Unit 5: Cell Cycles and Genetics Self
... D) Explain whether the new molecules are composed of 2 new strands, 2 old strands, or one old and one new strand. Why? 8) From the chapter 10 pages 204-206 titled "Protein Synthesis" be able to; A) Explain the primary function of RNA. B) Describe the three differences between RNA and DNA. C) Name an ...
... D) Explain whether the new molecules are composed of 2 new strands, 2 old strands, or one old and one new strand. Why? 8) From the chapter 10 pages 204-206 titled "Protein Synthesis" be able to; A) Explain the primary function of RNA. B) Describe the three differences between RNA and DNA. C) Name an ...
Biology: Exploring Life Resource Pro
... genetic information carried in molecules of protein or DNA? Two scientists, Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase, devised a simple, yet brilliant, experiment to answer this question. In this activity, you will model their experiment. • Examine the structure of the bacteriophage (also called a phage). Not ...
... genetic information carried in molecules of protein or DNA? Two scientists, Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase, devised a simple, yet brilliant, experiment to answer this question. In this activity, you will model their experiment. • Examine the structure of the bacteriophage (also called a phage). Not ...
Coastal Ocean Institute - Final Project Report
... decades of study, the ability to predict how nutrients and CO2 influence the growth of different coastal HABforming phytoplankton species is still limited. Recent advances in DNA/RNA sequencing make it possible to study the physiological response of HAB species to nutrient availability with unpreced ...
... decades of study, the ability to predict how nutrients and CO2 influence the growth of different coastal HABforming phytoplankton species is still limited. Recent advances in DNA/RNA sequencing make it possible to study the physiological response of HAB species to nutrient availability with unpreced ...
Biology and computers
... S-Spike protein, receptor binding, cell fusion, major antigen HE-Envelope protein M-Membrane protein, for budding and envelope formation N-phosphoprotein, associates with RNA genome ...
... S-Spike protein, receptor binding, cell fusion, major antigen HE-Envelope protein M-Membrane protein, for budding and envelope formation N-phosphoprotein, associates with RNA genome ...
Mortlock_lab_Nucleobond_maxiprep
... DNA. The 260/280 absorbance ratio should be approx. 1.85, and the 260/230 absorbance ratio should be greater than 2.0. It is also critical to check that the DNA really is BAC DNA by agarose gel analysis of a restriction digest. ...
... DNA. The 260/280 absorbance ratio should be approx. 1.85, and the 260/230 absorbance ratio should be greater than 2.0. It is also critical to check that the DNA really is BAC DNA by agarose gel analysis of a restriction digest. ...
Nucleic Acid Biotechnology Techniques
... • DNA samples can be studied and compared by DNA fingerprinting • DNA is digested with restriction enzymes and then run on an agarose gel • When soaked in ethidium bromide – can be seen directly under UV light ...
... • DNA samples can be studied and compared by DNA fingerprinting • DNA is digested with restriction enzymes and then run on an agarose gel • When soaked in ethidium bromide – can be seen directly under UV light ...
TRANSPOSABLE ELEMENTS IN BACTERIA Transposable
... (transposase) that catalyses the transposition event. Thus, transposition requires that the IS element carry a promoter recognized by the RNA polymerase of the host cell. Typically the gene for the transposase is the only gene within the element. Molecules of the transposase bind to the ITR sequence ...
... (transposase) that catalyses the transposition event. Thus, transposition requires that the IS element carry a promoter recognized by the RNA polymerase of the host cell. Typically the gene for the transposase is the only gene within the element. Molecules of the transposase bind to the ITR sequence ...
lecture23_AnnotatePr..
... CS Constrained sequence: a genomic region associated with evidence of negative selection (that is, rejection of mutations relative to neutral regions) GENCODE Integrated annotation of existing cDNA and protein resources to define transcripts with both manual review and experimental testing procedure ...
... CS Constrained sequence: a genomic region associated with evidence of negative selection (that is, rejection of mutations relative to neutral regions) GENCODE Integrated annotation of existing cDNA and protein resources to define transcripts with both manual review and experimental testing procedure ...
Document
... • The genetic code matches each codon to its amino acid or function. The genetic code matches each RNA codon with its amino acid or function. ...
... • The genetic code matches each codon to its amino acid or function. The genetic code matches each RNA codon with its amino acid or function. ...
