Chapter 2. Left in the Genes - SciTech Connect
... hemisphere language dominating over that for right hemisphere localization. The other gene controls the side of handedness. The dominant allele locates handedness on the side opposite or contralateral to the languagelateralized hemisphere while the other allele results in a same-sided or ipsilateral ...
... hemisphere language dominating over that for right hemisphere localization. The other gene controls the side of handedness. The dominant allele locates handedness on the side opposite or contralateral to the languagelateralized hemisphere while the other allele results in a same-sided or ipsilateral ...
Genetic Factors Affecting Facial Growth
... modification is sufficient to alter preexisting structure.(Buschang & Hinton, 2005) As every orthodontist knows, the ability of the practitioner to affect a change is dependent both on the time of intervention (treatment) and the patient’s stage of development. Knowing whether the cause of the probl ...
... modification is sufficient to alter preexisting structure.(Buschang & Hinton, 2005) As every orthodontist knows, the ability of the practitioner to affect a change is dependent both on the time of intervention (treatment) and the patient’s stage of development. Knowing whether the cause of the probl ...
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
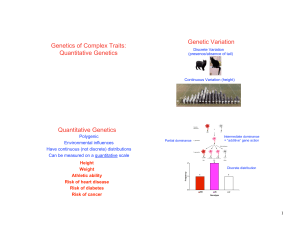
... is also only 2.0 units high. Total genetic variance, V G , is actually the sum of all the genetic variance. In the simplified case presented here this is (4) V G = V A + V D The implied equation for V P from the discussion so far is (1′) V P = V A + V D + V E But this equation still oversimplifies t ...
... is also only 2.0 units high. Total genetic variance, V G , is actually the sum of all the genetic variance. In the simplified case presented here this is (4) V G = V A + V D The implied equation for V P from the discussion so far is (1′) V P = V A + V D + V E But this equation still oversimplifies t ...
PDF
... not with genetic divergence [28,29]. These correlations are inferred to be due to an indirect effect of recombination due to the interaction between selection and linkage and their strength can be used to make inferences about the pervasiveness of natural selection. Positive selection on favourable ...
... not with genetic divergence [28,29]. These correlations are inferred to be due to an indirect effect of recombination due to the interaction between selection and linkage and their strength can be used to make inferences about the pervasiveness of natural selection. Positive selection on favourable ...
QuantGen posted
... win the Kentucky Derby. If she breeds her mare to a really fast stallion, how likely is it that the colt will be faster than all the other three-year-olds when it runs in the Derby? ...
... win the Kentucky Derby. If she breeds her mare to a really fast stallion, how likely is it that the colt will be faster than all the other three-year-olds when it runs in the Derby? ...
QuantGen posted
... win the Kentucky Derby. If she breeds her mare to a really fast stallion, how likely is it that the colt will be faster than all the other three-year-olds when it runs in the Derby? ...
... win the Kentucky Derby. If she breeds her mare to a really fast stallion, how likely is it that the colt will be faster than all the other three-year-olds when it runs in the Derby? ...
Artificial selection shifts flowering phenology and other correlated
... Interannual environmental variation may affect flowering time and influence heritability estimates. To remove these environmental effects, flowering time was adjusted by subtracting the mean flowering time of the control lines for a specific generation from each individual’s trait value in that gene ...
... Interannual environmental variation may affect flowering time and influence heritability estimates. To remove these environmental effects, flowering time was adjusted by subtracting the mean flowering time of the control lines for a specific generation from each individual’s trait value in that gene ...
Bridging differences in concepts of selection between farmers
... unfavourable destroyed...This preservation... I have called Natural Selection..." (Darwin 1883 [1868]b:6). Thus, Darwin used the terms "selection" and "natural selection" interchangeably to refer to the process that results in evolution, and implying evolution itself. Today these are known to be the ...
... unfavourable destroyed...This preservation... I have called Natural Selection..." (Darwin 1883 [1868]b:6). Thus, Darwin used the terms "selection" and "natural selection" interchangeably to refer to the process that results in evolution, and implying evolution itself. Today these are known to be the ...
evolution - Santa Fe Institute
... But what is the origin of this observed robustness? Is it merely an accident, or a consequence of natural selection in the face of mutations and environmental variation? And what are the evolutionary consequences of robustness? The amount of phenotypic diversity within or among populations can vary ...
... But what is the origin of this observed robustness? Is it merely an accident, or a consequence of natural selection in the face of mutations and environmental variation? And what are the evolutionary consequences of robustness? The amount of phenotypic diversity within or among populations can vary ...
11.1-11.3 Notes
... For example, there are two possible outcomes of a coin flip: The coin may land either heads up or tails up. The chance, or probability, of either outcome is equal. Therefore, the probability that a single coin flip will land heads up is 1 chance in 2. This amounts to 1/2, or 50 percent. ...
... For example, there are two possible outcomes of a coin flip: The coin may land either heads up or tails up. The chance, or probability, of either outcome is equal. Therefore, the probability that a single coin flip will land heads up is 1 chance in 2. This amounts to 1/2, or 50 percent. ...
Of Mice and Metaphysics: Natural Selection and
... problem in Section 2, I sketch a causal account of realization in Section 3. I argue that a causal account of realization can be used to provide an adequate answer to the grounding question. If the population-level properties involved in the process of selection are realized in this way, then they a ...
... problem in Section 2, I sketch a causal account of realization in Section 3. I argue that a causal account of realization can be used to provide an adequate answer to the grounding question. If the population-level properties involved in the process of selection are realized in this way, then they a ...
