Genetic mapping and manipulation: Chapter 8
... 5. Genetic tests for dominance classes To attempt to distinguish between various classes of dominant mutations, a number of genetic tests can be performed. For example, to determine if a mutant phenotype observed in a heterozygous animal is due to haploinsufficiency, one can directly examine animals ...
... 5. Genetic tests for dominance classes To attempt to distinguish between various classes of dominant mutations, a number of genetic tests can be performed. For example, to determine if a mutant phenotype observed in a heterozygous animal is due to haploinsufficiency, one can directly examine animals ...
Simulation of Population Genetics Models with SAS
... Much of the early work in population genetics has fooused on models involving single loci o~ small numbers of linked lo¢i (usually two) [1]. However, there is mounting evidence for high degrees of polymorphism [1,2J, and it has been established that synergistic effects "totally unpredictable from. t ...
... Much of the early work in population genetics has fooused on models involving single loci o~ small numbers of linked lo¢i (usually two) [1]. However, there is mounting evidence for high degrees of polymorphism [1,2J, and it has been established that synergistic effects "totally unpredictable from. t ...
Uses and abuses of genetic engineering
... was being screened for an inherited genetic disorder. However, this decision has recently been under judicial review. The direction such selection procedures could potentially take is illustrated by a recent case in which a child was deliberately conceived using donor insemination by a male with a g ...
... was being screened for an inherited genetic disorder. However, this decision has recently been under judicial review. The direction such selection procedures could potentially take is illustrated by a recent case in which a child was deliberately conceived using donor insemination by a male with a g ...
In-class Interactive Case Discussion PowerPoint
... The case continues… 1. Dominique would like to know with 100% certainty if she has the BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations that increase the risk of earlyonset breast cancer. 2. Women of African descent with a family history of breast or ovarian cancer were significantly less likely to undergo genetic co ...
... The case continues… 1. Dominique would like to know with 100% certainty if she has the BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations that increase the risk of earlyonset breast cancer. 2. Women of African descent with a family history of breast or ovarian cancer were significantly less likely to undergo genetic co ...
File
... A condition in which the alleles of a gene pair in a heterozygote are fully expressed thereby resulting in offspring with a phenotype that is neither dominant nor recessive. SupplementA typical example showing codominance is the ABO blood group system. For instance, a person having A allele and B al ...
... A condition in which the alleles of a gene pair in a heterozygote are fully expressed thereby resulting in offspring with a phenotype that is neither dominant nor recessive. SupplementA typical example showing codominance is the ABO blood group system. For instance, a person having A allele and B al ...
Estimating Allele Frequencies for a Specific Trait within a Sample
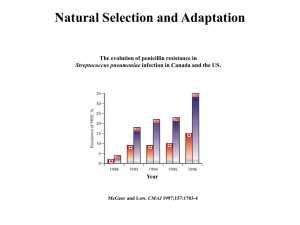
... consciously adapt to their environments. For example, that the peppered moth can change its color, the giraffe can permanently stretch its neck, the polar bear can turn itself white – all so that they can better survive in their environments. In reality, populations of organisms, not the individuals ...
... consciously adapt to their environments. For example, that the peppered moth can change its color, the giraffe can permanently stretch its neck, the polar bear can turn itself white – all so that they can better survive in their environments. In reality, populations of organisms, not the individuals ...
DNA Structure - StudyTime NZ
... As egg cells are a type of gamete, they will undergo Meiosis. This is because they are only involved in reproduction, and have no need to perform growth or repair. Meiosis involves two cell divisions but only one DNA replication. This results in daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes pre ...
... As egg cells are a type of gamete, they will undergo Meiosis. This is because they are only involved in reproduction, and have no need to perform growth or repair. Meiosis involves two cell divisions but only one DNA replication. This results in daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes pre ...
Document
... advantage, and 3) the size of the population. In the following, we deal with the mean fixation time of those mutations that will eventually become fixed in the population. This variable is call conditional fixation time. In the case of a new mutation whose initial frequency in a diploid population i ...
... advantage, and 3) the size of the population. In the following, we deal with the mean fixation time of those mutations that will eventually become fixed in the population. This variable is call conditional fixation time. In the case of a new mutation whose initial frequency in a diploid population i ...
What is Genetic Counselling? Cont.
... Testing Parents for Carrier Status • Carrier testing is used to identify people who carry one copy of a gene mutation that, when present in two copies, causes a genetic disorder. • Offered to individuals who have a family history of a genetic disorder & to people in ethnic groups with an increased ...