CHAPTER 17 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
... b. Nearly all transcriptionally active genes have increased DNase I sensitivity. The DNA in these regions may still be organized into nucleosomes, but is less highly coiled than inactive regions. c. Regions hypersensitive to DNase I have also been identified. Most are upstream from transcription sta ...
... b. Nearly all transcriptionally active genes have increased DNase I sensitivity. The DNA in these regions may still be organized into nucleosomes, but is less highly coiled than inactive regions. c. Regions hypersensitive to DNase I have also been identified. Most are upstream from transcription sta ...
Gene Section USP6 (ubiquitin specific protease 6 (Tre-2 oncogene))
... which encodes a GTPase-activating protein of the Rab family of GTPases, and a UBP domain with a ubiquitin specific protease activity. A USP6 splicing variant, also known as ‘onco-TRE17 or TRE17-onco’, encodes a 786 aminoacid protein with a truncated UBP domain. See figure 1. ...
... which encodes a GTPase-activating protein of the Rab family of GTPases, and a UBP domain with a ubiquitin specific protease activity. A USP6 splicing variant, also known as ‘onco-TRE17 or TRE17-onco’, encodes a 786 aminoacid protein with a truncated UBP domain. See figure 1. ...
Methylation
... allowed to bind protein. Bound and unbound populations are separated, and strands are cleaved at the modified bases. Bases critical for protein binding will not appear as bands in the bound population. Methylation and uracil interference techniques differ in the base(s) targeted, and in the method u ...
... allowed to bind protein. Bound and unbound populations are separated, and strands are cleaved at the modified bases. Bases critical for protein binding will not appear as bands in the bound population. Methylation and uracil interference techniques differ in the base(s) targeted, and in the method u ...
part 1 genetics notes—ch 10-13
... 2. Fertilization is when the egg and sperm __________________, or fuses together to form a fertilized egg called a _________________________. 3. Pollination is the same as fertilization but it happens in _____________________. Pollen has the ____________ inside of it. 4. Alleles- ___________________ ...
... 2. Fertilization is when the egg and sperm __________________, or fuses together to form a fertilized egg called a _________________________. 3. Pollination is the same as fertilization but it happens in _____________________. Pollen has the ____________ inside of it. 4. Alleles- ___________________ ...
8/22/13 Comp 555 Fall 2013 1 - UNC Computational Systems Biology
... • Proteins are generally unaffected by small variations in their code sequence, particularly changes to a small number of bases • Minor variations in genes, called allels, are responsible for individual variations (blood-type, hair color, etc.) • Errors in translation (the substitution for one a ...
... • Proteins are generally unaffected by small variations in their code sequence, particularly changes to a small number of bases • Minor variations in genes, called allels, are responsible for individual variations (blood-type, hair color, etc.) • Errors in translation (the substitution for one a ...
The Genetic Basis of Development
... the myoD gene further, and activates genes encoding other muscle-specific transcription factors, which in turn activate genes for muscle proteins. MyoD also turns on genes that block the cell cycle, thus stopping cell division. The nondividing myoblasts fuse to become mature multinucleate muscle cel ...
... the myoD gene further, and activates genes encoding other muscle-specific transcription factors, which in turn activate genes for muscle proteins. MyoD also turns on genes that block the cell cycle, thus stopping cell division. The nondividing myoblasts fuse to become mature multinucleate muscle cel ...
Gene Section NFKB1 (nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide
... ubiquitin-proteasome dependent degradation of the Cterminal portion of NF-kB1. Further studies by Lin and Ghosh suggested that a glycine-rich region (GRR) within the region of 375 to 400 of NF-kB1 is necessary and sufficient for directing the cleavage of NF-kB1. However, recent studies challenged th ...
... ubiquitin-proteasome dependent degradation of the Cterminal portion of NF-kB1. Further studies by Lin and Ghosh suggested that a glycine-rich region (GRR) within the region of 375 to 400 of NF-kB1 is necessary and sufficient for directing the cleavage of NF-kB1. However, recent studies challenged th ...
1_genomics
... Following Mendel’s laws, Garrod concluded that alkaptonuria is a congenital disorder(先天性的变异), not the result of a bacterial infection as was commonly thought. ...
