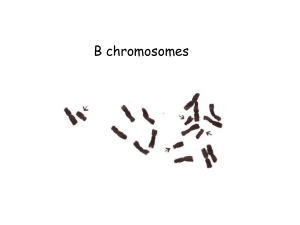Gorillas: an example of an issue report
... Zygotene, Pachytene, Diplotene Diakinesis" an area book does not cover in much depth. The IVF success rate data, source (13), gave two different success rate values, one for women over 38 and one for women below. If there is so much variance for humans applying it too gorillas undermines its validit ...
... Zygotene, Pachytene, Diplotene Diakinesis" an area book does not cover in much depth. The IVF success rate data, source (13), gave two different success rate values, one for women over 38 and one for women below. If there is so much variance for humans applying it too gorillas undermines its validit ...
THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE
... • The unique pattern of inheritance in sexlinked genes. • How alteration of chromosome number or structurally altered chromosomes (deletions, duplications, etc.) can cause genetic disorders. • How genetic imprinting and inheritance of mitochondrial DNA are exceptions to standard ...
... • The unique pattern of inheritance in sexlinked genes. • How alteration of chromosome number or structurally altered chromosomes (deletions, duplications, etc.) can cause genetic disorders. • How genetic imprinting and inheritance of mitochondrial DNA are exceptions to standard ...
Co-Dominance
... an individual inherits one such unit from each parent for each trait that a trait may not show up in an individual but can still be passed on to the next generation. ...
... an individual inherits one such unit from each parent for each trait that a trait may not show up in an individual but can still be passed on to the next generation. ...
HGEN: Chapters 2, 5 and 6 Study Guide Test on TUESDAY, 10/15
... development, arresting at Prophase 1 and not beginning again until puberty begins. Then, each month a single immature ova completes Meiosis 1 prior to ovulation and will complete Meiosis 2 following fertilization by a mature sperm. ...
... development, arresting at Prophase 1 and not beginning again until puberty begins. Then, each month a single immature ova completes Meiosis 1 prior to ovulation and will complete Meiosis 2 following fertilization by a mature sperm. ...
here
... plants, and that seeds are the next plant generation. (In peas, the green balls that we eat as peas as technically seeds.) 2. Describe why Mendel can be considered the Father of Genetics. (What was his contribution?) The three Laws of Inheritance are important, but they will be developed in a later ...
... plants, and that seeds are the next plant generation. (In peas, the green balls that we eat as peas as technically seeds.) 2. Describe why Mendel can be considered the Father of Genetics. (What was his contribution?) The three Laws of Inheritance are important, but they will be developed in a later ...
Sexual Reproduction
... Ex. Frog has 8 half = 4, human has 46, half =23 Involves 2divisions of the nucleus # of chromosomes cut in half (haploid- n) homologous chromosomes are separated cell division similar to mitosis BUT 2x’s cells produced through meiosis are called gametes or sex cells, which contain only h ...
... Ex. Frog has 8 half = 4, human has 46, half =23 Involves 2divisions of the nucleus # of chromosomes cut in half (haploid- n) homologous chromosomes are separated cell division similar to mitosis BUT 2x’s cells produced through meiosis are called gametes or sex cells, which contain only h ...
Field Botany - Royal Botanical Gardens
... plants. This work will aid our understanding of hybridization and provide insight on the morphological characteristics that are distinct to red mulberry trees. ...
... plants. This work will aid our understanding of hybridization and provide insight on the morphological characteristics that are distinct to red mulberry trees. ...
Genetics
... Mutation and sexual reproduction lead to genetic variation in a population. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. ...
... Mutation and sexual reproduction lead to genetic variation in a population. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. ...
Genetics study guide 2 key
... There is _3/4_ probability that offspring plants will show the dominant trait when a heterozygous plant self-pollinates. (give fraction not percent) 37. The offspring in square 1 would have the genotype _TT_. The organism’s appearance is known as its _Phenotype_. 38. The offspring in square 2 would ...
