The Crusades
... and Moslem Syria under one rule • In 1185, he signed a four-year truce with the Latin kingdom but the Christians violated it by attacking a Moslem caravan and capturing Saladin’s sister • He declared a holy war against the Christians and captured Jerusalem in 1187 – His terms were much more generous ...
... and Moslem Syria under one rule • In 1185, he signed a four-year truce with the Latin kingdom but the Christians violated it by attacking a Moslem caravan and capturing Saladin’s sister • He declared a holy war against the Christians and captured Jerusalem in 1187 – His terms were much more generous ...
Document
... A. The Crusades were Medieval military expeditions organized by the Church for the liberation of the Holy Land and the defense of Christianity. 1. There were eight crusades during 1096-1270. B. Reasons for the Crusades 1. In the West – to bring about Christian unity…to end the feudal wars. 2. In the ...
... A. The Crusades were Medieval military expeditions organized by the Church for the liberation of the Holy Land and the defense of Christianity. 1. There were eight crusades during 1096-1270. B. Reasons for the Crusades 1. In the West – to bring about Christian unity…to end the feudal wars. 2. In the ...
The Fourth Crusade
... • Pope Gregory VII tried to expand the political power of the pope – The pope can be judged by no one; – The Roman church has never erred and never will err till the end of time; – The pope alone can depose and restore ...
... • Pope Gregory VII tried to expand the political power of the pope – The pope can be judged by no one; – The Roman church has never erred and never will err till the end of time; – The pope alone can depose and restore ...
crusade
... • the second, headed by Louis VII, 1145-47; • the third, conducted by Philip Augustus and Richard Coeur-de-Lion, 1188-92; • the fourth, during which Constantinople was taken, 1204; • the fifth, which included the conquest of Damietta, 1217; • the sixth, in which Frederick II took part (1228-29); als ...
... • the second, headed by Louis VII, 1145-47; • the third, conducted by Philip Augustus and Richard Coeur-de-Lion, 1188-92; • the fourth, during which Constantinople was taken, 1204; • the fifth, which included the conquest of Damietta, 1217; • the sixth, in which Frederick II took part (1228-29); als ...
Epic: A Journey through Church History
... such contemporary, Guibert of Nogent wrote of Peter, “I have seen towns and villages crowded to listen to his preaching. I cannot remember anyone else who was given such a remarkable reception – the crowds surrounded him; he was overwhelmed with gifts and acclaimed a saint. He was most generous in g ...
... such contemporary, Guibert of Nogent wrote of Peter, “I have seen towns and villages crowded to listen to his preaching. I cannot remember anyone else who was given such a remarkable reception – the crowds surrounded him; he was overwhelmed with gifts and acclaimed a saint. He was most generous in g ...
Epic: A Journey through Church History
... such contemporary, Guibert of Nogent wrote of Peter, “I have seen towns and villages crowded to listen to his preaching. I cannot remember anyone else who was given such a remarkable reception – the crowds surrounded him; he was overwhelmed with gifts and acclaimed a saint. He was most generous in g ...
... such contemporary, Guibert of Nogent wrote of Peter, “I have seen towns and villages crowded to listen to his preaching. I cannot remember anyone else who was given such a remarkable reception – the crowds surrounded him; he was overwhelmed with gifts and acclaimed a saint. He was most generous in g ...
The Crusades 1095-1291
... Rugs, Tapestries, Spices, and exotic foods 13. What happened between the years of 1147 and 1149? The Second Crusade begins in France; it ends with the crusaders failing to regain what had been lost 14. What happened in 1212? The ill-fated “Children’s Crusade”, thousands of children leave for the Hol ...
... Rugs, Tapestries, Spices, and exotic foods 13. What happened between the years of 1147 and 1149? The Second Crusade begins in France; it ends with the crusaders failing to regain what had been lost 14. What happened in 1212? The ill-fated “Children’s Crusade”, thousands of children leave for the Hol ...
