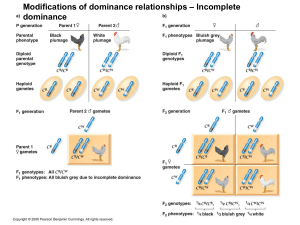
Modifications of dominance relationships – Incomplete dominance
... At the molecular level, the mutation that causes TSD is in a gene that encodes for the enzyme hexaminidase A (hex A). Enzyme is responsible for the breakdown of gangliosides. ...
... At the molecular level, the mutation that causes TSD is in a gene that encodes for the enzyme hexaminidase A (hex A). Enzyme is responsible for the breakdown of gangliosides. ...
Co-Dominance
... Two coins both heads = 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4 Pair of dice both coming up 6 = 1/6 x 1/6 = 1/36 One di and one coin coming up with a head and a six = 1/2 x 1/6 = 1/12 AaRr x AaRr the chance for getting AaRr = 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4 ...
... Two coins both heads = 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4 Pair of dice both coming up 6 = 1/6 x 1/6 = 1/36 One di and one coin coming up with a head and a six = 1/2 x 1/6 = 1/12 AaRr x AaRr the chance for getting AaRr = 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4 ...
Genetics - Kawameeh Middle School
... O A trait controlled by a recessive allele will only show if the dominant allele is not present ...
... O A trait controlled by a recessive allele will only show if the dominant allele is not present ...
IX P L
... reduced symptoms on lines containing Tsn1. Stagonospora (Phaeosphaeria) nodorum is a related pathogen, which also infects wheat. Whole genome sequence analysis of S. nodorum revealed the presence of a gene that is nearly identical to ToxA, called SnToxA, adjacent to a transposase-like gene. SnToxA w ...
... reduced symptoms on lines containing Tsn1. Stagonospora (Phaeosphaeria) nodorum is a related pathogen, which also infects wheat. Whole genome sequence analysis of S. nodorum revealed the presence of a gene that is nearly identical to ToxA, called SnToxA, adjacent to a transposase-like gene. SnToxA w ...
slides
... A HuGE Review iden*fies human gene*c varia*ons at specific places in the genome (called “loci,” which is plural for locus or loca*on) and describes: • -‐ what is known about the frequency of these ...
... A HuGE Review iden*fies human gene*c varia*ons at specific places in the genome (called “loci,” which is plural for locus or loca*on) and describes: • -‐ what is known about the frequency of these ...
Section 6.4- Traits, Genes, Alleles
... •Remember- dominate alleles are not necessarily better or occur more. It simply means when 2 different alleles are together, one masks the other. ...
... •Remember- dominate alleles are not necessarily better or occur more. It simply means when 2 different alleles are together, one masks the other. ...
111-297-1-SM
... Understanding the molecular mechanisms of host and parasite interactions should facilitate the development of novel strategies to control plant diseases. Host interactions with biotrophic and hemi-biotrophic pathogens are known to follow a gene-for-gene specificity. The plant expresses a resistance ...
... Understanding the molecular mechanisms of host and parasite interactions should facilitate the development of novel strategies to control plant diseases. Host interactions with biotrophic and hemi-biotrophic pathogens are known to follow a gene-for-gene specificity. The plant expresses a resistance ...
6.4 Traits, Genes, and Alleles
... – Each parent donates one allele for every gene. – H___________s describes two alleles that are the same at a specific locus. – H___________s describes two alleles that are different at a specific locus. ...
... – Each parent donates one allele for every gene. – H___________s describes two alleles that are the same at a specific locus. – H___________s describes two alleles that are different at a specific locus. ...
Figure 4
... production of an edible vaccine appeared in a patent application published under the international patent co-operatin treaty. It described a means to express a surface protein (spa A) from Streptococus mutans in tobacco plants to a level of 0.02% of total leaf protein, the gene had been stably inser ...
... production of an edible vaccine appeared in a patent application published under the international patent co-operatin treaty. It described a means to express a surface protein (spa A) from Streptococus mutans in tobacco plants to a level of 0.02% of total leaf protein, the gene had been stably inser ...
Genetics Unit 1 - Staff Web Pages
... • He got 3 tall plants to every short plant or a 3tall:1short ratio • This is known as the F2 generation ...
... • He got 3 tall plants to every short plant or a 3tall:1short ratio • This is known as the F2 generation ...
pGLO Bacterial Transformation- Pre-Lab
... literally means change caused by genes and it involves the insertion of a gene(s) into an organism in order to change the organism's trait(s). Genetic transformation is used in many areas of biotechnology. In agriculture, genes coding for traits such as frost, pest, or spoilage resistance can be gen ...
... literally means change caused by genes and it involves the insertion of a gene(s) into an organism in order to change the organism's trait(s). Genetic transformation is used in many areas of biotechnology. In agriculture, genes coding for traits such as frost, pest, or spoilage resistance can be gen ...
pGLO Bacterial Transformation- Pre-Lab
... literally means change caused by genes and it involves the insertion of a gene(s) into an organism in order to change the organism's trait(s). Genetic transformation is used in many areas of biotechnology. In agriculture, genes coding for traits such as frost, pest, or spoilage resistance can be gen ...
