The Cell
... The cells of prokaryotes and the nuclei of eukaryotes contain DNA and RNA, both nucleic acids— deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid, respectively. These two chemical compounds are composed of purines: adenine and guanine, and pyrimidines: thymine and cytosine. But thymine is replaced by uracil ...
... The cells of prokaryotes and the nuclei of eukaryotes contain DNA and RNA, both nucleic acids— deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid, respectively. These two chemical compounds are composed of purines: adenine and guanine, and pyrimidines: thymine and cytosine. But thymine is replaced by uracil ...
bio 201 – genetics
... one or more genes is called a genetic disorder. Some mutations alter a gene's DNA base sequence but do not change the function of the protein made by the gene. Studies have shown that only 7% of point mutations in noncoding DNA of yeast are deleterious and 12% in coding DNA are deleterious. The res ...
... one or more genes is called a genetic disorder. Some mutations alter a gene's DNA base sequence but do not change the function of the protein made by the gene. Studies have shown that only 7% of point mutations in noncoding DNA of yeast are deleterious and 12% in coding DNA are deleterious. The res ...
dna structure - Siegel Science
... Wanted to determine what part of a virus caused infection in host… ...
... Wanted to determine what part of a virus caused infection in host… ...
PCB 6528 Exam – Organelle genomes and gene expression
... http://www.arabidopsis.org/servlets/TairObject?name=AT2G21640&type=locus). The transcript is up-regulated in response to a wide suite of hydrogen peroxide, superoxide and singlet oxygen generating agents (Gadjev et al. , Plant Physiol. 141: 436). The protein product, however, was up-regulated in Ara ...
... http://www.arabidopsis.org/servlets/TairObject?name=AT2G21640&type=locus). The transcript is up-regulated in response to a wide suite of hydrogen peroxide, superoxide and singlet oxygen generating agents (Gadjev et al. , Plant Physiol. 141: 436). The protein product, however, was up-regulated in Ara ...
Genetics - Tomball FFA
... The structure of DNA was discovered by Watson and Crick in 1953. It is a twisted double helix molecule, containing sugar, phosphates, and nitrogenous bases. The sugar is deoxyribose and the phosphoric acid molecules are always the same and provides for the structure (side of the ladder). The only di ...
... The structure of DNA was discovered by Watson and Crick in 1953. It is a twisted double helix molecule, containing sugar, phosphates, and nitrogenous bases. The sugar is deoxyribose and the phosphoric acid molecules are always the same and provides for the structure (side of the ladder). The only di ...
Gene therapy attempts to treat genetic diseases at the molecular
... This photograph is of an adenovirus. Viruses are often used by researchers to deliver the correct gene to cells. Viruses deposit their own genetic material into host cells to instruct those cells to make more viruses. In gene therapy, the DNA for the desired gene is inserted into the genetic materia ...
... This photograph is of an adenovirus. Viruses are often used by researchers to deliver the correct gene to cells. Viruses deposit their own genetic material into host cells to instruct those cells to make more viruses. In gene therapy, the DNA for the desired gene is inserted into the genetic materia ...
Cutting-Edge Forensics
... include creating a so-called biological profile of a crime victim or set of remains. This involves taking several measurements, especially of skeletal and cranial features, that can indicate age, gender, stature, and even ancestry. ...
... include creating a so-called biological profile of a crime victim or set of remains. This involves taking several measurements, especially of skeletal and cranial features, that can indicate age, gender, stature, and even ancestry. ...
Analytical and Chromatography - Sigma
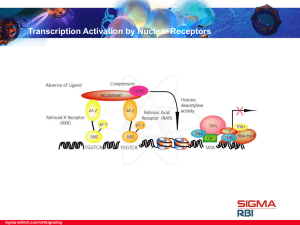
... • Retinoid X receptor (RXR) and Retinoic Acid receptor (RAR) are nuclear receptors that bind either all trans-retinoic (tRA) or 9-cis-retinoic acid (9cis-RA). In the absence of ligand, corepressors, such as Nuclear Receptor Corepressor (NCoR), Silencing Mediator of Retinoid and Thyroid Hormone Recep ...
... • Retinoid X receptor (RXR) and Retinoic Acid receptor (RAR) are nuclear receptors that bind either all trans-retinoic (tRA) or 9-cis-retinoic acid (9cis-RA). In the absence of ligand, corepressors, such as Nuclear Receptor Corepressor (NCoR), Silencing Mediator of Retinoid and Thyroid Hormone Recep ...
phenylketonuria (PKU): linked to genes on chromosome 12.
... We have two copies of that gene, on each Chromosome 12. We get one copy from the maternal gene, and one from the paternal gene. In a normal person, usually some protein is being made from each copy of the gene. ...
... We have two copies of that gene, on each Chromosome 12. We get one copy from the maternal gene, and one from the paternal gene. In a normal person, usually some protein is being made from each copy of the gene. ...
First Midterm Exam
... Which describes the early symptoms of the most life-threatening form of foodborne illness? A. B. C. D. ...
... Which describes the early symptoms of the most life-threatening form of foodborne illness? A. B. C. D. ...
Gene Mutations - Lyndhurst School
... one from which it was produced WATCH - BrainPop: Dolly the Sheep ...
