Chapter 18 notes
... c) Combinatorial control of expression 1) enhancers have binding sites for multiple proteins (control elements) 2) however only one or two proteins may bind enhancer 3) combination of control elements controls transcription. ...
... c) Combinatorial control of expression 1) enhancers have binding sites for multiple proteins (control elements) 2) however only one or two proteins may bind enhancer 3) combination of control elements controls transcription. ...
File
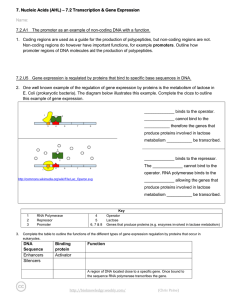
... 7. Nucleic Acids (AHL) – 7.2 Transcription & Gene Expression Name: 7.2.A1 The promoter as an example of non-coding DNA with a function. 1. Coding regions are used as a guide for the production of polypeptides, but non-coding regions are not. Non-coding regions do however have important functions, fo ...
... 7. Nucleic Acids (AHL) – 7.2 Transcription & Gene Expression Name: 7.2.A1 The promoter as an example of non-coding DNA with a function. 1. Coding regions are used as a guide for the production of polypeptides, but non-coding regions are not. Non-coding regions do however have important functions, fo ...
BY2208 SF Genetics Central Dogma McConnell_1.1
... duplicate itself and control the development of the rest of the cell in a specific way.” ...
... duplicate itself and control the development of the rest of the cell in a specific way.” ...
Protein Synthesis - Manhasset Public Schools
... 3) mRNA strand leaves the DNA strand when a “stop codon” is reached 3) the mRNA strand carries the code for the production of one polypeptide (protein) to the ribosome ...
... 3) mRNA strand leaves the DNA strand when a “stop codon” is reached 3) the mRNA strand carries the code for the production of one polypeptide (protein) to the ribosome ...
Lecture 7 Oct 10th
... If these sequences flank (are on either side) of a particular region of a particular organism's DNA, and NO OTHER ORGANISM'S DNA (or a different size product). This region would be a target sequence for PCR. The first step for PCR would be to synthesize "primers" that will be exactly the same as the ...
... If these sequences flank (are on either side) of a particular region of a particular organism's DNA, and NO OTHER ORGANISM'S DNA (or a different size product). This region would be a target sequence for PCR. The first step for PCR would be to synthesize "primers" that will be exactly the same as the ...
1 Genetics 301 Sample Second Midterm Examination Solutions
... support the growth of wild type bacteria, normally containing glucose + simple salts. ...
... support the growth of wild type bacteria, normally containing glucose + simple salts. ...
RNA chapter 13.1 - Red Hook Central Schools
... – Transcription: DNA segments serve as templates in creating complementary strands of RNA; occurs in the nucleus – RNA polymerase: the enzyme that binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands so transcription of one strand of DNA can take place – Promoters: a region of DNA that shows the RNA polymeras ...
... – Transcription: DNA segments serve as templates in creating complementary strands of RNA; occurs in the nucleus – RNA polymerase: the enzyme that binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands so transcription of one strand of DNA can take place – Promoters: a region of DNA that shows the RNA polymeras ...
Read on to find out…
... This hustle and bustle has been seen in mice and zebrafish, but there are hints that genes are also active for some time in deceased humans. This discovery could have implications for the safety of organ transplants as well as help pathologists pinpoint a time of death more precisely, perhaps to wit ...
... This hustle and bustle has been seen in mice and zebrafish, but there are hints that genes are also active for some time in deceased humans. This discovery could have implications for the safety of organ transplants as well as help pathologists pinpoint a time of death more precisely, perhaps to wit ...
Replication, Transcription, and Translation
... Helicase unzips/unwinds the DNA molecule DNA Polymerase brings in new nucleotides Ligase zips the new DNA back together Why is DNA Replication important? The important idea is that an exact duplication of the DNA message is required, so that each new cell in the body has the same set of genetic in ...
... Helicase unzips/unwinds the DNA molecule DNA Polymerase brings in new nucleotides Ligase zips the new DNA back together Why is DNA Replication important? The important idea is that an exact duplication of the DNA message is required, so that each new cell in the body has the same set of genetic in ...
Inferring genetic regulatory logic from expression data
... uncertainty about modeling variables and their dependencies. ...
... uncertainty about modeling variables and their dependencies. ...
Leukaemia Section t(4;21)(q31;q22) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... transactivation domain; forms heterodimers; widely expressed; nuclear localisation; transcription factor (activator) for various hematopoietic-specific genes. ...
