Heredity
... determined by your genes, or can you control some of them? Where, or more correctly, from whom did you get these traits? Did you get all of them from you mother? …from your father? Or did one or more traits seem to skip your parents and come from your grandparents? If your siblings have the same par ...
... determined by your genes, or can you control some of them? Where, or more correctly, from whom did you get these traits? Did you get all of them from you mother? …from your father? Or did one or more traits seem to skip your parents and come from your grandparents? If your siblings have the same par ...
Essential Genetics for Horsemen
... from either the sire or dam and an ‘e’ allele from the other parent will have black as their base coat color. If the foal receives an ‘e’ allele from both parents the color will be chestnut. A black base coat color will be EE’ or ‘Ee’. A chestnut base coat color will be ‘ee’. Other genes can interac ...
... from either the sire or dam and an ‘e’ allele from the other parent will have black as their base coat color. If the foal receives an ‘e’ allele from both parents the color will be chestnut. A black base coat color will be EE’ or ‘Ee’. A chestnut base coat color will be ‘ee’. Other genes can interac ...
Slide 1
... polymorphisms used in the association model explain the observed linkage or whether other polymorphisms in that region are expected to be of influence QTDT: simple, quick, straigtforward, but not so flexible in terms of models Mx: can be considered less simple, but highly flexible ...
... polymorphisms used in the association model explain the observed linkage or whether other polymorphisms in that region are expected to be of influence QTDT: simple, quick, straigtforward, but not so flexible in terms of models Mx: can be considered less simple, but highly flexible ...
Introduction, Consequences of being a plant
... Fitness and natural selection – with genetic structure now clearly important to local demography, how do we assess fitness and the occurrence of natural selection? The genetic structure of a population is influenced by: gene flow: changes in allele frequency caused by migration natural selection: N ...
... Fitness and natural selection – with genetic structure now clearly important to local demography, how do we assess fitness and the occurrence of natural selection? The genetic structure of a population is influenced by: gene flow: changes in allele frequency caused by migration natural selection: N ...
Genetics - Garnet Valley
... Genetically Engineering PlantsPlants are created by genetically inserting the desired genes of one plant into another plant you want to show those genes. ...
... Genetically Engineering PlantsPlants are created by genetically inserting the desired genes of one plant into another plant you want to show those genes. ...
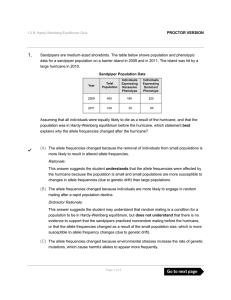
Sandpipers are medium-sized shorebirds. The table below shows
... This answer suggests the student may understand that in order to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, a population cannot have mutations, but does not understand that the rate at which mutations occur does not increase in response to environmental stresses, or that the allele frequencies changed as a r ...
... This answer suggests the student may understand that in order to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, a population cannot have mutations, but does not understand that the rate at which mutations occur does not increase in response to environmental stresses, or that the allele frequencies changed as a r ...
heredity article and questions
... Some of these are hair color, hair texture, eye color, shape of ear lobes, skin type, and height. Traits like height, weight, and the shape of your body and face are the kinds of traits that are inherited, but they can also be greatly influenced by your environment. For example, your diet, state of ...
... Some of these are hair color, hair texture, eye color, shape of ear lobes, skin type, and height. Traits like height, weight, and the shape of your body and face are the kinds of traits that are inherited, but they can also be greatly influenced by your environment. For example, your diet, state of ...
Multiplex STR Analysis by Capillary Electrophoresis
... Most short tandem repeat loci used in identity testing have repeats that are four base pairs in length, with allele sizes between 100bp and 300bp. Table 1 lists some of the commonly used STRs. The relatively small size of STR alleles reduces the effects of preferential amplification. Thus, more high ...
... Most short tandem repeat loci used in identity testing have repeats that are four base pairs in length, with allele sizes between 100bp and 300bp. Table 1 lists some of the commonly used STRs. The relatively small size of STR alleles reduces the effects of preferential amplification. Thus, more high ...
CST Review Questions for mini
... If a corn plant has a genotype of TtYy, what are the possible genetic combinations present in a single grain of pollen from this plant? What is crossing over? When does it occur? Why does it occur? Describe the amount of chromosomes in an egg or sperm cell. How does that compare to a fertilized embr ...
... If a corn plant has a genotype of TtYy, what are the possible genetic combinations present in a single grain of pollen from this plant? What is crossing over? When does it occur? Why does it occur? Describe the amount of chromosomes in an egg or sperm cell. How does that compare to a fertilized embr ...
Chapter 11 Practice Test PArt 1
... _____ 6. A male and female bison that are both heterozygous for normal skin pigmentation (Aa) produce an albino offspring (aa). Which of Mendel’s principles applies? a. dominance only c. dominance and segregation b. independent assortment only d. segregation only _____ 7. When one allele is not comp ...
... _____ 6. A male and female bison that are both heterozygous for normal skin pigmentation (Aa) produce an albino offspring (aa). Which of Mendel’s principles applies? a. dominance only c. dominance and segregation b. independent assortment only d. segregation only _____ 7. When one allele is not comp ...
Chapter 12
... generation plants selfpollinate and produce new plants. He called this new generation of offspring the second filial generation or F2 generation. Notice how many of each trait was produced— what’s the deal? ...
... generation plants selfpollinate and produce new plants. He called this new generation of offspring the second filial generation or F2 generation. Notice how many of each trait was produced— what’s the deal? ...
Document
... individual are the same, the individual is said to be homozygous. (dominant or recessive) • If the alleles of a particular gene present in an individual are different, the individual is heterozygous. • In heterozygous individuals, only the dominant allele is expressed; the recessive allele is presen ...
... individual are the same, the individual is said to be homozygous. (dominant or recessive) • If the alleles of a particular gene present in an individual are different, the individual is heterozygous. • In heterozygous individuals, only the dominant allele is expressed; the recessive allele is presen ...
Heat-shock protein (HSP70-2) allelic frequencies in three
... included in the study, the splendor of the Nahua ethnic group was achieved in the 15th century, but underwent anihilation by the Aztec civilization.7 The restriction pattern observed in all amplified DNA samples generated by endonuclease PstI is consistent with the pattern described in previous stud ...
... included in the study, the splendor of the Nahua ethnic group was achieved in the 15th century, but underwent anihilation by the Aztec civilization.7 The restriction pattern observed in all amplified DNA samples generated by endonuclease PstI is consistent with the pattern described in previous stud ...
I-1 to I-7
... 1) Straightforward-but-tedious way: Consider all possible matings. 2) Easier way – use intuition : random mating = random union of haploid gametes. – if intuition is correct, then: frequencies of A and a among the gametes produced = frequencies in mating adults: p and q = 1– p . As with the haploid ...
... 1) Straightforward-but-tedious way: Consider all possible matings. 2) Easier way – use intuition : random mating = random union of haploid gametes. – if intuition is correct, then: frequencies of A and a among the gametes produced = frequencies in mating adults: p and q = 1– p . As with the haploid ...
Adaptation, natural selection and evolution
... • Farmers spray insecticides to stop crops being eaten by insects • GM crops have been modified to contain a gene that produces a toxin; if insects eat the crop they die • Fewer chemicals are used due to the plants inbuilt resistance • The effectiveness of this technique has reduced because insects ...
... • Farmers spray insecticides to stop crops being eaten by insects • GM crops have been modified to contain a gene that produces a toxin; if insects eat the crop they die • Fewer chemicals are used due to the plants inbuilt resistance • The effectiveness of this technique has reduced because insects ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.