1. Offspring that are the result of mating between two genetically
... inheritance of traits from parent to offspring. A 19th century central European monk scientist who published his ideas about genetics in 1866 but largely went unrecognized until 1900, which was long after his death. He acquired his understanding of genetics mostly through pea plant breeding experime ...
... inheritance of traits from parent to offspring. A 19th century central European monk scientist who published his ideas about genetics in 1866 but largely went unrecognized until 1900, which was long after his death. He acquired his understanding of genetics mostly through pea plant breeding experime ...
Document
... He also had a lot of free time. As for the peas? Well, they were: * easy to grow * inexpensive * easy to pollinate (either self or cross) * easy to study their TRAITS (characteristics) such as: height, seed pod shape, seed color, seed pod color, seed texture, flower position, and seed shape ...
... He also had a lot of free time. As for the peas? Well, they were: * easy to grow * inexpensive * easy to pollinate (either self or cross) * easy to study their TRAITS (characteristics) such as: height, seed pod shape, seed color, seed pod color, seed texture, flower position, and seed shape ...
Ei dian otsikkoa
... DNA repair enzymes. The transferred DNA is thus, either degraded or used as a substrate for DNA repair, resulting in its potential rearrangement and incorporation in the genomic DNA (Takano et al. (1997) Plant J 11: 353-361 ). Furthermore, specific transforming plasmid structure and construct proper ...
... DNA repair enzymes. The transferred DNA is thus, either degraded or used as a substrate for DNA repair, resulting in its potential rearrangement and incorporation in the genomic DNA (Takano et al. (1997) Plant J 11: 353-361 ). Furthermore, specific transforming plasmid structure and construct proper ...
Genetics PowerPoint - Ms. Melissa King Math and Science
... Law of Dominance: A law which says that one trait from the pair of alleles will be expressed, whereas the other is unexpressed. The allele expressed for a particular trait is regarded as the dominant whereas the other (which is unexpressed) is considered recessive. In the monohybrid cross (mating o ...
... Law of Dominance: A law which says that one trait from the pair of alleles will be expressed, whereas the other is unexpressed. The allele expressed for a particular trait is regarded as the dominant whereas the other (which is unexpressed) is considered recessive. In the monohybrid cross (mating o ...
Investigating the Results of Inherited Traits
... Heredity is the passing on of traits, or characteristics from parent to offspring. The units of heredity are called genes. Genes are found on the chromosomes in the cell. The combinations of genes for each trait occur by chance. When one gene in a gene pair is stronger than the other gene, the trait ...
... Heredity is the passing on of traits, or characteristics from parent to offspring. The units of heredity are called genes. Genes are found on the chromosomes in the cell. The combinations of genes for each trait occur by chance. When one gene in a gene pair is stronger than the other gene, the trait ...
Conjugative DNA transfer, antibiotic resistance and MDR bacteria
... Transposable Genetic Elements are also key to antibiotic resistance Transposable genetic elements (transposons) = DNA segments that can insert themselves at one or more sites in a genome. Remarkably, almost 50% of our chromosomes consist of transposable elements ...
... Transposable Genetic Elements are also key to antibiotic resistance Transposable genetic elements (transposons) = DNA segments that can insert themselves at one or more sites in a genome. Remarkably, almost 50% of our chromosomes consist of transposable elements ...
B1 6 Variation Inheritance and Cloning
... Rainbow trout with human genes and tomatoes grown with traits of flounder fish are the latest products of food scientists. It is good news for producers – the trout grow bigger and more quickly, while the tomatoes have a lower freezing point, preventing them becoming damaged. But consumer groups fea ...
... Rainbow trout with human genes and tomatoes grown with traits of flounder fish are the latest products of food scientists. It is good news for producers – the trout grow bigger and more quickly, while the tomatoes have a lower freezing point, preventing them becoming damaged. But consumer groups fea ...
Genetics PowerPoint Notes
... DNA: The ____________________________ that carries information about an organism that is passed on from _____________________ to _____________________. Chromosome: A collection of ____________. Human DNA has ____ chromosomes. Genes: A segments of your DNA on a _________________ that code for specifi ...
... DNA: The ____________________________ that carries information about an organism that is passed on from _____________________ to _____________________. Chromosome: A collection of ____________. Human DNA has ____ chromosomes. Genes: A segments of your DNA on a _________________ that code for specifi ...
genetics ppt - Schoolwires.net
... “Mom may be holding a full house while Dad has a straight flush, yet when junior gets a random half of each of their cards his poker hand may be a loser.” David Lykken (2001) ...
... “Mom may be holding a full house while Dad has a straight flush, yet when junior gets a random half of each of their cards his poker hand may be a loser.” David Lykken (2001) ...
Behavior Genetics: Predicting Individual Differences
... “Mom may be holding a full house while Dad has a straight flush, yet when junior gets a random half of each of their cards his poker hand may be a loser.” David Lykken (2001) ...
... “Mom may be holding a full house while Dad has a straight flush, yet when junior gets a random half of each of their cards his poker hand may be a loser.” David Lykken (2001) ...
Behavior Genetics: Predicting Individual Differences
... “Mom may be holding a full house while Dad has a straight flush, yet when junior gets a random half of each of their cards his poker hand may be a loser.” David Lykken (2001) ...