... Following Mendel’s laws, Garrod concluded that alkaptonuria is a congenital disorder(先天性的变异), not the result of a bacterial infection as was commonly thought. ...
amazing facts about human dna and genome
... commonly used fingerprint markers. DNA also helps in regulation of gene expression by selective import of proteins into the nucleus. Proteins responsible for genome structure and organisation are all imported into the nucleus selectively. They include histones, DNA polymerases, RNA Polymerases, tran ...
... commonly used fingerprint markers. DNA also helps in regulation of gene expression by selective import of proteins into the nucleus. Proteins responsible for genome structure and organisation are all imported into the nucleus selectively. They include histones, DNA polymerases, RNA Polymerases, tran ...
Final Review Click Here - Garnet Valley School District
... 1.) surrounds and protects the cell, made of proteins and phospholipids, is semipermeable, or selectively permeable (allows some substances to enter)2.) only in plant cells, surrounds and protects the cell, made of cellulose3.) stores genetic information, controls all cell activities7.) found in nuc ...
... 1.) surrounds and protects the cell, made of proteins and phospholipids, is semipermeable, or selectively permeable (allows some substances to enter)2.) only in plant cells, surrounds and protects the cell, made of cellulose3.) stores genetic information, controls all cell activities7.) found in nuc ...
Pseudogene function: regulation of gene expression
... of whatever type, may only imply a function that does not require a conserved sequence (or, in the present case, at least a highly conserved sequence), not absence of all function. The recent cited studies unequivocally bear this fact out for pseudogenes. Note that, in terms of both overall similari ...
... of whatever type, may only imply a function that does not require a conserved sequence (or, in the present case, at least a highly conserved sequence), not absence of all function. The recent cited studies unequivocally bear this fact out for pseudogenes. Note that, in terms of both overall similari ...
Ch. 9: Presentation Slides
... • Genomic sequencing has made possible a new approach to genetics called functional genomics, which focuses on genome-wide patterns of gene expression and the mechanisms by which gene expression is coordinated • DNA microarray (or chip) – a flat surface about the size of a postage stamp with up to 1 ...
... • Genomic sequencing has made possible a new approach to genetics called functional genomics, which focuses on genome-wide patterns of gene expression and the mechanisms by which gene expression is coordinated • DNA microarray (or chip) – a flat surface about the size of a postage stamp with up to 1 ...
BIOTECHNOLOGY
... Usually in the first well, DNA markers of set length are added, so the scientist can estimate the sizes of the pieces in the other wells. Once the gel has finished, it is stained using ethidium bromide, a carcinogen that can attach to DNA and fluoresce under UV light. Once the scientist finds the DN ...
... Usually in the first well, DNA markers of set length are added, so the scientist can estimate the sizes of the pieces in the other wells. Once the gel has finished, it is stained using ethidium bromide, a carcinogen that can attach to DNA and fluoresce under UV light. Once the scientist finds the DN ...
Application Note LabImage 1D
... compare the expression of these cellular components within a given gel and across several gels. We are also able to determine the relative expression of specific protein subtypes within a given sample with accurate results. The utility of LabImage 1D to simply and uniformly calculate the optical den ...
... compare the expression of these cellular components within a given gel and across several gels. We are also able to determine the relative expression of specific protein subtypes within a given sample with accurate results. The utility of LabImage 1D to simply and uniformly calculate the optical den ...
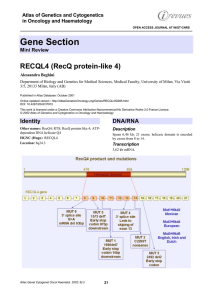
Gene Section RECQL4 (RecQ protein-like 4) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... domain with a potential ATP binding site from aa 502 to 509, and the DEAH box from aa 605 to 608. ...
... domain with a potential ATP binding site from aa 502 to 509, and the DEAH box from aa 605 to 608. ...
Primary transcript

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.There are several steps contributing to the production of primary transcripts. All these steps involve a series of interactions to initiate and complete the transcription of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Certain factors play key roles in the activation and inhibition of transcription, where they regulate primary transcript production. Transcription produces primary transcripts that are further modified by several processes. These processes include the 5' cap, 3'-polyadenylation, and alternative splicing. In particular, alternative splicing directly contributes to the diversity of mRNA found in cells. The modifications of primary transcripts have been further studied in research seeking greater knowledge of the role and significance of these transcripts. Experimental studies based on molecular changes to primary transcripts the processes before and after transcription have led to greater understanding of diseases involving primary transcripts.