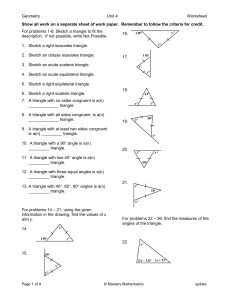
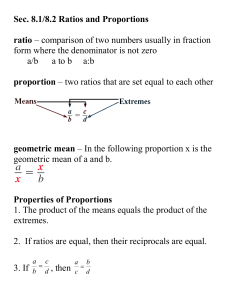
Identifying Triangles
... There are 3 different ways to identify triangles based on information given (angles and sides) ...
... There are 3 different ways to identify triangles based on information given (angles and sides) ...
Apollonian network
In combinatorial mathematics, an Apollonian network is an undirected graph formed by a process of recursively subdividing a triangle into three smaller triangles. Apollonian networks may equivalently be defined as the planar 3-trees, the maximal planar chordal graphs, the uniquely 4-colorable planar graphs, and the graphs of stacked polytopes. They are named after Apollonius of Perga, who studied a related circle-packing construction.