HGT
... • HGT, also known as Lateral Gene Transfer (LGT), is the transfer of genetic material between organisms other than through vertical gene that studies vertical transfer of What is the science genes? transfer • They are “alien” regions in the genome (chromosome or plasmids) ...
... • HGT, also known as Lateral Gene Transfer (LGT), is the transfer of genetic material between organisms other than through vertical gene that studies vertical transfer of What is the science genes? transfer • They are “alien” regions in the genome (chromosome or plasmids) ...
Gene Section OSGIN1 (oxidative stress induced growth inhibitor 1)
... inhibitor, belongs to OKL38 protein family. ...
... inhibitor, belongs to OKL38 protein family. ...
4th Edition CHAPTER 16 1. The advantages of biological over
... 7. Creating a chimeric cry1C-cry1Ab protein is 3-34 times more affective than using just the cry1C toxin, because the cry1Ab portion (even though it is cleaved off) increases the stability and therefore the half-life of the protein. The protein degrades slower giving it more time to kill insects. 9. ...
... 7. Creating a chimeric cry1C-cry1Ab protein is 3-34 times more affective than using just the cry1C toxin, because the cry1Ab portion (even though it is cleaved off) increases the stability and therefore the half-life of the protein. The protein degrades slower giving it more time to kill insects. 9. ...
Noncoding DNA - University of Mysore
... Noncoding RNA species help sequester different families of proteins and thus may regulate their activity A large variety of proteins are involved in processing (like splicing) and transport of the different protein-coding transcripts synthesized by the DNA templates. Since the cellular activities ar ...
... Noncoding RNA species help sequester different families of proteins and thus may regulate their activity A large variety of proteins are involved in processing (like splicing) and transport of the different protein-coding transcripts synthesized by the DNA templates. Since the cellular activities ar ...
Biology 340 Molecular Biology
... --Most are multicellular and made of different cell types. --Different cells express distinct subsets of genes. --Gene expression is regulated so genes are turned on when they are needed during development and in the correct cell types. --Most genes in higher eukaryotes are regulated by controlling ...
... --Most are multicellular and made of different cell types. --Different cells express distinct subsets of genes. --Gene expression is regulated so genes are turned on when they are needed during development and in the correct cell types. --Most genes in higher eukaryotes are regulated by controlling ...
Document
... RNA is produced one nucleotide at a time by matching base pairs with the nucleotides in DNA. ...
... RNA is produced one nucleotide at a time by matching base pairs with the nucleotides in DNA. ...
Slides PPT
... • When you want to identify or distinguish one organism from another, such as in forensic testing, you investigate the genome. ...
... • When you want to identify or distinguish one organism from another, such as in forensic testing, you investigate the genome. ...
Protocol
... The following protocol is an example for quantifying RNA with StrandBrite™ Green. Allow the StrandBrite™ Green to warm to room temperature before opening the vial. Note 1: Always use clean disposable gloves while handling all materials to prevent RNase contamination. Note 2: No data are available ad ...
... The following protocol is an example for quantifying RNA with StrandBrite™ Green. Allow the StrandBrite™ Green to warm to room temperature before opening the vial. Note 1: Always use clean disposable gloves while handling all materials to prevent RNase contamination. Note 2: No data are available ad ...
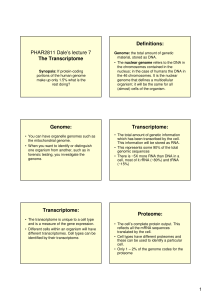
PHAR2811 Dale`s lecture 7 The Transcriptome Definitions: Genome
... material, stored as DNA. • The nuclear genome refers to the DNA in the chromosomes contained in the nucleus; in the case of humans the DNA in the 46 chromosomes. It is the nuclear genome that defines a multicellular organism; it will be the same for all (almost) cells of the organism. ...
... material, stored as DNA. • The nuclear genome refers to the DNA in the chromosomes contained in the nucleus; in the case of humans the DNA in the 46 chromosomes. It is the nuclear genome that defines a multicellular organism; it will be the same for all (almost) cells of the organism. ...
Bacterial Genetic
... • E. coli chromosome has 100 times more DNA than in a typical virus, but much less than a eukaryotic cell. • Packed into nucleoid region of cell • Plasmid small circular extra piece of DNA ...
... • E. coli chromosome has 100 times more DNA than in a typical virus, but much less than a eukaryotic cell. • Packed into nucleoid region of cell • Plasmid small circular extra piece of DNA ...
Control of Gene Expression
... 7. Repressible operons are involved in anabolic pathways that synthesize substances needed by cells. Eukaryotic Gene Expression - short verison When genes are expressed, the genetic information (base sequence) on DNA is first transcribed (copied) to a molecule of messenger RNA in a process similar t ...
... 7. Repressible operons are involved in anabolic pathways that synthesize substances needed by cells. Eukaryotic Gene Expression - short verison When genes are expressed, the genetic information (base sequence) on DNA is first transcribed (copied) to a molecule of messenger RNA in a process similar t ...
File
... A female has two X chromosomes in her cells. A male has an X and Y chromosome in his cells. Not everything can be inherited from parent to child. Scientists used a chart called a pedigree to study how something is inherited in a family. A person that has one allele for a disease but is not affected ...
