Chapter 16 Evolution of Populations
... of evolutionary change. In small populations, alleles can become more or less common simply by chance. This kind of change in allele frequency is called genetic drift. It occurs when individuals with a particular allele leave more descendants than other individuals, just by chance. Over time, this c ...
... of evolutionary change. In small populations, alleles can become more or less common simply by chance. This kind of change in allele frequency is called genetic drift. It occurs when individuals with a particular allele leave more descendants than other individuals, just by chance. Over time, this c ...
Heredity
... example, your diet, state of health, and the amount of exercise you get can change your body size and appearance. Exposure to the sun can change the pigments in skin, making it darker when they "tan." The genes you inherit give you the potential for many traits. But the person you become depends ver ...
... example, your diet, state of health, and the amount of exercise you get can change your body size and appearance. Exposure to the sun can change the pigments in skin, making it darker when they "tan." The genes you inherit give you the potential for many traits. But the person you become depends ver ...
Genetics - Cloudfront.net
... • Because the testicles of these males do not form normally, affected males may have low levels of the hormone, testosterone, beginning during puberty • A lack of this hormone can cause breast development, reduced facial and body hair, and the inability to father children (infertility) ...
... • Because the testicles of these males do not form normally, affected males may have low levels of the hormone, testosterone, beginning during puberty • A lack of this hormone can cause breast development, reduced facial and body hair, and the inability to father children (infertility) ...
Mendelian Genetics Gregor Mendel Generations Law of
... independently of the other pairs. • All possible combinations of factors can occur in the gametes. ...
... independently of the other pairs. • All possible combinations of factors can occur in the gametes. ...
Ch 9.1 and 2 SR
... 2. Name two ways pollination can occur. a. ___________________________________________________________________ b. ___________________________________________________________________ 3. What is a true-breeding plant? _______________________________________________ ____________________________________ ...
... 2. Name two ways pollination can occur. a. ___________________________________________________________________ b. ___________________________________________________________________ 3. What is a true-breeding plant? _______________________________________________ ____________________________________ ...
Heredity - adaptingtotheenviroment
... exercise you get can change your body size and appearance. Exposure to the sun can change the pigments in skin, making it darker when they "tan." The genes you inherit give you the potential for many traits. But the person you become depends very much on your ...
... exercise you get can change your body size and appearance. Exposure to the sun can change the pigments in skin, making it darker when they "tan." The genes you inherit give you the potential for many traits. But the person you become depends very much on your ...
Heredity By Cindy Grigg 1 What makes children look like their
... exercise you get can change your body size and appearance. Exposure to the sun can change the pigments in skin, making it darker when they "tan." The genes you inherit give you the potential for many traits. But the person you become depends very much on your ...
... exercise you get can change your body size and appearance. Exposure to the sun can change the pigments in skin, making it darker when they "tan." The genes you inherit give you the potential for many traits. But the person you become depends very much on your ...
Microevolution and Population Genetics
... a. differences in DNA sequence at one or moe loci 2. Differences in ____________________ a. many traits are affected by immediate or recent environmental conditions b. environmental conditions may change throughout life c. may be effected by environmental conditions during development 3. ___________ ...
... a. differences in DNA sequence at one or moe loci 2. Differences in ____________________ a. many traits are affected by immediate or recent environmental conditions b. environmental conditions may change throughout life c. may be effected by environmental conditions during development 3. ___________ ...
AP Chapter 14 Lecture - TJ
... Chance of at least 2 recessive traits = 6/16 or 3/8 14.3 Inheritance patterns are often more complex than predicted by simple Mendelian genetics I. Extending Mendelian genetics for a single gene A. Degrees of dominance 1. Complete dominance a. Mendel’s work b. One allele overshadows/masks the other ...
... Chance of at least 2 recessive traits = 6/16 or 3/8 14.3 Inheritance patterns are often more complex than predicted by simple Mendelian genetics I. Extending Mendelian genetics for a single gene A. Degrees of dominance 1. Complete dominance a. Mendel’s work b. One allele overshadows/masks the other ...
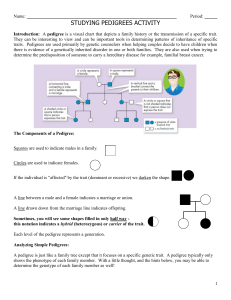
Pedigree Problems:
... there is evidence of a genetically inherited disorder in one or both families. They are also used when trying to determine the predisposition of someone to carry a hereditary disease for example, familial breast cancer. ...
... there is evidence of a genetically inherited disorder in one or both families. They are also used when trying to determine the predisposition of someone to carry a hereditary disease for example, familial breast cancer. ...
Heredity
... Study the diagram at the right. It represents four people: two parents and their two children. Parents are indicated by the symbols in the top row. Children are indicated by the symbols in the bottom row. Circles represent females and squares represent males. In this family, only the daughter expres ...