... “Mom may be holding a full house while Dad has a straight flush, yet when junior gets a random half of each of their cards his poker hand may be a loser.” David Lykken (2001) ...
Cell Evolution in Fast Motion - Max-Planck
... the hereditary material of the incorporated bacteria into the nuclear genome of the host cell. Today, the organellar genomes contain only a few dozen genes, although the bacteria from which they originated probably contained at least a few thousand genes. Sequence similarities between nuclear genes ...
... the hereditary material of the incorporated bacteria into the nuclear genome of the host cell. Today, the organellar genomes contain only a few dozen genes, although the bacteria from which they originated probably contained at least a few thousand genes. Sequence similarities between nuclear genes ...
Genetics - Midway ISD
... • Principle of probability can be used to predict the outcomes of genetic crosses. • Probability is the likelihood that a particular event will occur. – Probability can predict the outcome of genetic crosses because alleles segregate randomly. ...
... • Principle of probability can be used to predict the outcomes of genetic crosses. • Probability is the likelihood that a particular event will occur. – Probability can predict the outcome of genetic crosses because alleles segregate randomly. ...
Overview - Plant Root Genomics Consortium Project
... genetics, high through-put robotics and bioinformatics to derive large amounts of high quality biological information that will allow a greater understanding of the organism being studied. ...
... genetics, high through-put robotics and bioinformatics to derive large amounts of high quality biological information that will allow a greater understanding of the organism being studied. ...
Physcomitrella patens
... So why the interest in Physcomitrella patens? The haploidy of the predominant gametophyte generation in mosses provides technical advantages. In haploid organisms, we do not need to be concerned with genetic dominance, as we cannot have heterozygous haploid tissue. As a consequence, a lossof-functio ...
... So why the interest in Physcomitrella patens? The haploidy of the predominant gametophyte generation in mosses provides technical advantages. In haploid organisms, we do not need to be concerned with genetic dominance, as we cannot have heterozygous haploid tissue. As a consequence, a lossof-functio ...
Chapter 2 lesson 2
... medical advances. Knowing detailed information about human genes could help millions of people who suffer from illnesses caused by mistakes in their gene code. They could someday undergo genetic treatments to correct the problems. Doctors may also be able to detect and prevent illnesses like cancer ...
... medical advances. Knowing detailed information about human genes could help millions of people who suffer from illnesses caused by mistakes in their gene code. They could someday undergo genetic treatments to correct the problems. Doctors may also be able to detect and prevent illnesses like cancer ...
Introduction to Genetics Terms
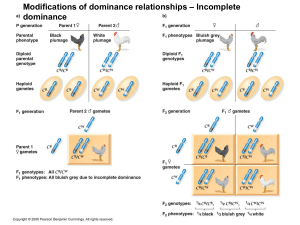
... 17. Incomplete Dominance: This is when one allele is not completely dominant over the other allele. For example, red and white flowers producing pink offspring. 18. Codominant Alleles: This is when both alleles contribute to the phenotype. For example, chickens that have black and white alleles have ...
... 17. Incomplete Dominance: This is when one allele is not completely dominant over the other allele. For example, red and white flowers producing pink offspring. 18. Codominant Alleles: This is when both alleles contribute to the phenotype. For example, chickens that have black and white alleles have ...
2. Biotechnology and Development
... equally important. Biotechnology is a subject of intense current interest in the developed world. In Europe and in the United States especially, it is viewed as one of the more promising “high technology” options available for resuscitating sagging industrial economics; however, biotechnology also o ...
... equally important. Biotechnology is a subject of intense current interest in the developed world. In Europe and in the United States especially, it is viewed as one of the more promising “high technology” options available for resuscitating sagging industrial economics; however, biotechnology also o ...
Science and GMO-relevant technology
... – Genes with inverted repeat DNA create double-stranded RNA, ...
... – Genes with inverted repeat DNA create double-stranded RNA, ...
Genetics_regulars
... his work with pea plants. known as the Father of Genetics chose traits that did not appear to blend was the first to follow single traits from generation to generation ...
... his work with pea plants. known as the Father of Genetics chose traits that did not appear to blend was the first to follow single traits from generation to generation ...
Homologous Pairs- Pairs of chromosomes with the same genes on
... • Alleles on the same chromosome are often inherited together. • The closer the genes are to each other on a chromosome the more likely they are to be inherited together. • Alleles that are far apart can be separated by crossing over. ...
... • Alleles on the same chromosome are often inherited together. • The closer the genes are to each other on a chromosome the more likely they are to be inherited together. • Alleles that are far apart can be separated by crossing over. ...
Heredity Presentation
... Dominant Trait: The trait observed when at least one dominant allele for a characteristic is inherited. ...
... Dominant Trait: The trait observed when at least one dominant allele for a characteristic is inherited. ...
Modifications of dominance relationships – Incomplete dominance
... At the molecular level, the mutation that causes TSD is in a gene that encodes for the enzyme hexaminidase A (hex A). Enzyme is responsible for the breakdown of gangliosides. ...
... At the molecular level, the mutation that causes TSD is in a gene that encodes for the enzyme hexaminidase A (hex A). Enzyme is responsible for the breakdown of gangliosides. ...