensus sequences may be found in the regulatory promoters. Main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is in assembly of ...
Name: ____________ Pd.: ______ Date: Cells cannot make
... of amino acids which make up proteins) 4. The double helix structure explains how DNA can be replicated, or copied, but it does not explain how a gene works. Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins within the cell. The first step in decoding these genetic messages is ...
... of amino acids which make up proteins) 4. The double helix structure explains how DNA can be replicated, or copied, but it does not explain how a gene works. Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins within the cell. The first step in decoding these genetic messages is ...
power point presentation
... Substituting 1 base seems to be perfectly fine as the data in blue boxes lies perfectly on the prediction line. Substitution of 2 bases seems to be ok, but then about half of the data points lie distinctively far away from the line. ...
... Substituting 1 base seems to be perfectly fine as the data in blue boxes lies perfectly on the prediction line. Substitution of 2 bases seems to be ok, but then about half of the data points lie distinctively far away from the line. ...
Dr. Becker`s Review – Exam 4 Notes provided by Kadie Keen
... ribosomes attached to the ER (rough ER). Proteins that will be used within the cell are processed by the ribosomes that are free in the cytosol (cytoplasm) Translation Anticodon pairs with codon on mRNA There are 3 nucleotides in each 64 codons total 20 amino acids Amino acids have multipl ...
... ribosomes attached to the ER (rough ER). Proteins that will be used within the cell are processed by the ribosomes that are free in the cytosol (cytoplasm) Translation Anticodon pairs with codon on mRNA There are 3 nucleotides in each 64 codons total 20 amino acids Amino acids have multipl ...
In experiments with a 3 base codon system it was shown that the
... A change in the base configuration is called a tautomeric shift where a base goes from the keto to the enol form. For example, if a tautomeric shift occurs in a thymine, it will be paired to guanine instead of adenine. If adenine undergoes a tautomeric shift it will now be read as a guanine and be p ...
... A change in the base configuration is called a tautomeric shift where a base goes from the keto to the enol form. For example, if a tautomeric shift occurs in a thymine, it will be paired to guanine instead of adenine. If adenine undergoes a tautomeric shift it will now be read as a guanine and be p ...
BIOLOGY (Theory)
... present on the mRNA and in this way the initiator tRNA plays a role in initiation of protein synthesis. ...
... present on the mRNA and in this way the initiator tRNA plays a role in initiation of protein synthesis. ...
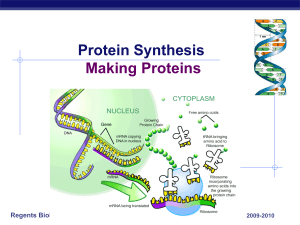
Protein Synthesis Making Proteins
... aa made by a “protein factory” in cytoplasm aa protein factory = ribosome aa ...
... aa made by a “protein factory” in cytoplasm aa protein factory = ribosome aa ...
You Light Up My Life
... Genetic Code • 64 base triplets • Triplets = codons – 61 = amino acids – 3 = stop ...
... Genetic Code • 64 base triplets • Triplets = codons – 61 = amino acids – 3 = stop ...
abstract
... past geochemical processes. Messenger RNA (mRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) are relatively labile molecules that are rich in biological information, and thus can serve as useful proxies for reconstructing present microbial activities. I will present examples of studies utilizing RNA proxies which inve ...
... past geochemical processes. Messenger RNA (mRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) are relatively labile molecules that are rich in biological information, and thus can serve as useful proxies for reconstructing present microbial activities. I will present examples of studies utilizing RNA proxies which inve ...
iclicker - University of Colorado-MCDB
... This paper is about A. RNA can inhibit gene expression B. RNA can destabilize mRNA C. Single stranded RNA can affect gene expression D. Double stranded RNA can affect gene expression E. All of above. ...
... This paper is about A. RNA can inhibit gene expression B. RNA can destabilize mRNA C. Single stranded RNA can affect gene expression D. Double stranded RNA can affect gene expression E. All of above. ...
mRNA
... How is RNA Assembled? • Transcription begins when an RNA polymerase and regulatory proteins attach to a DNA site called a promoter – RNA polymerase moves over a gene region and unwinds the double helix a bit so it can “read” the base sequence of the DNA strand – The polymerase joins free RNA nucleo ...
... How is RNA Assembled? • Transcription begins when an RNA polymerase and regulatory proteins attach to a DNA site called a promoter – RNA polymerase moves over a gene region and unwinds the double helix a bit so it can “read” the base sequence of the DNA strand – The polymerase joins free RNA nucleo ...
One Gene-one polypeptide:
... mRNA splicing—occurs in the nucleus and removes introns from pre-mRNAs and joins the exons together. This is part of pre-mRNA processing which takes place in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Takes place in a spliceosome. The snRNPs are what actually removes the introns. The snRNPs that have small nuclear ...
