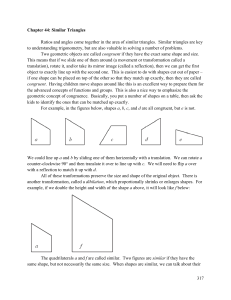
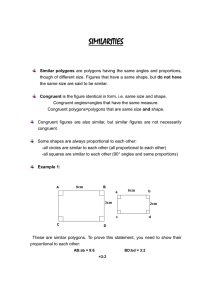
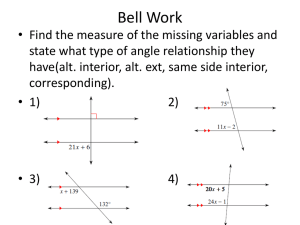
student objectives (competencies/outcomes)
... Identify and classify triangles by angles and by sides ...
... Identify and classify triangles by angles and by sides ...
Lesson Plan Format
... Since a triangle has three sides, it has three perpendicular bisectors. When you construct the perpendicular bisectors, you find that they have an interesting property. When three or more lines intersect at one point, the lines are said to be ________________. The ______________ concurrency is the p ...
... Since a triangle has three sides, it has three perpendicular bisectors. When you construct the perpendicular bisectors, you find that they have an interesting property. When three or more lines intersect at one point, the lines are said to be ________________. The ______________ concurrency is the p ...
Classify These Triangles by Sides and Angles
... • The measure of the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two nonadjacent interior angles ...
... • The measure of the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two nonadjacent interior angles ...
Unwrapped Standards: G.CO.10 - Prove theorems about triangles
... I can prove the base angles (and two sides) of an isosceles triangle are congruent (and the converse). I can prove an equilateral triangle is equiangular (and the converse). I can prove the segment joining midpoints of two sides of a triangle are parallel to the third side and half the length. I can ...
... I can prove the base angles (and two sides) of an isosceles triangle are congruent (and the converse). I can prove an equilateral triangle is equiangular (and the converse). I can prove the segment joining midpoints of two sides of a triangle are parallel to the third side and half the length. I can ...
Apollonian network
In combinatorial mathematics, an Apollonian network is an undirected graph formed by a process of recursively subdividing a triangle into three smaller triangles. Apollonian networks may equivalently be defined as the planar 3-trees, the maximal planar chordal graphs, the uniquely 4-colorable planar graphs, and the graphs of stacked polytopes. They are named after Apollonius of Perga, who studied a related circle-packing construction.