... There is _3/4_ probability that offspring plants will show the dominant trait when a heterozygous plant self-pollinates. (give fraction not percent) 37. The offspring in square 1 would have the genotype _TT_. The organism’s appearance is known as its _Phenotype_. 38. The offspring in square 2 would ...
Activity 1 Diversity in Living Things
... Hodgkin’s disease, a leukemia-like disease. As the human population on Madagascar grew, the habitat for the periwinkle shrank.The periwinkle almost became extinct. Fortunately, botanists collected and grew some of these plants before they were gone forever.The medicines made from the Madagascar peri ...
... Hodgkin’s disease, a leukemia-like disease. As the human population on Madagascar grew, the habitat for the periwinkle shrank.The periwinkle almost became extinct. Fortunately, botanists collected and grew some of these plants before they were gone forever.The medicines made from the Madagascar peri ...
Population Genetics
... populations: exists both as what we can see (e.g., eye color) and what we cannot see (e.g., blood type). ...
... populations: exists both as what we can see (e.g., eye color) and what we cannot see (e.g., blood type). ...
Heredity and Genetics - Imagine School at Lakewood Ranch
... expressed differently Ex: A butterfly’s offspring being different colors or blending in ...
... expressed differently Ex: A butterfly’s offspring being different colors or blending in ...
KARYOTYPE ANALYSIS OF TWO SPECIES OF SALSOLA FROM
... morphologically differences among young and adult plant, it is difficult for botanists to identify different species of this plant [1]. Based on various values of this genus, its unknown research aspects such as genetic studies toward promoting genetic potential are focused. The first step toward id ...
... morphologically differences among young and adult plant, it is difficult for botanists to identify different species of this plant [1]. Based on various values of this genus, its unknown research aspects such as genetic studies toward promoting genetic potential are focused. The first step toward id ...
NOTES: CH 14, part 1 - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... ● Second, for each character an organism inherits two alleles, (a genetic locus is actually represented twice) ● Third, if the two alleles at a locus differ, then one, the DOMINANT ALLELE, ...
... ● Second, for each character an organism inherits two alleles, (a genetic locus is actually represented twice) ● Third, if the two alleles at a locus differ, then one, the DOMINANT ALLELE, ...
How can Karyotype Analysis Explain Genetic Disorders
... Amador Valley High School Campus. The researchers have observed various forms of the insect and have concluded that many of these forms are the result of genetic disorders. You will prepare Karyotypes of the insects found on AVHS’s campus and analyze them for chromosomal abnormalities. Furthermore y ...
... Amador Valley High School Campus. The researchers have observed various forms of the insect and have concluded that many of these forms are the result of genetic disorders. You will prepare Karyotypes of the insects found on AVHS’s campus and analyze them for chromosomal abnormalities. Furthermore y ...
Chromosome Variations
... **4. The Notch mutation is a deletion on the X chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Females heterozygous for Notch have an indentation on the margin of their wings; Notch is lethal in the homozygous and hemizygous conditions. The Notch deletion covers the region of the X chromosome that contains t ...
... **4. The Notch mutation is a deletion on the X chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Females heterozygous for Notch have an indentation on the margin of their wings; Notch is lethal in the homozygous and hemizygous conditions. The Notch deletion covers the region of the X chromosome that contains t ...
Midterm Practice II
... 23. Explain why a sex linked trait is more likely to appear in males versus females. ...
... 23. Explain why a sex linked trait is more likely to appear in males versus females. ...
Document
... •The basic morphology of plants reflects that plants draw resources from two very different environments: the soil and the air. •Plants have evolved two systems: a subterranean root system to obtain water and minerals from the soil and an aerial shoot system of stems and leaves used to transform li ...
... •The basic morphology of plants reflects that plants draw resources from two very different environments: the soil and the air. •Plants have evolved two systems: a subterranean root system to obtain water and minerals from the soil and an aerial shoot system of stems and leaves used to transform li ...