... mRNA splicing—occurs in the nucleus and removes introns from pre-mRNAs and joins the exons together. This is part of pre-mRNA processing which takes place in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Takes place in a spliceosome. The snRNPs are what actually removes the introns. The snRNPs that have small nuclear ...
Name: :______ Genetic Mutations—Online Model Go to: http
... 1. RNA polymerase and other proteins form a transcription complex. The transcription complex recognizes the start of a gene and unwinds a segment of it. 2. Nucleotides pair with one strand of the DNA. 3. RNA polymerase reads one side of the DNA template and strings together a complementary strand of ...
... 1. RNA polymerase and other proteins form a transcription complex. The transcription complex recognizes the start of a gene and unwinds a segment of it. 2. Nucleotides pair with one strand of the DNA. 3. RNA polymerase reads one side of the DNA template and strings together a complementary strand of ...
Transfer RNA and Protein Building Name_________________
... important molecules used for: building cell parts, as transport molecules, as enzymes and hormones and numerous other functions. Proteins are built of long chains of ______________________________. Each protein must be built with the correct sequence of amino acids. How does mRNA direct the ribosome ...
... important molecules used for: building cell parts, as transport molecules, as enzymes and hormones and numerous other functions. Proteins are built of long chains of ______________________________. Each protein must be built with the correct sequence of amino acids. How does mRNA direct the ribosome ...
DNA Discovery, Structure, Replication, Transcription, Translation
... 31. What is labeled at J? 32. What is labeled at K? 33. What is labeled at L? 34. Explain what happens in translation. Include the role of mRNA, the ribosome, tRNA, amino acids, the start codon, mRNA codons, tRNA anti-codons ...
... 31. What is labeled at J? 32. What is labeled at K? 33. What is labeled at L? 34. Explain what happens in translation. Include the role of mRNA, the ribosome, tRNA, amino acids, the start codon, mRNA codons, tRNA anti-codons ...
Ch17WordLectureOutline w pics
... While very similar in structure and function, prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes have enough differences that certain antibiotic drugs (like tetracycline) can paralyze prokaryotic ribosomes without inhibiting eukaryotic ribosomes. ...
... While very similar in structure and function, prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes have enough differences that certain antibiotic drugs (like tetracycline) can paralyze prokaryotic ribosomes without inhibiting eukaryotic ribosomes. ...
C. The Synthesis of Protein
... If the genetic code consisted of a single nucleotide or even pairs of nucleotides per amino acid, there would not be enough combinations (4 and 16 respectively) to code for all 20 amino acids. ...
... If the genetic code consisted of a single nucleotide or even pairs of nucleotides per amino acid, there would not be enough combinations (4 and 16 respectively) to code for all 20 amino acids. ...
Unit 7 Molecular Genetics Chp 17 Protein Synthesis
... If the genetic code consisted of a single nucleotide or even pairs of nucleotides per amino acid, there would not be enough combinations (4 and 16 respectively) to code for all 20 amino acids. ...
... If the genetic code consisted of a single nucleotide or even pairs of nucleotides per amino acid, there would not be enough combinations (4 and 16 respectively) to code for all 20 amino acids. ...
m5zn_a4ac3a22336dedd
... interactions with the general transcription machinery (RNA polymerase and general transcription factors). Transcription factor : is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the flow (or transcription) of genetic information from DNA to mRNA. Transcription factors perform t ...
... interactions with the general transcription machinery (RNA polymerase and general transcription factors). Transcription factor : is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the flow (or transcription) of genetic information from DNA to mRNA. Transcription factors perform t ...
Chapter Outline - Ltcconline.net
... 4. The one gene–one enzyme hypothesis: 5. The function of a gene is to: 6. A protein may consist of two or more different polypeptides G. From Nucleotides to Amino Acids: An Overview 1. Genetic information in DNA is: 2. A codon is: H. The Genetic Code 1. The genetic code is: 2. Of the 64 triplets, a ...
... 4. The one gene–one enzyme hypothesis: 5. The function of a gene is to: 6. A protein may consist of two or more different polypeptides G. From Nucleotides to Amino Acids: An Overview 1. Genetic information in DNA is: 2. A codon is: H. The Genetic Code 1. The genetic code is: 2. Of the 64 triplets, a ...
Vocabulary From DNA to Proteins
... Double helix –the structure of DNA, composed of two strands of DNA that are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases, shaped like a twisted ladder. Nitrogen base – Type of molecule that forms an important part of nucleic acid, composed of a nitrogen-containing ring structure. Hydr ...
... Double helix –the structure of DNA, composed of two strands of DNA that are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases, shaped like a twisted ladder. Nitrogen base – Type of molecule that forms an important part of nucleic acid, composed of a nitrogen-containing ring structure. Hydr ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.