... one from which it was produced WATCH - BrainPop: Dolly the Sheep ...
II. Principles of Cell
... • For successful cell-based DNA cloning two points have to be met: 1. A method to select the host cells containing the recombinant molecule. This is achieved by: ...
... • For successful cell-based DNA cloning two points have to be met: 1. A method to select the host cells containing the recombinant molecule. This is achieved by: ...
Student Note Packet
... between the observed and expected frequencies. Ex. If you flip a coin 10 times you should get 5 heads and 5 tails. The point of the Chi-square test is to either accept or reject the Null Hypothesis. Ex. If you flip a coin 10 times, the results would be anything other than 5 heads and 5 tails, due ...
... between the observed and expected frequencies. Ex. If you flip a coin 10 times you should get 5 heads and 5 tails. The point of the Chi-square test is to either accept or reject the Null Hypothesis. Ex. If you flip a coin 10 times, the results would be anything other than 5 heads and 5 tails, due ...
Name Date Period BioTechnology: Web Quest Part 1
... Go to http://www.dnai.org/d/index.html You have already investigated one application of biotechnology in the above “fingerprinting” activity. In this section other applications of the technology are explained. Choose between the Genes & Medicine or the Human Origins modules and explore it. Pick an a ...
... Go to http://www.dnai.org/d/index.html You have already investigated one application of biotechnology in the above “fingerprinting” activity. In this section other applications of the technology are explained. Choose between the Genes & Medicine or the Human Origins modules and explore it. Pick an a ...
Slide 1
... enzymes which are composed of a complex of proteins and RNA. They catalyze removal of introns from RNA (RNA splicing). Different types of snRNPs recognize different regions of introns by complemetary base-pairing (e.g. U1 snRNP recognize 5’splice site). ...
... enzymes which are composed of a complex of proteins and RNA. They catalyze removal of introns from RNA (RNA splicing). Different types of snRNPs recognize different regions of introns by complemetary base-pairing (e.g. U1 snRNP recognize 5’splice site). ...
Rare Genetic Diseases
... have repercussions in the field of rare genetic diseases like AGS, most probably through the identification of altered genes that lead to the onset of the disease, but the availability of the full human sequence represents also some major challenges. Indeed it is a toolbox that is so immense and com ...
... have repercussions in the field of rare genetic diseases like AGS, most probably through the identification of altered genes that lead to the onset of the disease, but the availability of the full human sequence represents also some major challenges. Indeed it is a toolbox that is so immense and com ...
Biochemistry ± DNA Chemistry and Analysis DNA o Adenosine
... Hypochromic Effect: when DNA heated to the melting temp, and an increase in UV light absorbance occurs x Stacked bases in dsDNA shield UV absorption x Melting causes UV to increase absorbance by bases ± monitor melting based on absorbance in soln Heating causes H-bonds to disrupt, 2 strands sepa ...
... Hypochromic Effect: when DNA heated to the melting temp, and an increase in UV light absorbance occurs x Stacked bases in dsDNA shield UV absorption x Melting causes UV to increase absorbance by bases ± monitor melting based on absorbance in soln Heating causes H-bonds to disrupt, 2 strands sepa ...
figure 9-9
... of many organisms, including that of humans, have been sequenced in their entirety and are now available in public databases. ...
... of many organisms, including that of humans, have been sequenced in their entirety and are now available in public databases. ...
Eukaryotic Genome: Organization, Regulation, and Evolution
... Translation of specific mRNAs can be blocked by regulatory proteins that bind to specific sequences or structures within the 5’ leader region of mRNA. ...
... Translation of specific mRNAs can be blocked by regulatory proteins that bind to specific sequences or structures within the 5’ leader region of mRNA. ...
• - cloudfront.net
... 29. What is a codon? How many bases/nucleotides are needed to code for one amino acid? 30. Explain why there are so many different types of proteins when there are only 20 different amino acids. 31. What is translation? What happens during translation? 32. What is an anticodon? Which type of RNA car ...
... 29. What is a codon? How many bases/nucleotides are needed to code for one amino acid? 30. Explain why there are so many different types of proteins when there are only 20 different amino acids. 31. What is translation? What happens during translation? 32. What is an anticodon? Which type of RNA car ...
Heredity Unit Notes (1)
... (4) VARIATION IN TRAITS • “Different Types of Traits” = Different nitrogenous base sequences for a gene. • Sexual Reproduction increases genetic variations and diversity in a population. • Sex Cells are produced through a special type of cell division called “Meiosis”. • In Meiosis, these different ...
... (4) VARIATION IN TRAITS • “Different Types of Traits” = Different nitrogenous base sequences for a gene. • Sexual Reproduction increases genetic variations and diversity in a population. • Sex Cells are produced through a special type of cell division called “Meiosis”. • In Meiosis, these different ...
Binary Ti vector plasmids
... • They may span hundreds of basepairs and can contain cassettes of repeated sequences, each of which may function independently as cis-elements • They can function in either orientation in the chromosome and can be located at a considerable distance from the coding region of the gene • They can also ...
... • They may span hundreds of basepairs and can contain cassettes of repeated sequences, each of which may function independently as cis-elements • They can function in either orientation in the chromosome and can be located at a considerable distance from the coding region of the gene • They can also ...