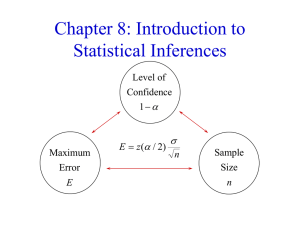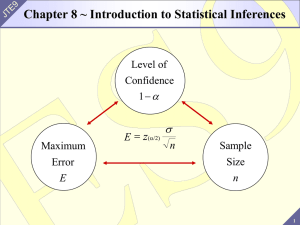
Sec. 8.1 PowerPoint
... parameter, what would it be? If you were estimating a population mean , you would probably use x . If you were estimating a population proportion p, you might use pˆ . In both cases, you would be providing a point estimate of the parameter of interest. ...
... parameter, what would it be? If you were estimating a population mean , you would probably use x . If you were estimating a population proportion p, you might use pˆ . In both cases, you would be providing a point estimate of the parameter of interest. ...
Unit 24 Hypothesis Tests about Means
... background music. Then, ∑d represents the sum of these differences and d represents the mean of these differences. Enter the values of ∑d and d in the appropriate places in Table 24-2. (You should find that ∑d = +4.2 and d = +0.6.) Also, ∑(d – d )2 represents the sum of the squared deviations of the ...
... background music. Then, ∑d represents the sum of these differences and d represents the mean of these differences. Enter the values of ∑d and d in the appropriate places in Table 24-2. (You should find that ∑d = +4.2 and d = +0.6.) Also, ∑(d – d )2 represents the sum of the squared deviations of the ...
Statistical Inference
... in addition to its previous values 2 and 8 then a = P[ type I error] = p(0) + p(1) + p(9) + p(10) = 0.021, where again p(x) are binomial probabilities with p = ½ and n = 10 . . b = P[ type II error] = p(2) + p(3) + p(4) + p(5) + p(6) + p(7) + p(8). Tabled values of are given on the next page. ...
... in addition to its previous values 2 and 8 then a = P[ type I error] = p(0) + p(1) + p(9) + p(10) = 0.021, where again p(x) are binomial probabilities with p = ½ and n = 10 . . b = P[ type II error] = p(2) + p(3) + p(4) + p(5) + p(6) + p(7) + p(8). Tabled values of are given on the next page. ...
Statistical Inference
... in addition to its previous values 2 and 8 then a = P[ type I error] = p(0) + p(1) + p(9) + p(10) = 0.021, where again p(x) are binomial probabilities with p = ½ and n = 10 . . b = P[ type II error] = p(2) + p(3) + p(4) + p(5) + p(6) + p(7) + p(8). Tabled values of are given on the next page. ...
... in addition to its previous values 2 and 8 then a = P[ type I error] = p(0) + p(1) + p(9) + p(10) = 0.021, where again p(x) are binomial probabilities with p = ½ and n = 10 . . b = P[ type II error] = p(2) + p(3) + p(4) + p(5) + p(6) + p(7) + p(8). Tabled values of are given on the next page. ...