... transactivation domain; forms heterodimers; widely expressed; nuclear localisation; transcription factor (activator) for various hematopoietic-specific genes. ...
The Molecular Study and Sequence Analysis of Wdhn13 (LEA
... The result of analysis showed that the Wdhn13 gene sequences in Sardari wheat were the most similar to the sequences in NCBI and the Wdhn13 gene sequences in urartu have the lowest similarity to the sequences in NCBI one. This difference is due to amino acid changes in the DNA sequence of samples. B ...
... The result of analysis showed that the Wdhn13 gene sequences in Sardari wheat were the most similar to the sequences in NCBI and the Wdhn13 gene sequences in urartu have the lowest similarity to the sequences in NCBI one. This difference is due to amino acid changes in the DNA sequence of samples. B ...
Pharmacogenomics: Translating Functional Genomics into Rational
... Genetic variation at the galactosemia locus • gene encodes galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase (GALT) • recessive mutation results in inability to metabolize galactose • causes mental retardation and death • some protection afforded by complete removal of milk from the diet • variant alleles e ...
... Genetic variation at the galactosemia locus • gene encodes galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase (GALT) • recessive mutation results in inability to metabolize galactose • causes mental retardation and death • some protection afforded by complete removal of milk from the diet • variant alleles e ...
summing-up - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... introns and separate sequences of the gene, called exons, which code for each part of the polypeptide chain. The genes that exhibit both introns and exons are called interrupted genes (or split genes). About half of human genes are interrupted genes. The production of mRNA from an ...
... introns and separate sequences of the gene, called exons, which code for each part of the polypeptide chain. The genes that exhibit both introns and exons are called interrupted genes (or split genes). About half of human genes are interrupted genes. The production of mRNA from an ...
DNA - Statistical Genetics, Kyoto University
... Association study of Complex Traits with DNA-markers Non-susceptible ...
... Association study of Complex Traits with DNA-markers Non-susceptible ...
RG 11 - Regulation of Gene Expression
... 6. Speculate the advantage(s) of a lysogenic cycle. 7. Explain how the replication of retroviruses (like HIV) is different from that of other viruses. 8. Listed below are the steps in the replication of a retrovirus. Put the steps in the correct order. _____ Attachment of virus _____ Reverse transcr ...
... 6. Speculate the advantage(s) of a lysogenic cycle. 7. Explain how the replication of retroviruses (like HIV) is different from that of other viruses. 8. Listed below are the steps in the replication of a retrovirus. Put the steps in the correct order. _____ Attachment of virus _____ Reverse transcr ...
Protein Synthesis - Helena High School
... Use notes from the PowerPoint and complete the following questions. This will be the study guide for questions about transcription/translation. 1. DNA codes for what macromolecule? Provide three examples of proteins necessary in our bodies a. b. c. 2. Where is the code within the DNA molecule that p ...
... Use notes from the PowerPoint and complete the following questions. This will be the study guide for questions about transcription/translation. 1. DNA codes for what macromolecule? Provide three examples of proteins necessary in our bodies a. b. c. 2. Where is the code within the DNA molecule that p ...
BIO 101: Transcription and Translation
... been completely transcribed In eukaryotes, this is pre-mRNA and must be further processed ...
... been completely transcribed In eukaryotes, this is pre-mRNA and must be further processed ...
BIO 101: Transcription and Translation
... been completely transcribed In eukaryotes, this is pre-mRNA and must be further processed ...
... been completely transcribed In eukaryotes, this is pre-mRNA and must be further processed ...
Transcriptome - Nematode bioinformatics. Analysis tools and data
... • With appropriate biological replicates, it is possible to select statistically meaningful genes/patterns. • Sensitivity and selectivity are inversely related - e.g. increased selection of true positives WILL result in more false positive and less false negatives. • False negatives are lost opportu ...
... • With appropriate biological replicates, it is possible to select statistically meaningful genes/patterns. • Sensitivity and selectivity are inversely related - e.g. increased selection of true positives WILL result in more false positive and less false negatives. • False negatives are lost opportu ...
Control of Gene Expression (PowerPoint) Madison 2009
... individual. Yet these three organs are obviously different. In what ways are they different? ...
... individual. Yet these three organs are obviously different. In what ways are they different? ...
RNA-Seq

RNA-seq (RNA sequencing), also called whole transcriptome shotgun sequencing (WTSS), is a technology that uses the capabilities of next-generation sequencing to reveal a snapshot of RNA presence and quantity from a genome at a given moment in time.