... Testing Parents for Carrier Status • Carrier testing is used to identify people who carry one copy of a gene mutation that, when present in two copies, causes a genetic disorder. • Offered to individuals who have a family history of a genetic disorder & to people in ethnic groups with an increased ...
PART ONE - flickbio
... 2. Find your first partner and mate to make your first offspring. 3. The offspring are made by randomly selecting one card from each person. The resulting baby will have a genotype based on the cards chosen. For example, the baby may be aa. Each person should take back the card that they contributed ...
... 2. Find your first partner and mate to make your first offspring. 3. The offspring are made by randomly selecting one card from each person. The resulting baby will have a genotype based on the cards chosen. For example, the baby may be aa. Each person should take back the card that they contributed ...
Genetics and Inheritance
... He was the first person to succeed in predicting how traits are transferred from one generation to the next. ...
... He was the first person to succeed in predicting how traits are transferred from one generation to the next. ...
No Slide Title
... 3.If two alleles differ, then one, the dominant allele, is fully expressed in the the organism’s appearance. • The other, the recessive allele, has no noticeable effect on the organism’s appearance. – Mendel’s F1 plants had purple flowers because the purple-flower allele is dominant and the white-f ...
... 3.If two alleles differ, then one, the dominant allele, is fully expressed in the the organism’s appearance. • The other, the recessive allele, has no noticeable effect on the organism’s appearance. – Mendel’s F1 plants had purple flowers because the purple-flower allele is dominant and the white-f ...
Supplemental File S4. Predisposition to Cancer
... BRCA1+/BRCA1+. In addition, in order for male II-2 to have affected daughters with unaffected woman II-1, he would have the BRCA1- mutation on his X-chromosome. Consequently, all of II-2’s daughters would likely be affected, but here III-1 is unaffected. X-linked recessive and autosomal recessive ar ...
... BRCA1+/BRCA1+. In addition, in order for male II-2 to have affected daughters with unaffected woman II-1, he would have the BRCA1- mutation on his X-chromosome. Consequently, all of II-2’s daughters would likely be affected, but here III-1 is unaffected. X-linked recessive and autosomal recessive ar ...
Pedigree Charts
... • Every generation (row) is represented by a Roman numeral, • Each member in a generation is represented by an Arabic numeral. (Arabic numerals numbered from the left.) ...
... • Every generation (row) is represented by a Roman numeral, • Each member in a generation is represented by an Arabic numeral. (Arabic numerals numbered from the left.) ...
Jeopardy Higher Level Genetics HANNAH
... OFFSPRING HAVE THE SAME PHENOTYPE AS THE PARENT. WHAT CAN BE CONCLUDED FROM THIS RESULT? THAT THE PARENT IS HETEROZYGOUS FOR THE TRAIT ...
... OFFSPRING HAVE THE SAME PHENOTYPE AS THE PARENT. WHAT CAN BE CONCLUDED FROM THIS RESULT? THAT THE PARENT IS HETEROZYGOUS FOR THE TRAIT ...
Heredity - Mr.I's Science Resource Page
... DNA are called mutations and can be harmful or advantages to an organism. (diseases or a 4 leaf clover) There can also be chromosome disorders. These disorders occur when an organism contains to few or to many chromosomes. When this happens the fetus or embryo usually dies before birth. If it ...
... DNA are called mutations and can be harmful or advantages to an organism. (diseases or a 4 leaf clover) There can also be chromosome disorders. These disorders occur when an organism contains to few or to many chromosomes. When this happens the fetus or embryo usually dies before birth. If it ...
- Philsci-Archive
... genetic system, mating system, and population structure: Assume a randomly interbreeding, large (mathematically, infinite) population of diploid organisms with one genetic locus and two alleles. In fact, these assumptions are fundamental to most standard presentations of population genetics. Given t ...
... genetic system, mating system, and population structure: Assume a randomly interbreeding, large (mathematically, infinite) population of diploid organisms with one genetic locus and two alleles. In fact, these assumptions are fundamental to most standard presentations of population genetics. Given t ...
1 AGRO/ANSC/BIO/GENE/HORT 305 Fall, 2016 Extension of
... Affected individuals have additional fingers and/or toes. Refer to Figure 4.3 A single copy of the polydactyly allele is usually sufficient to cause this condition. In some cases, however, individuals carry the dominant allele but do not exhibit the trait. The term indicates that a dominant allele d ...
... Affected individuals have additional fingers and/or toes. Refer to Figure 4.3 A single copy of the polydactyly allele is usually sufficient to cause this condition. In some cases, however, individuals carry the dominant allele but do not exhibit the trait. The term indicates that a dominant allele d ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.