Chapter 14: MENDEL AND THE GENE IDEA
... The dominant allele is the one that is expressed (it exerts its phenotypic effect) in a heterozygote. It is identified with a uppercase (capital) letter, usually the first letter of the trait. Recessive Allele whose phenotypic effect is not observed in a heterozygote; its expression is masked by ...
... The dominant allele is the one that is expressed (it exerts its phenotypic effect) in a heterozygote. It is identified with a uppercase (capital) letter, usually the first letter of the trait. Recessive Allele whose phenotypic effect is not observed in a heterozygote; its expression is masked by ...
introduction to genetic epidemiology
... The heuristic interpretation is that aggregation exists when cases of disease appear in families more often than one would expect if diseased cases were spread uniformly and randomly over individuals: “it runs in the family” Actual approaches for detecting aggregation depend on the nature of the ...
... The heuristic interpretation is that aggregation exists when cases of disease appear in families more often than one would expect if diseased cases were spread uniformly and randomly over individuals: “it runs in the family” Actual approaches for detecting aggregation depend on the nature of the ...
The Frequency Distribution of Nucleotide Variation in Drosophila
... frequencies of unpreferred versus preferred polymorphisms are not significantly different for the X-linked genes (P 5 0.16) or for the 3R genes (P 5 0.54) considered separately. When fixed mutations (frequency 5 1.0) are included in the estimation of mean frequencies, the frequency of preferred muta ...
... frequencies of unpreferred versus preferred polymorphisms are not significantly different for the X-linked genes (P 5 0.16) or for the 3R genes (P 5 0.54) considered separately. When fixed mutations (frequency 5 1.0) are included in the estimation of mean frequencies, the frequency of preferred muta ...
Genetics Questions - G. Holmes Braddock
... ____ 29. The arctic fox is blue-gray in the summer and white in the winter. What most likely influence(s) this change? a. genes and the environment b. dominant alleles c. the environment alone d. codominant alleles ____ 30. The number of chromosomes in a gamete is represented by the symbol a. Z. b. ...
... ____ 29. The arctic fox is blue-gray in the summer and white in the winter. What most likely influence(s) this change? a. genes and the environment b. dominant alleles c. the environment alone d. codominant alleles ____ 30. The number of chromosomes in a gamete is represented by the symbol a. Z. b. ...
Analysis of CAG and CCG repeats in Huntingtin gene
... individuals varied between 17 and 70 years. The range of the CAG repeat number on expanded HD chromosomes was 41–56, while the range of the normal allele on the homologous chromosome was 13–29 repeats. We noted an inverse correlation between age at presentation and CAG repeat number. In seven of the ...
... individuals varied between 17 and 70 years. The range of the CAG repeat number on expanded HD chromosomes was 41–56, while the range of the normal allele on the homologous chromosome was 13–29 repeats. We noted an inverse correlation between age at presentation and CAG repeat number. In seven of the ...
Genetic Algorithms and Related Optimization Techniques: An
... scalar. This will be used by the GA to rank the worth of a solution. This fitness (or evaluation) function needs to be very efficient, as it may need to be called thousands even millions - of times. But you do not need... ...the final solution to be optimal. ...speed (this varies) RMI Workshop - Oct ...
... scalar. This will be used by the GA to rank the worth of a solution. This fitness (or evaluation) function needs to be very efficient, as it may need to be called thousands even millions - of times. But you do not need... ...the final solution to be optimal. ...speed (this varies) RMI Workshop - Oct ...
Genetics, Genetics, and More Genetics
... Tell two different GENOTYPES a Reebop could have if it had TYPE A blood. _______ _______ If one of your Reebops WITH AB TYPE blood was injured and needed a blood transfusion, tell all the possible blood types that could act as donors. ______ ______ ______ Which blood type is considered to be the “un ...
... Tell two different GENOTYPES a Reebop could have if it had TYPE A blood. _______ _______ If one of your Reebops WITH AB TYPE blood was injured and needed a blood transfusion, tell all the possible blood types that could act as donors. ______ ______ ______ Which blood type is considered to be the “un ...
1 Of Mice and Metaphysics: Natural Selection and Realized
... mutations, genetic recombination events, etc. Yet this completeness principle alone does not rule out a strong emergentist view of selection, for it is compatible with the existence of a novel, completely distinct force of selection that acts independently of Darwinian events in the production of ev ...
... mutations, genetic recombination events, etc. Yet this completeness principle alone does not rule out a strong emergentist view of selection, for it is compatible with the existence of a novel, completely distinct force of selection that acts independently of Darwinian events in the production of ev ...
Full-text PDF
... Yoruba people in Ibadan Nigeria, West Africa (YRI). The NAT2 gene are said to be related to the susceptibility to some toxicities and cancers [7], [10]. Thus it is very important to study the differences of the NAT 2 genes among different populations to elucidate the ethnic difference in such suscep ...
... Yoruba people in Ibadan Nigeria, West Africa (YRI). The NAT2 gene are said to be related to the susceptibility to some toxicities and cancers [7], [10]. Thus it is very important to study the differences of the NAT 2 genes among different populations to elucidate the ethnic difference in such suscep ...
Genetic drift

Genetic drift (or allelic drift) is the change in the frequency of a gene variant (allele) in a population due to random sampling of organisms.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces. A population's allele frequency is the fraction of the copies of one gene that share a particular form. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation.When there are few copies of an allele, the effect of genetic drift is larger, and when there are many copies the effect is smaller. In the early twentieth century vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at the most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims that most instances where a genetic change spreads across a population (although not necessarily changes in phenotypes) are caused by genetic drift. There is currently a scientific debate about how much of evolution has been caused by natural selection, and how much by genetic drift.