... A female has two X chromosomes in her cells. A male has an X and Y chromosome in his cells. Not everything can be inherited from parent to child. Scientists used a chart called a pedigree to study how something is inherited in a family. A person that has one allele for a disease but is not affected ...
Candidate Gene Approach
... 1. Maternally supplied genes i.e. the reason why maternal effect screen had to be conducted separately. 2. Involved in patterning/differentiation of internal structures 3. Only first instance of essential function may be scored ...
... 1. Maternally supplied genes i.e. the reason why maternal effect screen had to be conducted separately. 2. Involved in patterning/differentiation of internal structures 3. Only first instance of essential function may be scored ...
DNA AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
... IDENTICLE DNA WILL FRAGMENT IN THE SAME LOCATION WHICH WILL PRODUCE THE SAME FRAGMENT PATTERNS ON A GEL DNA FROM DIFFERENT PEOPLE WILL FRAGMENT AT DIFFERENT PLACES AND THE FRAGMENT PATTERNS WILL BE DIFFERENT ...
... IDENTICLE DNA WILL FRAGMENT IN THE SAME LOCATION WHICH WILL PRODUCE THE SAME FRAGMENT PATTERNS ON A GEL DNA FROM DIFFERENT PEOPLE WILL FRAGMENT AT DIFFERENT PLACES AND THE FRAGMENT PATTERNS WILL BE DIFFERENT ...
Chapter 7A
... The control of gene expression by transcription activation and repression has been studied extensively in bacteria. As an example, the E. coli lac operon, which encodes 3 genes (lacZYA) involved in lactose metabolism, uses both mechanisms of control (Fig. 7.3). A specific repressor protein (the lac ...
... The control of gene expression by transcription activation and repression has been studied extensively in bacteria. As an example, the E. coli lac operon, which encodes 3 genes (lacZYA) involved in lactose metabolism, uses both mechanisms of control (Fig. 7.3). A specific repressor protein (the lac ...
DNA
... inherited disorder in which afflicted individuals have defective hemoglobin, and thus are unable to properly transport oxygen to tissues. Heterozygotes usually appear normal. Homozygotes have Sickle-Cell, but are resistant to malaria. ...
... inherited disorder in which afflicted individuals have defective hemoglobin, and thus are unable to properly transport oxygen to tissues. Heterozygotes usually appear normal. Homozygotes have Sickle-Cell, but are resistant to malaria. ...
投影片 1
... back to the cytoplasm. Most found in cytosol and ER. Three binding site for tRNA: E, P, and A site. During the process of protein synthesis, no more than two sites contain tRNA mocules at a time. ...
... back to the cytoplasm. Most found in cytosol and ER. Three binding site for tRNA: E, P, and A site. During the process of protein synthesis, no more than two sites contain tRNA mocules at a time. ...
20070903115012101
... 1. Randomly assign the n genes to k classes. 2. Optimise parameters for each class 3. Compute the posterior probability for each gene with the parameters from each class. 4. Move each gene into the class for which it has highest posterior probability 5. Go to step 2, when no genes change class ...
... 1. Randomly assign the n genes to k classes. 2. Optimise parameters for each class 3. Compute the posterior probability for each gene with the parameters from each class. 4. Move each gene into the class for which it has highest posterior probability 5. Go to step 2, when no genes change class ...
Directed Reading B
... 13. When a base is left out, the change is called a(n) ______________________. 14. When an extra base is added, the change is called a(n) ______________________. 15. When the wrong base is used, the change is called a(n) ______________________. Do Mutations Matter? Circle the letter of the best answ ...
... 13. When a base is left out, the change is called a(n) ______________________. 14. When an extra base is added, the change is called a(n) ______________________. 15. When the wrong base is used, the change is called a(n) ______________________. Do Mutations Matter? Circle the letter of the best answ ...
Chapter 14 Outline
... Incomplete Dominance: where the phenotype of the heterozygote is intermediate between the two homozygotes. Co-Dominance: where the phenotypic effects of two alleles can be seen concurrently Eg. ABO blood system IA and IB are co-dominant and both are dominant to i. IA and IB code for enzymes that add ...
... Incomplete Dominance: where the phenotype of the heterozygote is intermediate between the two homozygotes. Co-Dominance: where the phenotypic effects of two alleles can be seen concurrently Eg. ABO blood system IA and IB are co-dominant and both are dominant to i. IA and IB code for enzymes that add ...
The community effect in animal development
... • exhibits the community effect, and • confirms and refines Davidson’s work. • Future work: • controlling the community effect in space ...
... • exhibits the community effect, and • confirms and refines Davidson’s work. • Future work: • controlling the community effect in space ...
Document
... • A probe is a labeled (usually radioactive or fluorescent) single-stranded oligonucleotide, synthesized to be complementary to the sequence of interest – probe sequence is known • Attach single-stranded DNA to a membrane (or other solid support) and incubate with the probe so that it hybridizes • V ...
... • A probe is a labeled (usually radioactive or fluorescent) single-stranded oligonucleotide, synthesized to be complementary to the sequence of interest – probe sequence is known • Attach single-stranded DNA to a membrane (or other solid support) and incubate with the probe so that it hybridizes • V ...
RNA-Seq

RNA-seq (RNA sequencing), also called whole transcriptome shotgun sequencing (WTSS), is a technology that uses the capabilities of next-generation sequencing to reveal a snapshot of RNA presence and quantity from a genome at a given moment in time.