... Study the diagram at the right. It represents four people: two parents and their two children. Parents are indicated by the symbols in the top row. Children are indicated by the symbols in the bottom row. Circles represent females and squares represent males. In this family, only the daughter expres ...
Chapter 9 - Fundamentals of Genetics
... 1. dominant allele represented by capital letter (G) 2.recessive allele represented by lower case same letter (g) 3. homozygous (pure strain) - both alleles of pair are alike GG - homozygous dominant gg - homozygous recessive 4. heterozygous (hybrid) - two alleles of pair are different- Gg 5. genoty ...
... 1. dominant allele represented by capital letter (G) 2.recessive allele represented by lower case same letter (g) 3. homozygous (pure strain) - both alleles of pair are alike GG - homozygous dominant gg - homozygous recessive 4. heterozygous (hybrid) - two alleles of pair are different- Gg 5. genoty ...
CHERCHER PREPARATORY SCHOOL Department of Natural
... CHERCHER PREPARATORY SCHOOL Department of Natural Science Worksheet on Genetic crosses for Grade 12 Natural Science Students, 2005/2012 1. If a plant cell having 16 chromosomes undergoes meiotic cell division, how many chromosomes would the resulting daughter cells have? 2. What percentage of tall p ...
... CHERCHER PREPARATORY SCHOOL Department of Natural Science Worksheet on Genetic crosses for Grade 12 Natural Science Students, 2005/2012 1. If a plant cell having 16 chromosomes undergoes meiotic cell division, how many chromosomes would the resulting daughter cells have? 2. What percentage of tall p ...
114KB - NZQA
... where relatively small changes in allele numbers can have a big impact on the frequency of alleles in the total population. Allele is two or more alternative forms of a gene. Allele frequency is the % / number of each allele in a gene pool. Natural selection is where individuals with alleles most fa ...
... where relatively small changes in allele numbers can have a big impact on the frequency of alleles in the total population. Allele is two or more alternative forms of a gene. Allele frequency is the % / number of each allele in a gene pool. Natural selection is where individuals with alleles most fa ...
Chapter 11 Intro to Genetics
... 3. Peas are self-pollinators a. Have stamen (male) to produce pollen and pistils (female) to produce egg on same plant b. The pollen self-pollinates the egg on the same plant c. Offspring are identical to parent d. Also called true-breeds or pure breeds 4. Mendel’s experiment a. Removed stamen (lef ...
... 3. Peas are self-pollinators a. Have stamen (male) to produce pollen and pistils (female) to produce egg on same plant b. The pollen self-pollinates the egg on the same plant c. Offspring are identical to parent d. Also called true-breeds or pure breeds 4. Mendel’s experiment a. Removed stamen (lef ...
9BCC Bio 103 Mendelian Patterns of Inheritance CONCEPTS ONLY
... • We know that this is not always the case • This discrepancy—when white and red flowers would show up in further generations—was explained by some instability in the breeding system ...
... • We know that this is not always the case • This discrepancy—when white and red flowers would show up in further generations—was explained by some instability in the breeding system ...
Chapter 3 Mendelian Genetics
... acids for specific protein construction. 0 Allele: alternative forms of a gene; options. For Mendel’s pea plants, each gene had 2 alleles. 0 Homozygous: identical alleles; CC or cc 0 Heterozygous : not identical alleles; Cc ...
... acids for specific protein construction. 0 Allele: alternative forms of a gene; options. For Mendel’s pea plants, each gene had 2 alleles. 0 Homozygous: identical alleles; CC or cc 0 Heterozygous : not identical alleles; Cc ...
NCEA Level 2 Biology (91157) 2015
... where relatively small changes in allele numbers can have a big impact on the frequency of alleles in the total population. Allele is two or more alternative forms of a gene. Allele frequency is the % / number of each allele in a gene pool. Natural selection is where individuals with alleles most fa ...
... where relatively small changes in allele numbers can have a big impact on the frequency of alleles in the total population. Allele is two or more alternative forms of a gene. Allele frequency is the % / number of each allele in a gene pool. Natural selection is where individuals with alleles most fa ...
Single-Gene Inheritance (Learning Objectives) • Review the
... Understand and define: characteristic, trait, true-breeder, genotype, phenotype, allele, autosomal dominant and recessive traits, and a monohybrid cross. Explain Mendel’s law of allele segregation. Learn what is meant by a test cross and when it is used. Explain Mendel’s law of independent assortmen ...
... Understand and define: characteristic, trait, true-breeder, genotype, phenotype, allele, autosomal dominant and recessive traits, and a monohybrid cross. Explain Mendel’s law of allele segregation. Learn what is meant by a test cross and when it is used. Explain Mendel’s law of independent assortmen ...
trait - Plain Local Schools
... is determined by a single gene in humans with the ability to taste given by the dominant allele T and inability to taste by the recessive allele t. Suppose two heterozygous tasters (Tt) have a large family. ...
... is determined by a single gene in humans with the ability to taste given by the dominant allele T and inability to taste by the recessive allele t. Suppose two heterozygous tasters (Tt) have a large family. ...