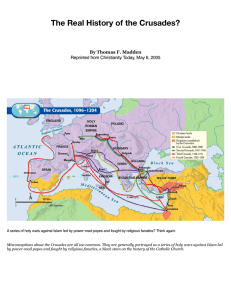
History of the Crusades
... Christians had hoped. The aged Frederick drowned while crossing a river on horseback, so his army returned home before reaching the Holy Land. Philip and Richard came by boat, but their incessant bickering only added to an already divisive situation on the ground in Palestine. After recapturing Acre ...
... Christians had hoped. The aged Frederick drowned while crossing a river on horseback, so his army returned home before reaching the Holy Land. Philip and Richard came by boat, but their incessant bickering only added to an already divisive situation on the ground in Palestine. After recapturing Acre ...
THE CRUSADES
... • A long series or Wars between Christians and Muslims • They fought over control of Jerusalem which was called the Holy Land because it was the region where Jesus had lived, preached and died ...
... • A long series or Wars between Christians and Muslims • They fought over control of Jerusalem which was called the Holy Land because it was the region where Jesus had lived, preached and died ...
14.1 Church Reform and the Crusades
... • Younger sons hope to earn land or win glory by fighting (although historian Rodney Stark in God’s Battalions: The Case for the Crusades disagrees with that theory because the first three crusades were led by the heads of the royal families of Europe). • Later, merchants join Crusades to try to gai ...
... • Younger sons hope to earn land or win glory by fighting (although historian Rodney Stark in God’s Battalions: The Case for the Crusades disagrees with that theory because the first three crusades were led by the heads of the royal families of Europe). • Later, merchants join Crusades to try to gai ...
The Crusades - Crusadinghistory
... Why was Saladin unable to complete the task of expelling the Franks? Why did Richard fail to recapture Jerusalem? Both answers so far have focused on lack of manpower/miltary structure(s) Markowski (1997) has argued that Richard ...
... Why was Saladin unable to complete the task of expelling the Franks? Why did Richard fail to recapture Jerusalem? Both answers so far have focused on lack of manpower/miltary structure(s) Markowski (1997) has argued that Richard ...
The Crusades - Mr. Kelleher
... • Pope- free the Holy Land from the Muslims who didn’t believe in Christianity, help Christians in the Byzantine Empire to defend their territory from the Seljuk Turks. ...
... • Pope- free the Holy Land from the Muslims who didn’t believe in Christianity, help Christians in the Byzantine Empire to defend their territory from the Seljuk Turks. ...
Borrowing or Adaptation of Medieval Weaponry between the
... appropriation of military technology for a specific purpose. Adaptation is defined here as the long-term integration of military technology within the culture itself. ...
... appropriation of military technology for a specific purpose. Adaptation is defined here as the long-term integration of military technology within the culture itself. ...
The Crusades
... Causes of the Crusades 1. Muslim invasions of and attacks on Christian lands, especially Jerusalem 2. Desire to spread and unite Christianity 3. Desire to open up trade routes to the East 4. Individuals hoped to gain land and riches 5. Protection of Christian pilgrims headed to Jerusalem ...
... Causes of the Crusades 1. Muslim invasions of and attacks on Christian lands, especially Jerusalem 2. Desire to spread and unite Christianity 3. Desire to open up trade routes to the East 4. Individuals hoped to gain land and riches 5. Protection of Christian pilgrims headed to Jerusalem ...
High Middle Ages Notes Packet: Part I (The Growth of the
... Causes????? *The Second Crusade was organized to recapture the Crusader state of _____________________. *Outcome????? *European Crusaders were defeated by Muslim forces led by ______________________. ...
... Causes????? *The Second Crusade was organized to recapture the Crusader state of _____________________. *Outcome????? *European Crusaders were defeated by Muslim forces led by ______________________. ...
People and Land in the High Middle Ages
... Jerusalem. In both cases, the Muslim and Jewish inhabitants were massacred. The region as a whole was divided into the principality of Antioch, the counties of Tripoli and Edessa, and the kingdom of Jerusalem. Antioch, Edessa, and Tripoli were all held as fiefs under the rule of the kingdom of Jerus ...
