Chapter 52: Population Ecology
... Insect Cicada show a 13-17 year cycle In some species crowding effects the endocrine system=reduced fertility ...
... Insect Cicada show a 13-17 year cycle In some species crowding effects the endocrine system=reduced fertility ...
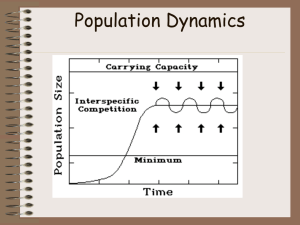
Population Dynamics
... Logistic Growth Occurs when resources become less available (Slows population growth rate) Slow population growth rate due to 1. Decrease in birthrate 2. Increase in deathrate 3. Immigration decreases 4. Emigration increases ...
... Logistic Growth Occurs when resources become less available (Slows population growth rate) Slow population growth rate due to 1. Decrease in birthrate 2. Increase in deathrate 3. Immigration decreases 4. Emigration increases ...
Populations - Helena High School
... Later, another portion is captured and the number of marked individuals within the sample is counted. Marked is assumed to be proportional to population ...
... Later, another portion is captured and the number of marked individuals within the sample is counted. Marked is assumed to be proportional to population ...
Characteristics of population growth pp
... • If only a few remain, inbreeding will occur. This reduces genetic variations. • Populations with low genetic variability are less able to adapt to changing environmental conditions. ...
... • If only a few remain, inbreeding will occur. This reduces genetic variations. • Populations with low genetic variability are less able to adapt to changing environmental conditions. ...
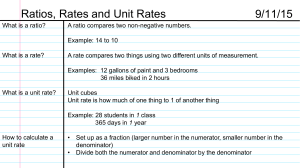
Ratios, Rates, and Unit Rates Ratios, Rates and Unit Rates
... Ratios, Rates and Unit Rates (cont.) Example: 657 Meeker students in 3 grades 657 Meeker students ...
... Ratios, Rates and Unit Rates (cont.) Example: 657 Meeker students in 3 grades 657 Meeker students ...
Chapter 13 Populations.pdf
... shrews. Owl pellets contain the parts of food that the owl could not digest. ...
... shrews. Owl pellets contain the parts of food that the owl could not digest. ...
Three Key Features of a Population
... • Declining birth rate or increasing death rate are caused by several limiting factors including: • Competition: ...
... • Declining birth rate or increasing death rate are caused by several limiting factors including: • Competition: ...
Document
... Survivorship curves- plot the proportion of individuals alive at each age Type I curve- produce few offspring, but give them good care, increasing survival to maturity (humans and large mammals) Type II curve- intermediate, mortality constant over life span (invertebrates and rodents) Type I ...
... Survivorship curves- plot the proportion of individuals alive at each age Type I curve- produce few offspring, but give them good care, increasing survival to maturity (humans and large mammals) Type II curve- intermediate, mortality constant over life span (invertebrates and rodents) Type I ...
ch5,6review
... • Birth or Death rate: #birthordeath/population • Population Growth Rate (r): birth-death/total population (convert to percent) ...
... • Birth or Death rate: #birthordeath/population • Population Growth Rate (r): birth-death/total population (convert to percent) ...
Document
... Predators kill few prey when the prey population is low, they kill more prey when the population is higher Detected by plotting mortality against population density and finding positive slope ...
... Predators kill few prey when the prey population is low, they kill more prey when the population is higher Detected by plotting mortality against population density and finding positive slope ...
populations - Ms. Leyda`s Homepage
... A. Density-dependent limiting factors: When population is high these take effect. 1. Competition: Organisms compete for food, water, space, sunlight, and other essentials. Example: Birds and mice both eat seeds. Effect on Evolution: Both species are put under pressure to change in ways that decreas ...
... A. Density-dependent limiting factors: When population is high these take effect. 1. Competition: Organisms compete for food, water, space, sunlight, and other essentials. Example: Birds and mice both eat seeds. Effect on Evolution: Both species are put under pressure to change in ways that decreas ...
Chapter 7 (Human population) Study Guide
... number of population (e.g. if r is positive and constant the population decrease each year) 3. Compare the population growth rate in developing vs. developed country. 4. Factors that controls population (e.g average births/woman) 5. Exponential growth of population. 6. Be able to read and analyze th ...
... number of population (e.g. if r is positive and constant the population decrease each year) 3. Compare the population growth rate in developing vs. developed country. 4. Factors that controls population (e.g average births/woman) 5. Exponential growth of population. 6. Be able to read and analyze th ...
Three Key Features of Populations Size
... Short life span Small body size Reproduce quickly Have many young Little parental care Ex: cockroaches, ...
... Short life span Small body size Reproduce quickly Have many young Little parental care Ex: cockroaches, ...
Population Growth
... • Stage 3: birth rate falls to meet the death rate Factors that influence human birth and death rates: nutrition, sanitation, medical treatment, education, higher standard of living ...
... • Stage 3: birth rate falls to meet the death rate Factors that influence human birth and death rates: nutrition, sanitation, medical treatment, education, higher standard of living ...
14.3 Factors Affecting Population Change
... • Wolves kill and eat deer. The wolves starve if no deer are present. The deer overpopulate and starve if their numbers increase. The relationship between wolves and deer is predation ...
... • Wolves kill and eat deer. The wolves starve if no deer are present. The deer overpopulate and starve if their numbers increase. The relationship between wolves and deer is predation ...
global population
... (a) Its performance is usually best at intermediate values. (b) Its performance can be shown with a tolerance curve. (c) Tolerance levels cannot change over the lifetime. (d) Tolerance levels can change through acclimation. ...
... (a) Its performance is usually best at intermediate values. (b) Its performance can be shown with a tolerance curve. (c) Tolerance levels cannot change over the lifetime. (d) Tolerance levels can change through acclimation. ...
Birth rate
The birth rate (technically, births/population rate) is the total number of live births per 1,000 of a population in a year. The rate of births in a population is calculated in several ways: live births from a universal registration system for births, deaths, and marriages; population counts from a census, and estimation through specialized demographic techniques. The birth rate (along with mortality and migration rate) are used to calculate population growth.The crude birth rate is the number of live births per 1,000 people per year. Another term used interchangeably with birth rate is natality. When the crude death rate is subtracted from the crude birth rate, the result is the rate of natural increase (RNI). This is equal to the rate of population change (excluding migration).The total (crude) birth rate (which includes all births)—typically indicated as births per 1,000 population—is distinguished from an age-specific rate (the number of births per 1,000 persons in an age group). The first known use of the term ""birth rate"" in English occurred in 1859.In 2012 the average global birth rate was 19.15 births per 1,000 total population, compared to 20.09 per 1,000 total population in 2007.The raw birth rate (not births/population rate) is 4.3 births/second for the world (2014 est.).