Snímek 1
... How a supernumerary B chromosome survives over time? transmission higher than Mendelian kept in populations drive (pre-meiotic, meiotic, post-meiotic) = preferential maintenance of Bs post-meiotic drive common in plants during gametophyte maturation (examples: rye, maize) ...
... How a supernumerary B chromosome survives over time? transmission higher than Mendelian kept in populations drive (pre-meiotic, meiotic, post-meiotic) = preferential maintenance of Bs post-meiotic drive common in plants during gametophyte maturation (examples: rye, maize) ...
Eradication of Goats and Other Feral Herbivores
... fallow deer that still occur on the island of Rhodes (Dodecanese, Greece) may represent the only insular population of ancient anthropochorous origin that still survives in the Mediterranean. It is usually reported that the fallow deer was introduced from Asia Minor by the Knights of Saint John of J ...
... fallow deer that still occur on the island of Rhodes (Dodecanese, Greece) may represent the only insular population of ancient anthropochorous origin that still survives in the Mediterranean. It is usually reported that the fallow deer was introduced from Asia Minor by the Knights of Saint John of J ...
Chapter 13: Patterns of Inheritance
... 3. Performed reciprocal crosses white flower pollen on purple flower C. Allowed Self-Fertilization of Hybrids D. Allowed segregation of alternate forms of traits 1. Counted number of offspring of each type per generation 2. Quantification of results most important to studies V. What Mendel Found A.F ...
... 3. Performed reciprocal crosses white flower pollen on purple flower C. Allowed Self-Fertilization of Hybrids D. Allowed segregation of alternate forms of traits 1. Counted number of offspring of each type per generation 2. Quantification of results most important to studies V. What Mendel Found A.F ...
Document
... 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype • Female mammals have an XX genotype. – Expression of sex-linked genes is similar to autosomal genes in females. – X chromosome inactivation randomly “turns off” one X chromosome – ensures that females, like males, have one functional copy of the X chromosome in each b ...
... 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype • Female mammals have an XX genotype. – Expression of sex-linked genes is similar to autosomal genes in females. – X chromosome inactivation randomly “turns off” one X chromosome – ensures that females, like males, have one functional copy of the X chromosome in each b ...
Chapter 15
... ◦ For a recessive sex-linked trait to be expressed A female needs two copies of the allele A male needs only one copy of the allele ...
... ◦ For a recessive sex-linked trait to be expressed A female needs two copies of the allele A male needs only one copy of the allele ...
Hybrid (biology)

In biology a hybrid, also known as cross breed, is the result of mixing, through sexual reproduction, two animals or plants of different breeds, varieties, species or genera. Using genetic terminology, it may be defined as follows. Hybrid generally refers to any offspring resulting from the breeding of two genetically distinct individuals, which usually will result in a high degree of heterozygosity, though hybrid and heterozygous are not, strictly speaking, synonymous. a genetic hybrid carries two different alleles of the same gene a structural hybrid results from the fusion of gametes that have differing structure in at least one chromosome, as a result of structural abnormalities a numerical hybrid results from the fusion of gametes having different haploid numbers of chromosomes a permanent hybrid is a situation where only the heterozygous genotype occurs, because all homozygous combinations are lethal.From a taxonomic perspective, hybrid refers to: Offspring resulting from the interbreeding between two animal species or plant species. See also hybrid speciation. Hybrids between different subspecies within a species (such as between the Bengal tiger and Siberian tiger) are known as intra-specific hybrids. Hybrids between different species within the same genus (such as between lions and tigers) are sometimes known as interspecific hybrids or crosses. Hybrids between different genera (such as between sheep and goats) are known as intergeneric hybrids. Extremely rare interfamilial hybrids have been known to occur (such as the guineafowl hybrids). No interordinal (between different orders) animal hybrids are known. The third type of hybrid consists of crosses between populations, breeds or cultivars within a single species. This meaning is often used in plant and animal breeding, where hybrids are commonly produced and selected, because they have desirable characteristics not found or inconsistently present in the parent individuals or populations.↑ ↑ ↑ ↑