... Jerusalem. In both cases, the Muslim and Jewish inhabitants were massacred. The region as a whole was divided into the principality of Antioch, the counties of Tripoli and Edessa, and the kingdom of Jerusalem. Antioch, Edessa, and Tripoli were all held as fiefs under the rule of the kingdom of Jerus ...
The Crusades
... Crusades and counter crusades After the astonishing success the first crusade ,many crusaders fulfilled their vows by completing their pilgrimage at the church of the holy sepulchre, and went home. Others stayed however, and continued to build the society known as outremer (old French for “ over se ...
... Crusades and counter crusades After the astonishing success the first crusade ,many crusaders fulfilled their vows by completing their pilgrimage at the church of the holy sepulchre, and went home. Others stayed however, and continued to build the society known as outremer (old French for “ over se ...
14.1 Church Reform and the Crusades
... of children from Europe marched to the Holy Lands to fight the Muslims. God would turn Jerusalem over to them! (Muslims fight to hold back laughter). 5th Crusade: Loss 6th Crusade: Loss 7th Crusade: Loss 8th Crusade: Do you see a pattern here? ...
... of children from Europe marched to the Holy Lands to fight the Muslims. God would turn Jerusalem over to them! (Muslims fight to hold back laughter). 5th Crusade: Loss 6th Crusade: Loss 7th Crusade: Loss 8th Crusade: Do you see a pattern here? ...
Were the Crusaders Effective in Achieving Their
... exchange for the control of Jerusalem. King Louis turned down the deal; the Egyptians took back Damietta by force and the Crusaders lost everything. (Bocchieri) Secondly, the Christians were offered a chance to work with the Mongols against the Muslims. The Mongols were fighting Islam in the East, w ...
... exchange for the control of Jerusalem. King Louis turned down the deal; the Egyptians took back Damietta by force and the Crusaders lost everything. (Bocchieri) Secondly, the Christians were offered a chance to work with the Mongols against the Muslims. The Mongols were fighting Islam in the East, w ...
The Crusades - Homeschool Den
... trip across to the Holy Land because it was hot, the terrain was rugged, and there was little food and water. Eventually they reached Jerusalem. They constructed siege towers and eventually attacked and entered the city. Many inhabitants were massacred. After that many crusaders went home. Those who ...
... trip across to the Holy Land because it was hot, the terrain was rugged, and there was little food and water. Eventually they reached Jerusalem. They constructed siege towers and eventually attacked and entered the city. Many inhabitants were massacred. After that many crusaders went home. Those who ...
The Crusades! - Mrs. Abbott OPHS
... letter asking for help and called for a “holy war” or CRUSADE He said those who fought and died in the Crusades would be promised a spot in Heaven with all sins forgiven Remember the head of the Church is the Pope ...
... letter asking for help and called for a “holy war” or CRUSADE He said those who fought and died in the Crusades would be promised a spot in Heaven with all sins forgiven Remember the head of the Church is the Pope ...
FIFTH CRUSADE
... a ladder which enabled the Crusaders to reach the top of the tower and capture it (Powell, 1986, p. 162). By September, a steady flow of reinforcements had arrived which helped compensate for the number of crusaders who were leaving. The crusaders had been unable to secure a position on the east ban ...
... a ladder which enabled the Crusaders to reach the top of the tower and capture it (Powell, 1986, p. 162). By September, a steady flow of reinforcements had arrived which helped compensate for the number of crusaders who were leaving. The crusaders had been unable to secure a position on the east ban ...
Chapter_14_Powerpoint
... • Peasants and knights set out on the First Crusade in 1096. • Some Crusaders in Germany decided to fight the Jews located there. • Took three years to reach Jerusalem and once the Muslims were defeated and set up Christian states in the Holy Land. ...
... • Peasants and knights set out on the First Crusade in 1096. • Some Crusaders in Germany decided to fight the Jews located there. • Took three years to reach Jerusalem and once the Muslims were defeated and set up Christian states in the Holy Land. ...
First Crusade - White Plains Public Schools
... Why does the city of Constantinople’s geography make it such a desirable locale? ...
... Why does the city of Constantinople’s geography make it such a desirable locale? ...