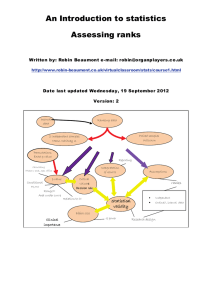
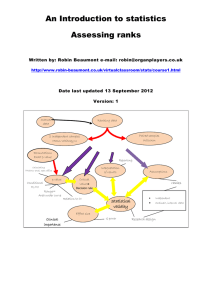
ordinal data
... normally distributed. In the previous chapters a great deal was made about the assumption that samples and the populations from which they come were normally distributed. But how can we be sure? This question has plagued a large number of researchers and differences of opinion as to how important th ...
... normally distributed. In the previous chapters a great deal was made about the assumption that samples and the populations from which they come were normally distributed. But how can we be sure? This question has plagued a large number of researchers and differences of opinion as to how important th ...
Measuring Skewness: A Forgotten Statistic?
... difficulty, they can see how the mean, median, and mode can indicate the center, and how standard deviation and range can describe variability. But the terms skewness and kurtosis are non-intuitive. Worse, skewness and kurtosis statistics and formulas are opaque to the average student, and lack conc ...
... difficulty, they can see how the mean, median, and mode can indicate the center, and how standard deviation and range can describe variability. But the terms skewness and kurtosis are non-intuitive. Worse, skewness and kurtosis statistics and formulas are opaque to the average student, and lack conc ...
KEY to exam 8-11-06 (34 Kb ) STT 315 Summer 2006
... Referring to the above, a test will be made of the null hypothesis H0: p = 0.2 versus the alternative H1: p > 0.2. Alpha = 0.02. b. Determine the test statistic. Do not evaluate. Test statistic = (pHAT-p0)/(Sqrt[p0 q0]/Sqrt[n]) = (0.22 – 0.2)/(Sqrt[0.2 0.8]/Sqrt[100]) c. If the test statistic is 2.3 ...
... Referring to the above, a test will be made of the null hypothesis H0: p = 0.2 versus the alternative H1: p > 0.2. Alpha = 0.02. b. Determine the test statistic. Do not evaluate. Test statistic = (pHAT-p0)/(Sqrt[p0 q0]/Sqrt[n]) = (0.22 – 0.2)/(Sqrt[0.2 0.8]/Sqrt[100]) c. If the test statistic is 2.3 ...
+ Confidence Intervals: The Basics
... In Chapter 7, we learned that different samples yield different results for our estimate. Statistical inference uses the language of probability to express the strength of our conclusions by taking chance variation due to random selection or random assignment into account. In this chapter, we’ll le ...
... In Chapter 7, we learned that different samples yield different results for our estimate. Statistical inference uses the language of probability to express the strength of our conclusions by taking chance variation due to random selection or random assignment into account. In this chapter, we’ll le ...