... literally means change caused by genes and it involves the insertion of a gene(s) into an organism in order to change the organism's trait(s). Genetic transformation is used in many areas of biotechnology. In agriculture, genes coding for traits such as frost, pest, or spoilage resistance can be gen ...
Tick Control
... Genetic resistance of ticks spreads by the reproduction of resistant individuals that have survived acaricidal concentrations insufficient to ensure the death of all. The acaricide acts as a selective screening process which concentrates resistant individuals already present in a population. The res ...
... Genetic resistance of ticks spreads by the reproduction of resistant individuals that have survived acaricidal concentrations insufficient to ensure the death of all. The acaricide acts as a selective screening process which concentrates resistant individuals already present in a population. The res ...
Introduction To Genetics
... alleles and are referred to have multiple alleles. a. This means that more than two possible alleles exist in a population. Example: colors of rabbits see page ...
... alleles and are referred to have multiple alleles. a. This means that more than two possible alleles exist in a population. Example: colors of rabbits see page ...
Genetics
... who in 1856 began experimenting with pea plants. He found that genes are always in pairs (each one passed on from a parent) and that some forms of a gene (alleles) are stronger than others. ...
... who in 1856 began experimenting with pea plants. He found that genes are always in pairs (each one passed on from a parent) and that some forms of a gene (alleles) are stronger than others. ...
SBI3C1: Genetics Test Review Part 1: Meiosis 1. Define the
... 11. List three ways in which biotechnology impacts your life 12. List some benefits obtained from genetically modifying plants. 13. What is the name of the agency responsible for regulating the development and testing of genetically modified foods in Canada? 14. What is Bt toxin? Why have people eng ...
... 11. List three ways in which biotechnology impacts your life 12. List some benefits obtained from genetically modifying plants. 13. What is the name of the agency responsible for regulating the development and testing of genetically modified foods in Canada? 14. What is Bt toxin? Why have people eng ...
genetics test study guide
... 17. List what the offspring look like. ________________________________________________________ 18. One way to increase the number of organisms in an endangered species is to let the few remaining individuals of that species breed. However, this breeding may also lead to species extinction because i ...
... 17. List what the offspring look like. ________________________________________________________ 18. One way to increase the number of organisms in an endangered species is to let the few remaining individuals of that species breed. However, this breeding may also lead to species extinction because i ...
Set 2 - The Science Spot
... 1. What term refers to the physical appearance of a trait? Example: Yellow body color 2. What term refers to the gene that is expressed when two different genes for a trait are present in a gene pair? 3. If your grandparents are the parental generation, what term would refer to your parents? 4. What ...
... 1. What term refers to the physical appearance of a trait? Example: Yellow body color 2. What term refers to the gene that is expressed when two different genes for a trait are present in a gene pair? 3. If your grandparents are the parental generation, what term would refer to your parents? 4. What ...
Mendelian Genetics
... • One gene influences more than one trait • Example: Sickle-cell anemia causes sickleshaped red blood cells but also resistance to malaria ...
... • One gene influences more than one trait • Example: Sickle-cell anemia causes sickleshaped red blood cells but also resistance to malaria ...
Heredity – notes - Effingham County Schools
... – Hybrids - Plants that were produced by parents with different traits In these experiments, he discovered that traits are inherited by parents passing __________________ to their offspring Individuals carry __________________ alleles for each trait, but only pass down one to their offspring One ___ ...
... – Hybrids - Plants that were produced by parents with different traits In these experiments, he discovered that traits are inherited by parents passing __________________ to their offspring Individuals carry __________________ alleles for each trait, but only pass down one to their offspring One ___ ...
Mendel`s Genetics
... 5. A gene is a section of DNA that codes for an expression of a trait. 6. Traits are controlled by alleles. An allele is one of a pair of genes for the same trait. 7. Organisms inherit one allele from each parent. 8. Some alleles are dominant over others. A dominant allele is one whose trait always ...
... 5. A gene is a section of DNA that codes for an expression of a trait. 6. Traits are controlled by alleles. An allele is one of a pair of genes for the same trait. 7. Organisms inherit one allele from each parent. 8. Some alleles are dominant over others. A dominant allele is one whose trait always ...
Heredity
... Mendel studied seven different pea plant traits. A trait is a specific characteristic such as seed color or plant height, which varies from one individual to the other. Mendel crossed plants with each of the seven contrasting characters and studied their offspring. Mendel called each original pair o ...
... Mendel studied seven different pea plant traits. A trait is a specific characteristic such as seed color or plant height, which varies from one individual to the other. Mendel crossed plants with each of the seven contrasting characters and studied their offspring. Mendel called each original pair o ...
Lesson 11: - Lake–Sumter State College
... • The phenotype is an accumulation of contributions by multiple genes • These traits show continuous variation and are referred to as quantitative traits – Ex. Human Height ...
... • The phenotype is an accumulation of contributions by multiple genes • These traits show continuous variation and are referred to as quantitative traits – Ex. Human Height ...























